A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
This article should specify the language of its non-English content, using {{lang}}, {{transliteration}} for transliterated languages, and {{IPA}} for phonetic transcriptions, with an appropriate ISO 639 code. Wikipedia's multilingual support templates may also be used. (July 2023) |
Faeroe Islands | |
|---|---|
| Anthem: "Tú alfagra land mítt" (Faroese) (English: "Thou, fairest land of mine") | |
 Location of the Faroe Islands (green) in Europe (green and dark grey) | |
 Location of the Faroe Islands (red; circled) in the Kingdom of Denmark (yellow) | |
| Sovereign state | Kingdom of Denmark |
| Settlement | early 9th century |
| Union with Norway | c. 1035 |
| Kalmar Union | 1397–1523 |
| Denmark-Norway | 1523–1814 |
| Cession to Denmark | 14 January 1814 |
| Independence referendum | 14 September 1946 |
| Home rule | 30 March 1948 |
| Further autonomy | 29 July 2005[1] |
| Capital and largest city | Tórshavn 62°00′N 06°47′W / 62.000°N 6.783°W |
| Official languages | |
| Ethnic groups | Faroe Islanders |
| Religion | Christianity (Church of the Faroe Islands) |
| Demonym(s) |
|
| Government | Devolved government within a parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
• Monarch | Frederik X |
| Lene Moyell Johansen | |
| Aksel V. Johannesen | |
| Legislature | Løgting |
| National representation | |
| 2 members | |
| Area | |
• Total | 1,393[4] km2 (538 sq mi) (not ranked) |
• Water (%) | 0.5 |
| Highest elevation | 882 m (2,894 ft) |
| Population | |
• March 2024 estimate | 54,591[5] (214th) |
• 2011 census | 48,346 |
• Density | 38.6/km2 (100.0/sq mi) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2019 estimate |
• Total | US$3.126 billion[6] (not ranked) |
• Per capita | US$58,585 (not ranked) |
| Gini (2018) | low · 1st place |
| HDI (2008) | 0.950[8] very high |
| Currency | (DKK) |
| Time zone | UTC±00:00 (WET) |
• Summer (DST) | UTC+01:00 (WEST) |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +298 |
| Postal code | FO-xxx |
| ISO 3166 code | FO |
| Internet TLD | .fo |
The Faroe or Faeroe Islands (/ˈfɛəroʊ/ FAIR-oh), or simply the Faroes (Faroese: Føroyar, pronounced [ˈfœɹjaɹ] ⓘ; Danish: Færøerne [ˈfeɐ̯ˌøˀɐnə]), are an archipelago in the North Atlantic Ocean and an autonomous territory of the Kingdom of Denmark. The official language of the country is Faroese, which is closely related to and partially mutually intelligible with Icelandic.
Located 320 kilometres (200 mi) north-northwest of the United Kingdom, the islands have a total area of about 1,400 square kilometres (540 sq mi) with a population of 54,676 as of August 2023.[10] The terrain is rugged, and the subpolar oceanic climate (Cfc) is windy, wet, cloudy, and cool. Despite the northerly climate, the temperatures are moderated by the Gulf Stream and average above freezing throughout the year, hovering around 12 °C (54 °F) in summer and 5 °C (41 °F) in winter.[11] As a result of its northerly latitude and proximity to the Arctic Circle, the islands experience perpetual civil twilight during summer nights and very short winter days. The capital and largest city, Tórshavn, receives the fewest hours of sunshine of any city in the world with 840 per year.[12]
While archaeological evidence points to earlier human habitation, Færeyinga Saga and the writings of Dicuil place initial Norse settlement in the early 9th century.[13][14] As with the subsequent Settlement of Iceland, the islands were mainly settled by Norwegians and Norse-Gaels, who additionally brought thralls (i.e. slaves or serfs) of Gaelic origin. Following the introduction of Christianity by Sigmundur Brestisson, the islands came under Norwegian rule in the early 11th century. The Faroe Islands followed Norway's integration into the Kalmar Union in 1397, and came under de facto Danish rule following that union's dissolution in 1523. Following the introduction of Lutheranism in 1538, usage of Faroese was banned in churches, schools and state institutions, and thus ceased to be a written language. The islands were formally ceded to Denmark in 1814 by the Treaty of Kiel along with Greenland and Iceland.
Following the re-establishment of an official Faroese orthography by Venceslaus Ulricus Hammershaimb, the Faroese language conflict saw Danish being gradually displaced by Faroese as the language of the church, public education and law in the first half of the 20th century. The islands were occupied by the British during the Second World War, who refrained from governing Faroese internal affairs: inspired by this period of relative self-government and the declaration of Iceland as a republic in 1944, the islands held a referendum in 1946 that resulted in a narrow majority for independence. The results were annulled by Christian X, and subsequent negotiations led to the Faroe Islands being granted home rule in 1948.[15]
While remaining part of the Kingdom of Denmark to this day, the Faroe Islands have extensive autonomy and control most areas apart from military defence, policing, justice and currency, with partial control over its foreign affairs.[16] Because the Faroe Islands are not part of the same customs area as Denmark, they have an independent trade policy and are able to establish their own trade agreements with other states. The islands have an extensive bilateral free trade agreement with Iceland, known as the Hoyvík Agreement. In the Nordic Council, they are represented as part of the Danish delegation. In certain sports, the Faroe Islands field their own national teams. They did not become a part of the European Economic Community in 1973, instead keeping autonomy over their own fishing waters; as a result, the Faroe Islands are not a part of the European Union today. The Løgting, though suspended from 1816 to 1852, holds a claim as one of the oldest continuously-running parliaments in the world. One Faroe Islander, Niels Ryberg Finsen, has won the Nobel Prize; due to the country's small population, the Faroe Islands resultingly hold the most Nobel laureates per capita.
Etymology
The English name Faroe Islands (alt. Faeroe or the Faroes) derives from the Old Norse Færeyjar;[17][18][19] which is also the origin of the modern-day endonym in Faroese, Føroyar. The second element oyar, meaning "islands", is a holdover from Old Faroese; in its present-day form, sound changes have rendered the word as oyggjar. Names for individual islands (such as Kalsoy and Suðuroy) also preserve the old form.
Multiple theories have been postulated for the name's etymological origin. The most widely-held theory, first popularised by Færeyinga Saga, holds that it derives from a compound of fær ('sheep') and eyjar ('islands'), meaning "sheep islands" in reference to their abundance on the archipelago. Clergymen Peder Clausson and Lucas Debes began casting doubt on this theory in the 16th and 17th centuries, as fær was of East Norse origin and thus would not have been commonly used by the West Norse-speaking settlers. With sauðr as the predominant word in West Norse (the Faroese word for sheep, seyður, derives from this word like in Norwegian and Icelandic), they argued that it would be unlikely for the name to have derived from this origin. Debes surmised that it could have derived from the Old Norse fjær ('far'), while Hammershaimb leaned towards fara ('to go, to travel').[20]
Others theorised an Old Irish origin: relating the name to the variably Celtic etymologies of neighbouring Orkney and Shetland, Scottish writers James Currie and William J. Watson suggested respectively the words feur ('pasture, eaten-up outfield') and fearann ('land, territory') as possible derivations, arguing that the original Celtic attestations of the islands' existence made this more likely.[20] Archaeologist Anton Wilhelm Brøgger concurred, elaborating on Watson's theory by positing that the Norse, having first learned of the islands from Scottish and Irish accounts as a fearann, could have coined Færeyjar as a phono-semantic match.[20]
History
Archaeological studies from 2021 found evidence of settlement on the islands before the arrival of Norse settlers, uncovering burnt grains of domesticated barley and peat ash deposited in two phases: the first dated between the mid-fourth and mid-sixth centuries, and another between the late-sixth and late-eighth centuries.[21][22] Researchers have also found sheep DNA in lake-bed sediments dating to the year 500. Barley and sheep had to have been brought to the islands by humans; as Scandinavians did not begin using sails until about 750, it is unlikely they could have reached the Faroes before then, leading to the study concluding that the settlers were more likely to originate from Scotland or Ireland.[23][24]
These findings concur with historical accounts from the same period: archaeologist Mike Church noted that Irish monk Dicuil describes a group of islands north of Scotland of very similar character to the Faroe Islands in his work De mensura orbis terrae ("Of the measure of the worlds of the earth"). In this text, Dicuil describes "a group of small islands (...) Nearly all of them (...) separated by narrow stretches of water" that were "always deserted since the beginning of time"[25] and previously populated by heremitae ex nostra Scotia ("hermits from our land of Ireland/Scotland") for almost a hundred years before being displaced by the arrival of Norse "pirates". Church argued that these were likely the eremitic Papar that had similarly resided in parts of Iceland and Scotland in the same period.[26] Writers like Brøgger and Peter Andreas Munch had drawn the same connections from Dicuil's writings, with the latter arguing that these Papar were also the ones to bring sheep to the islands.[25][20] A ninth-century voyage tale concerning Irish saint Brendan, one of Dicuil's contemporaries, details him visiting an unnamed northern group of islands; this has also been argued to be referring to the Faroe Islands, though not nearly as conclusively.[27] A number of toponyms around the islands refer to the Papar and the Irisish, such as Paparøkur near Vestmanna and Papurshílsur near Saksun. Vestmanna is itself short for Vestmannahøvn ("harbour of the Westmen"). Tombstones in a churchyard on Skúvoy display a possible Gaelic origin or influence.[28]
Old Norse-speaking settlers arrived in the early 9th century, and their Old West Norse dialect would later evolve into the modern Faroese language. A number of the settlers were Norse–Gaels who did not come directly from Scandinavia, but rather from Norse communities that spanned the Irish Sea, Northern Isles, and Outer Hebrides of Scotland, including the Shetland and Orkney islands; these settlers also brought thralls of Gaelic origin with them, and this admixture is reflected today in the Faroese genetic makeup and a number of loanwords from Old Irish. A traditional name for the islands in Irish, Na Scigirí, possibly derives from Eyja-Skeggjar, ("Island-Beards"), a nickname given to island dwellers.[citation needed] According to Færeyinga saga, many of the Norwegian settlers in particular were spurred by their disapproval of the monarchy of Harald Fairhair, whose rule was also seen as an inciting factor for the Settlement of Iceland.

The founding date of the Løgting is not historically documented, though the saga implies that it was a well-established institution by the middle of the 10th century, when a legal dispute between chieftains Havgrímur and Einar Suðuroyingur, resulting in the exile of Eldjárn Kambhøttur, is recounted in detail.[29]
Christianity was introduced to the islands in the late 10th and early 11th centuries by chieftain Sigmundur Brestisson.[30] Baptised as an adult by then-King of Norway Olaf Tryggvason, his mission to introduce Christianity was part of a greater plan to seize the islands on behalf of the Norwegian crown.[31] While Christianity arrived at the same time as in Iceland, the process was met with much more conflict and violence, and was defined particularly by Sigmundur's conflict with rival chieftain Tróndur í Gøtu, the latter of whom was converted under threat of decapitation. Although their conflict resulted in Sigmundur's murder, the Islands fell firmly under Norwegian rule following Tróndur's death in 1035.[30]
14th century onwards
While the Faroe Islands formally remained a Norwegian possession until 1814, Norway's merger into the Kalmar Union in 1397 gradually resulted in the islands coming under de facto Danish control. When the Protestant Reformation reached the Faroe Islands in 1538, the Faroese language was also outlawed in schools, churches and official documentation; thus Faroese remained exclusively a spoken language until the 19th century. Following the Napoleonic Wars, the union between Denmark and Norway was dissolved by the Treaty of Kiel in 1814; while Norway was transferred to the Swedish Crown, Denmark retained possession of Norway's North Atlantic territories, which included the Faroe Islands along with Greenland and Iceland. Shortly afterwards, Denmark asserted control and began to restrict the islands' autonomy. In 1816, the Faroe Islands was reconstituted as a county ((amt) within the Danish Kingdom: the Løgting, having operated continuously for almost a millennium, was dissolved and replaced by a Danish judiciary, and the post of løgmaður (lawspeaker) was likewise replaced by a Danish-appointed amtmand (equivalent to a governor-general).[32]
As part of its mercantilist economic policy, Denmark maintained a monopoly over trade with the Faroe Islands and forbade the Faroese from trading with other countries. The trade monopoly in the Faroe Islands was eventually abolished in 1856, after which the area developed into a modern fishing-based economy with its own fishing fleet. In 1846, the Faroe Islands finally regained formal political representation when they were allocated two seats in the Danish Rigsdag; the Løgting itself was reinstated as an advisory body to the amtmand in 1852.
An official Faroese orthography was first introduced in 1846 by Lutheran minister Venceslaus Ulricus Hammershaimb, returning the language to print after 300 years of only existing in oral form. With the return of written Faroese to the public sphere after more than 300 years, nationalism gained a foothold in Faroese society: the modern Faroese national movement is commonly agreed to have begun with the Christmas Meeting of 1888, held to "discuss how to defend the Faroese language and Faroese traditions". This meeting led to the rise of two of the movement's most prominent early figures: Jóannes Patursson and Rasmus Effersøe.
It was initially exclusively concerned with the status of the Faroese language, but it soon gained a political dimension with the advent of the Faroese language conflict in the early 20th century. Both sides of the conflict were represented by the country's first-ever political parties: the Union Party (Sambandsflokkurin), founded in 1906, which supported Faroese literature but opposed its usage in education; and the Self-Government party (Sjálvstýrisflokkurin), which sought to introduce Faroese as the official language in all public spheres and additionally demanded increased political autonomy for the islands. The Faroese language gradually won out; laws and protocols of the Løgting were written in Faroese from 1927 onwards, schools switched to Faroese as the language of instruction in 1938, and Faroese was fully authorised as the language of the Church the following year. Finally in 1944, Faroese gained equal status with Danish in legal proceedings.
In the first year of the Second World War, on 12 April 1940, British troops occupied the Faroe Islands in Operation Valentine. Nazi Germany had invaded Denmark and commenced the invasion of Norway on 9 April 1940 under Operation Weserübung. In 1942–1943, the British Royal Engineers, under the command of lieutenant colonel William Law, built the first and only airport in the Faroe Islands, Vágar Airport. The British refrained from governing Faroese internal affairs, and the islands became effectively self-governing during the war. After the war ended and the British army left, this period and Iceland's declaration as a republic in 1944 served as a precedent and a model in the mind of many Faroe Islanders.
The Løgting held an independence referendum on 14 September 1946, resulting in a very narrow majority for independence; 50.73% voted in favour and 49.27% against; the margin was only 161 votes.[33] The Løgting subsequently declared independence on 18 September 1946; this declaration was annulled by Denmark on 20 September, arguing that the number of invalid votes (481) being greater than the narrow margin in favour made the result invalid. As a result, King Christian X of Denmark ordered that the Faroese Løgting be dissolved on 24 September, with new elections held that November.[34] The Faroese parliamentary election of 1946 resulted in a majority for parties opposed to independence:[35] following protracted negotiations, Denmark granted home rule to the Faroe Islands on 30 March 1948. This agreement granted the islands a high degree of autonomy, and Faroese finally became the official language in all public spheres.[36]
In 1973 the Faroe Islands declined to join Denmark in entering the European Economic Community (EEC); as a result, the islands are not part of the European Union (EU) today (although as Danish citizens, Faroe Islanders are still considered EU citizens). Following the collapse of the fishing industry in the early 1990s, the Faroes experienced considerable economic difficulties.[37]
Geography
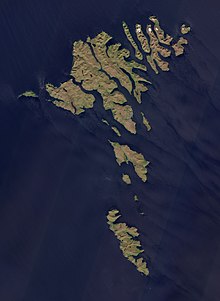
The Faroe Islands are an island group consisting of 18 major islands (and a total of 779 islands, islets, and skerries) about 655 kilometres (407 mi) off the coast of Northern Europe, between the Norwegian Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, about halfway between Iceland and Norway, the closest neighbours being the Northern Isles and the Outer Hebrides of Scotland. Its coordinates are 62°00′N 06°47′W / 62.000°N 6.783°W.
Distance from the Faroe Islands to:
- Rona, Scotland (uninhabited): 260 kilometres (160 mi)
- Shetland (Foula), Scotland: 285 kilometres (177 mi)
- Orkney (Westray), Scotland: 300 kilometres (190 mi)
- Scotland (mainland): 320 kilometres (200 mi)
- Iceland: 450 kilometres (280 mi)
- Norway: 580 kilometres (360 mi)
- Ireland: 670 kilometres (420 mi)
- Denmark: 990 kilometres (620 mi)
The islands cover an area of 1,399 square kilometres (540 sq. mi) and have small lakes and rivers, but no major ones. There are 1,117 kilometres (694 mi) of coastline.[38] The only significant uninhabited island is Lítla Dímun.
The islands are rugged and rocky with some low peaks; the coasts are mostly cliffs. The highest point is Slættaratindur in northern Eysturoy, 882 metres (2,894 ft) above sea level.
The Faroe Islands are made up of an approximately six-kilometres-thick succession of mostly basaltic lava that was part of the great North Atlantic Igneous Province during the Paleogene period.[39] The lavas were erupted during the opening of the North Atlantic ocean, which began about 60 million years ago, and what is today the Faroe Islands was then attached to Greenland.[40][41] The lavas are underlain by circa 30 km of unidentified ancient continental crust.[42][43]
Climate

The climate is classed as subpolar oceanic climate according to the Köppen climate classification: Cfc, with areas having a tundra climate, especially in the mountains, although some coastal or low-lying areas may have very mild-winter versions of a tundra climate. The overall character of the climate of the islands is influenced by the strong warming influence of the Atlantic Ocean, which produces the North Atlantic Current. This, together with the remoteness of any source of landmass-induced warm or cold airflows, ensures that winters are mild (mean temperature 3.0 to 4.0 °C or 37 to 39 °F) while summers are cool (mean temperature 9.5 to 10.5 °C or 49 to 51 °F).
The islands are windy, cloudy, and cool throughout the year with an average of 210 rainy or snowy days per year. The islands lie in the path of depressions moving northeast, making strong winds and heavy rain possible at all times of the year. Sunny days are rare and overcast days are common. Hurricane Faith struck the Faroe Islands on 5 September 1966 with sustained winds over 100 mph (160 km/h) and only then did the storm cease to be a tropical system.[44]

The climate varies greatly over small distances, due to the altitude, ocean currents, topography, and winds. Precipitation varies considerably throughout the archipelago. In some highland areas, snow cover may last for months with snowfalls possible for the greater part of the year (on the highest peaks, summer snowfall is by no means rare), while in some sheltered coastal locations, several years pass without any snowfall whatsoever. Tórshavn receives frosts more often than other areas just a short distance to the south. Snow also is seen at a much higher frequency than on outlying islands nearby. The area receives on average 49 frosts a year.[45]
The collection of meteorological data on the Faroe Islands began in 1867.[46] Winter recording began in 1891, and the warmest winter occurred in 2016–17 with an average temperature of 6.1 °C (43 °F).[47]
| Climate data for Tórshavn (1981–2010, extremes 1961–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 11.6 (52.9) |
12.0 (53.6) |
12.3 (54.1) |
18.3 (64.9) |
19.7 (67.5) |
20.0 (68.0) |
20.2 (68.4) |
22.0 (71.6) |
19.5 (67.1) |
15.2 (59.4) |
14.7 (58.5) |
13.2 (55.8) |
22.0 (71.6) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 5.8 (42.4) |
5.6 (42.1) |
6.0 (42.8) |
7.3 (45.1) |
9.2 (48.6) |
11.1 (52.0) |
12.8 (55.0) |
13.1 (55.6) |
11.5 (52.7) |
9.3 (48.7) |
7.2 (45.0) |
6.2 (43.2) |
8.8 (47.8) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 4.0 (39.2) |
3.6 (38.5) |
4.0 (39.2) |
5.2 (41.4) |
7.0 (44.6) |
9.0 (48.2) |
10.7 (51.3) |
11.0 (51.8) |
9.6 (49.3) |
7.5 (45.5) |
5.5 (41.9) |
4.3 (39.7) |
6.8 (44.2) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 1.7 (35.1) |
1.3 (34.3) |
1.7 (35.1) |
3.0 (37.4) |
5.1 (41.2) |
7.1 (44.8) |
9.0 (48.2) |
9.2 (48.6) |
7.6 (45.7) |
5.4 (41.7) |
3.4 (38.1) |
2.1 (35.8) |
4.7 (40.5) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −8.8 (16.2) |
−11.0 (12.2) |
−9.2 (15.4) |
−9.9 (14.2) |
−3.0 (26.6) |
0.0 (32.0) |
1.5 (34.7) |
1.5 (34.7) |
−0.6 (30.9) |
−4.5 (23.9) |
−7.2 (19.0) |
−10.5 (13.1) |
−11.0 (12.2) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 157.7 (6.21) |
115.2 (4.54) |
131.6 (5.18) |
89.5 (3.52) |
63.3 (2.49) |
57.5 (2.26) |
74.3 (2.93) |
96.0 (3.78) |
119.5 (4.70) |
147.4 (5.80) |
139.3 (5.48) |
135.3 (5.33) |
1,321.3 (52.02) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 26 | 23 | 26 | 22 | 19 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 23 | 26 | 26 | 27 | 273 |
| Average snowy days | 8.3 | 6.6 | 8.0 | 4.4 | 1.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 1.4 | 5.5 | 8.2 | 44.0 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 89 | 88 | 88 | 87 | 87 | 88 | 89 | 90 | 89 | 89 | 88 | 89 | 88 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 14.5 | 36.7 | 72.8 | 108.6 | 137.8 | 128.6 | 103.6 | 100.9 | 82.7 | 53.4 | 21.1 | 7.8 | 868.2 |
| Source: Danish Meteorological Institute (humidity 1961–1990, precipitation days 1961–1990, snowy days 1961–1990)[45][48][49] | |||||||||||||
Flora

The Faroes belong to the Faroe Islands boreal grasslands ecoregion.[50] The natural vegetation of the Faroe Islands is dominated by arctic-alpine plants, wildflowers, grasses, moss, and lichen. Most of the lowland area is grassland and some is heath, dominated by shrubby heathers, mainly Calluna vulgaris. Among the herbaceous flora that occur in the Faroe Islands is the cosmopolitan marsh thistle, Cirsium palustre.[51]
Although it is often asserted that the islands are naturally treeless, several tree species, among them shrubby willows (salix), junipers (juniperus), and stunted birches, colonized the island after the Ice Age, but disappeared later - apparently as a result of grazing impacts, possibly aggravated by a shift to relatively wetter cooler climatic conditions about the same time.[52] A limited number of species have been successfully introduced to the region, in particular trees from the Magellanic subpolar forests region of Chile. Conditions in the Magellanic subpolar forests are similar to those in the Faroe Islands, with cold summers and near-continuous subpolar winds. The following species from Tierra del Fuego, Drimys winteri, Nothofagus antarctica, Nothofagus pumilio, and Nothofagus betuloides, have been successfully introduced to the Faroe Islands. A non-Chilean species that has been introduced is the black cottonwood, also known as the California poplar (Populus trichocarpa).[citation needed]
A collection of Faroese marine algae resulting from a survey sponsored by NATO,[citation needed] the British Museum (Natural History) and the Carlsberg Foundation, is preserved in the Ulster Museum (catalogue numbers: F3195–F3307). It is one of ten exsiccatae sets. A few small plantations consisting of plants collected from similar climates such as Tierra del Fuego in South America and Alaska thrive on the islands.
Fauna

The bird fauna of the Faroe Islands is dominated by seabirds and birds attracted to open land such as heather, probably because of the lack of woodland and other suitable habitats. Many species have developed special Faroese sub-species: common eider, Common starling, Eurasian wren, common murre, and black guillemot.[53] The pied raven, a colour morph of the North Atlantic subspecies of the common raven, was endemic to the Faroe Islands, but now has become extinct; the ordinary, all-black morph remains fairly widespread in the archipelago.[citation needed]
Only a few species of wild land mammals are found in the Faroe Islands today, all introduced by humans. Three species are thriving on the islands today: mountain hare (Lepus timidus), brown rat (Rattus norvegicus), and the house mouse (Mus musculus). Apart from these, there is a local domestic sheep breed, the Faroe sheep (depicted on the coat of arms), and there once was a variety of feral sheep, which survived on Lítla Dímun until the mid-nineteenth century.[54]

Grey seals (Halichoerus grypus) are common around the shorelines away from human habitations.[55] Several species of cetacea live in the waters around the Faroe Islands. Best known are the long-finned pilot whales (Globicephala melaena), which still are hunted by the islanders in accordance with longstanding local tradition.[56] Orcas (Orcinus orca) are regular visitors around the islands.
The domestic animals of the Faroe Islands are a result of 1,200 years of isolated breeding. As a result, many of the islands' domestic animals are found nowhere else in the world. Faroese domestic breeds include Faroe pony, Faroe cow, Faroe sheep, Faroese goose, and Faroese duck.
Geology

The islands were built up during a period of high volcanic activity in the Early Palaeogene around 50–60 million years ago. The islands are built up in layers of different lava flows (basalt) alternating with thin layers of volcanic ash (tuff). The soft ash and the hard basalt thus lie layer upon layer in narrow and thick strips. The soft tuff or ash zones erode away relatively quickly, and the hard lump of basalt above the eroded tuff falls away, forming the first terrace.
Volcanic activity has varied over millions of years, with periods of quiescence and various periods of quiet eruptive fissures and explosive volcanism. In a few places, mainly on Suðuroy, thin layers of coal are present, which are the remains of swamp forests from the time between volcanic eruptions. The plateau has therefore been divided into different basalt series according to the course of volcanism and the age sequence of the layers.
There are major differences in the shapes of the islands' terraces. The lowest and oldest series are thick lava deposits that can be seen on the southern part of Suðuroy, Mykines and Tindhólmur and the western side of Vágar. The basalts of the lower basalt series are often pillared, which is shown by elongated, angular and regular pillars in the mountain side. Very regular vertical columns are found on northern Mykines, where they can be up to 30 metres (100 ft) high.
The middle basalt series consists of thin lava flows with a highly porous interlayer. This series has very little resistance to crumbling and weathering. As these erosion processes are more severe at higher altitudes than lower down, the lowlands are filled with weathering material from the heights, often resulting in a characteristic curved landscape shape. This can be clearly seen on Vágar, the northernmost part of Streymoy and the north-western part of Eysturoy.
Glacial activity has reduced plateau surfaces, especially on the northern islands, where the surfaces have been reduced to a series of narrower or wider zig-zag rows along the length of the islands: especially on the islands of Kunoy, Kalsoy and Borðoy, where an eastward and a westward ice mass have eroded the intervening mountain range into a narrow ridge.
Government and politics
The Faroe Islands are a self-governing country under the external sovereignty of the Kingdom of Denmark.[57] The Faroese government holds executive power in local government affairs. The head of the government is called the Løgmaður ("Chief Justice") and serves as Prime Minister and head of the Faroese Government. Any other member of the cabinet is called a Minister of the Faroese Government (landsstýrismaður/ráðharri if male, landsstýriskvinna/ráðfrú if female). The Faroese parliament – the Løgting ("Law Thing") – dates back to the early days of settlement and claims to be one of the longest functioning parliaments in the world, alongside the Icelandic Althing and the Manx Tynwald. The parliament currently has 33 members.[58]

Elections are held at municipal and national levels, additionally electing two members to the Folketing. Until 2007, there were seven electoral districts, which were abolished on 25 October of that year in favour of a single nationwide district.
Zdroj:https://en.wikipedia.org?pojem=Faroe_IslandsText je dostupný za podmienok Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších podmienok. Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky použitia.
Antropológia
Aplikované vedy
Bibliometria
Dejiny vedy
Encyklopédie
Filozofia vedy
Forenzné vedy
Humanitné vedy
Knižničná veda
Kryogenika
Kryptológia
Kulturológia
Literárna veda
Medzidisciplinárne oblasti
Metódy kvantitatívnej analýzy
Metavedy
Metodika
Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative
Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších
podmienok.
Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky
použitia.
www.astronomia.sk | www.biologia.sk | www.botanika.sk | www.dejiny.sk | www.economy.sk | www.elektrotechnika.sk | www.estetika.sk | www.farmakologia.sk | www.filozofia.sk | Fyzika | www.futurologia.sk | www.genetika.sk | www.chemia.sk | www.lingvistika.sk | www.politologia.sk | www.psychologia.sk | www.sexuologia.sk | www.sociologia.sk | www.veda.sk I www.zoologia.sk