A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Arsenic | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allotropes | grey (most common), yellow, black (see Allotropes of arsenic) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | metallic grey | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard atomic weight Ar°(As) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Arsenic in the periodic table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic number (Z) | 33 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group | group 15 (pnictogens) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Period | period 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Block | p-block | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrons per shell | 2, 8, 18, 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase at STP | solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sublimation point | 887 K (615 °C, 1137 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (at 20° C) | grey: 5.782 g/cm3[3] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| when liquid (at m.p.) | 5.22 g/cm3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Triple point | 1090 K, 3628 kPa[4] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Critical point | 1673 K, ? MPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | grey: 24.44 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of vaporization | 34.76 kJ/mol (?) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar heat capacity | 24.64 J/(mol·K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vapor pressure
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | −3, −2, −1, 0,[5] +1,[6] +2, +3, +4, +5 (a mildly acidic oxide) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | Pauling scale: 2.18 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic radius | empirical: 119 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 119±4 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Van der Waals radius | 185 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural occurrence | primordial | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal structure | grey: rhombohedral (hR2) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
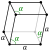
| Lattice constants | ar = 413.15 pm α = 54.133° pm ah = 375.99 pm ch = 1054.58 pm (at 20 °C)[3] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal expansion | 5.6 µm/(m⋅K)[7] (at r.t.) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | 50.2 W/(m⋅K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrical resistivity | 333 nΩ⋅m (at 20 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic ordering | diamagnetic[8] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar magnetic susceptibility | −5.5×10−6 cm3/mol[9] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Young's modulus | 8 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bulk modulus | 22 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mohs hardness | 3.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brinell hardness | 1440 MPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Number | 7440-38-2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery | Arabic alchemists (before AD 815) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isotopes of arsenic | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Arsenic is a chemical element; it has symbol As and atomic number 33. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. Arsenic is a notoriously toxic metalloid. It has various allotropes, but only the grey form, which has a metallic appearance, is important to industry.
The primary use of arsenic is in alloys of lead (for example, in car batteries and ammunition). Arsenic is a common n-type dopant in semiconductor electronic devices. It is also a component of the III–V compound semiconductor gallium arsenide. Arsenic and its compounds, especially the trioxide, are used in the production of pesticides, treated wood products, herbicides, and insecticides. These applications are declining with the increasing recognition of the toxicity of arsenic and its compounds.[11]
A few species of bacteria are able to use arsenic compounds as respiratory metabolites. Trace quantities of arsenic are an essential dietary element in rats, hamsters, goats, chickens, and presumably other species. A role in human metabolism is not known.[12][13] However, arsenic poisoning occurs in multicellular life if quantities are larger than needed. Arsenic contamination of groundwater is a problem that affects millions of people across the world.
The United States' Environmental Protection Agency states that all forms of arsenic are a serious risk to human health.[14] The United States' Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry ranked arsenic as number 1 in its 2001 Priority List of Hazardous Substances at Superfund sites.[15] Arsenic is classified as a Group-A carcinogen.[14]
Characteristics
Physical characteristics
Zdroj:https://en.wikipedia.org?pojem=ArsenicText je dostupný za podmienok Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších podmienok. Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky použitia.
Antropológia
Aplikované vedy
Bibliometria
Dejiny vedy
Encyklopédie
Filozofia vedy
Forenzné vedy
Humanitné vedy
Knižničná veda
Kryogenika
Kryptológia
Kulturológia
Literárna veda
Medzidisciplinárne oblasti
Metódy kvantitatívnej analýzy
Metavedy
Metodika
Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative
Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších
podmienok.
Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky
použitia.
www.astronomia.sk | www.biologia.sk | www.botanika.sk | www.dejiny.sk | www.economy.sk | www.elektrotechnika.sk | www.estetika.sk | www.farmakologia.sk | www.filozofia.sk | Fyzika | www.futurologia.sk | www.genetika.sk | www.chemia.sk | www.lingvistika.sk | www.politologia.sk | www.psychologia.sk | www.sexuologia.sk | www.sociologia.sk | www.veda.sk I www.zoologia.sk