A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
Republic of Serbia Република Србија, Republika Srbija (Serbian) | |
|---|---|
| Anthem: Боже правде Bože pravde (English: "God of Justice") | |
Location of Serbia (green) and the disputed territory of Kosovo (light green) in Europe (dark grey) | |
| Capital and largest city | Belgrade 44°48′N 20°28′E / 44.800°N 20.467°E |
| Official languages | Serbian[a] |
| Ethnic groups (2022; excluding Kosovo) |
|
| Religion (2022; excluding Kosovo) |
|
| Demonym(s) | Serbian |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary republic |
| Aleksandar Vučić | |
| Ivica Dačić (acting) | |
| Ana Brnabić | |
| Legislature | National Assembly |
| Establishment history | |
| 780 | |
• Kingdom | 1217 |
• Empire | 1346 |
| 1459–1804 | |
| 1804–1835 | |
| 1815 | |
| 1878 | |
| 1882 | |
| 1918 | |
• Republic | 1945 |
| 1992 | |
• Independence restored | 2006 |
| Area | |
• Total | 88,499 km2 (34,170 sq mi)[2] (111th) |
• Excluding Kosovo | 77,612 km2 (29,966 sq mi)[3] |
| Population | |
• 2022 census | |
• Density | 85.7/km2 (222.0/sq mi) (130th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2023 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2023 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| Gini (2019) | medium |
| HDI (2022) | very high (65th) |
| Currency | Serbian dinar (RSD) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
• Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Calling code | +381 |
| ISO 3166 code | RS |
| Internet TLD | |
Serbia,[c] officially the Republic of Serbia,[d] is a landlocked country at the crossroads of Southeast and Central Europe,[8][9] located in the Balkans and the Pannonian Plain. It borders Hungary to the north, Romania to the northeast, Bulgaria to the southeast, North Macedonia to the south, Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina to the west, and Montenegro to the southwest. Serbia claims a border with Albania through the disputed territory of Kosovo. Serbia has about 6.6 million inhabitants, excluding Kosovo. Its capital Belgrade is also the largest city.
Continuously inhabited since the Paleolithic Age, the territory of modern-day Serbia faced Slavic migrations in the 6th century, establishing several regional states in the early Middle Ages at times recognised as tributaries to the Byzantine, Frankish and Hungarian kingdoms. The Serbian Kingdom obtained recognition by the Holy See and Constantinople in 1217, reaching its territorial apex in 1346 as the Serbian Empire. By the mid-16th century, the Ottomans annexed the entirety of modern-day Serbia; their rule was at times interrupted by the Habsburg Empire, which began expanding towards Central Serbia from the end of the 17th century while maintaining a foothold in Vojvodina. In the early 19th century, the Serbian Revolution established the nation-state as the region's first constitutional monarchy, which subsequently expanded its territory.[10] In 1918, in the aftermath of World War I, the Kingdom of Serbia united with the former Habsburg crownland of Vojvodina; later in the same year it joined with other South Slavic nations in the foundation of Yugoslavia, which existed in various political formations until the Yugoslav Wars of the 1990s. During the breakup of Yugoslavia, Serbia formed a union with Montenegro,[11] which was peacefully dissolved in 2006, restoring Serbia's independence as a sovereign state for the first time since 1918.[12] In 2008, representatives of the Assembly of Kosovo unilaterally declared independence, with mixed responses from the international community while Serbia continues to claim it as part of its own sovereign territory.
Serbia is an upper-middle income economy, ranked "very high" in the Human Development Index domain. It is a unitary parliamentary constitutional republic, member of the UN, CoE, OSCE, PfP, BSEC, CEFTA, and is acceding to the WTO. Since 2014, the country has been negotiating its EU accession, with the possibility of joining the European Union by 2030.[13] Serbia formally adheres to the policy of military neutrality. The country provides universal health care and free primary and secondary education to its citizens.
Etymology
The origin of the name Serbia is unclear. Historically, authors have mentioned the Serbs (Serbian: Srbi / Срби) and the Sorbs of Eastern Germany (Upper Sorbian: Serbja; Lower Sorbian: Serby) in a variety of ways: Cervetiis (Servetiis), gentis (S)urbiorum, Suurbi, Sorabi, Soraborum, Sorabos, Surpe, Sorabici, Sorabiet, Sarbin, Swrbjn, Servians, Sorbi, Sirbia, Sribia, Zirbia, Zribia, Suurbelant, Surbia, Serbulia / Sorbulia among others.[14][15][16] These authors used these names to refer to Serbs and Sorbs in areas where their historical and current presence is not disputable (notably in the Balkans and Lusatia). However, there are also sourcesthat using similar names in other parts of the world (most notably in the Asiatic Sarmatia in the Caucasus).
There exist two prevailing theories on the origin of the ethnonym *Sŕbъ (plur. *Sŕby), one from a Proto-Slavic language with an appellative meaning of a "family kinship" and "alliance", while another from an Iranian-Sarmatian language with various meanings.[15][17] In his work, De Administrando Imperio, Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus suggests that the Serbs originated from White Serbia near Francia.
From 1815 to 1882, the official name for Serbia was the Principality of Serbia. From 1882 to 1918, it was renamed to the Kingdom of Serbia, later from 1945 to 1963, the official name for Serbia was the People's Republic of Serbia. This was again renamed the Socialist Republic of Serbia from 1963 to 1990. Since 1990, the official name of the country has been the Republic of Serbia.
History
Prehistory and antiquity
Archaeological evidence of Paleolithic settlements on the territory of present-day Serbia is scarce. A fragment of a human jaw found in Sićevo (Mala Balanica) is believed to be up to 525,000–397,000 years old.[18]
Approximately 6,500 BC, during the Neolithic, the Starčevo and Vinča cultures existed in the region of modern-day Belgrade. They dominated much of Southeast Europe as well as parts of Central Europe and Anatolia. Several important archaeological sites from this era, including Lepenski Vir and Vinča-Belo Brdo, still exist near the Danube.[19][20]
During the Iron Age, local tribes of Triballi, Dardani, and Autariatae were encountered by the Ancient Greeks during their cultural and political expansion into the region, from the 5th up to the 2nd century BC. The Celtic tribe of Scordisci settled throughout the area in the 3rd century BC. It formed a tribal state, building several fortifications, including their capital at Singidunum (present-day Belgrade) and Naissos (present-day Niš).
The Romans conquered much of the territory in the 2nd century BC. In 167 BC, the Roman province of Illyricum was established; the remainder was conquered around 75 BC, forming the Roman province of Moesia Superior; the modern-day Srem region was conquered in 9 BC; and Bačka and Banat in 106 AD after the Dacian Wars. As a result of this, contemporary Serbia extends fully or partially over several former Roman provinces, including Moesia, Pannonia, Praevalitana, Dalmatia, Dacia, and Macedonia. Seventeen Roman Emperors were born in the area of modern-day Serbia, second only to contemporary Italy.[21] The most famous of these was Constantine the Great, the first Christian Emperor, who issued an edict ordering religious tolerance throughout the Empire.

When the Roman Empire was divided in 395, most of Serbia remained under the Byzantine Empire, and its northwestern parts were included in the Western Roman Empire. By the 6th century, South Slavs migrated into the Byzantine territory in large numbers.[24] They merged with the local Romanised population that was gradually assimilated.[25][26][27]
Middle Ages
White Serbs, an early Slavic tribe from White Serbia eventually settled in an area between the Sava river and the Dinaric Alps.[28][29][30] By the beginning of the 9th century, Serbia achieved a level of statehood.[31] Christianization of Serbia was a gradual process, finalized by the middle of the 9th century.[32] In the mid-10th-century, the Serbian state experienced a fall. During the 11th and 12th century, Serbian state frequently fought with the neighbouring Byzantine Empire.[33] Between 1166 and 1371, Serbia was ruled by the Nemanjić dynasty, under whom the state was elevated to a kingdom in 1217,[34] and an empire in 1346,[35] under Stefan Dušan. Serbian Orthodox Church was organized as an autocephalous archbishopric in 1219,[36] through the effort of Sava, the country's patron saint, and in 1346 it was raised to the Patriarchate. Monuments of the Nemanjić period survive in many monasteries (several being World Heritage sites) and fortifications.

During these centuries the Serbian state (and influence) expanded significantly. The northern part (modern Vojvodina), was ruled by the Kingdom of Hungary. The period after 1371, known as the Fall of the Serbian Empire saw the once-powerful state fragmented into several principalities, culminating in the Battle of Kosovo (1389) against the rising Ottoman Empire.[37] By the end of the 14th century, the Turks had conquered and ruled the territories south of the Šar Mountains. The political center of Serbia shifted northwards, when the capital of the newly established Serbian Despotate was transferred to Belgrade in 1403,[38] before moving to Smederevo in 1430.[39] The Despotate was then under the double vassalage of Hungary and the Ottoman Empire.[40] The fall of Smederevo on 20 June 1459, which marked the full conquest of the Serbian Despotate by the Ottomans, also symbolically signified the end of the Serbian state.[41]
Ottoman and Habsburg rule

In all Serbian lands conquered by the Ottomans, the native nobility was eliminated and the peasantry was enserfed to Ottoman rulers, while much of the clergy fled or were confined to the isolated monasteries. Under the Ottoman system, Serbs and Christians were considered an inferior class and subjected to heavy taxes, and a portion of the Serbian population experienced Islamization. Many Serbs were recruited during the devshirme system, a form of slavery, in which boys from Balkan Christian families were forcibly converted to Islam and trained for infantry units of the Ottoman army known as the Janissaries.[43][44][45][46] The Serbian Patriarchate of Peć was extinguished in 1463,[47] but reestablished in 1557,[48][49][50] providing for limited continuation of Serbian cultural traditions within the Ottoman Empire, under the Millet system.[51][52]
After the loss of statehood to the Ottoman Empire, Serbian resistance continued in northern regions (modern Vojvodina), under titular despots (until 1537), and popular leaders like Jovan Nenad (1526–1527). From 1521 to 1552, Ottomans conquered Belgrade and regions of Syrmia, Bačka, and Banat.[53] Wars and rebellions constantly challenged Ottoman rule. One of the most significant was the Banat Uprising in 1594 and 1595, which was part of the Long War (1593–1606) between the Habsburgs and the Ottomans.[54][55] The area of modern Vojvodina endured a century-long Ottoman occupation before being ceded to the Habsburg monarchy, partially by the Treaty of Karlovci (1699),[56] and fully by the Treaty of Požarevac (1718).[57]

During the Habsburg-Ottoman war (1683–1699), much of Serbia switched from Ottoman rule to Habsburg control from 1688 to 1690.[58] However, the Ottoman army reconquered a large part of Serbia in the winter of 1689/1690, leading to a brutal massacre of the civilian population by uncontrolled Albanian and Tatar units. As a result of the persecutions, several tens of thousands of Serbs, led by the patriarch, Arsenije III Crnojević, fled northwards to settle in Hungary,[59] an event known as the Great Migration of 1690.[60] In August 1690, following several petitions, the Emperor Leopold I formally granted Serbs from the Habsburg monarchy a first set of "privileges",[61][62] primarily to guarantee them freedom of religion.[63] As a consequence, the ecclesiastical centre of the Serbs also moved northwards, to the Metropolitanate of Karlovci,[64] and the Serbian Patriarchate of Peć was once-again abolished by the Ottomans in 1766.[65][66]
In 1718–39, the Habsburg monarchy occupied much of Central Serbia and established the Kingdom of Serbia as crownland.[57] Those gains were lost by the Treaty of Belgrade in 1739, when the Ottomans retook the region.[67] Apart from territory of modern Vojvodina which remained under the Habsburg Empire, central regions of Serbia were occupied once again by the Habsburgs in 1788–1792.
Revolution and independence
The Serbian Revolution for independence from the Ottoman Empire lasted eleven years, from 1804 until 1815.[68][69][70][71] During the First Serbian Uprising (1804–1813), led by vožd Karađorđe Petrović, Serbia was independent for almost a decade before the Ottoman army was able to reoccupy the country.[72] The Second Serbian Uprising began in 1815, led by Miloš Obrenović; it ended with a compromise between Serbian revolutionaries and Ottoman authorities.[73] Serbia was one of the first nations in the Balkans to abolish feudalism.[74] The Akkerman Convention in 1826, the Treaty of Adrianople in 1829 and finally, the Hatt-i Sharif, recognised the suzerainty of Serbia. The First Serbian Constitution was adopted on 15 February 1835, making the country one of the first to adopt a democratic constitution in Europe.[75][76] 15 February is now commemorated as Statehood Day, a public holiday.[77]
Following the clashes between the Ottoman army and Serbs in Belgrade in 1862,[78] and under pressure from the Great Powers, by 1867 the last Turkish soldiers left the Principality, making the country de facto independent.[79] By enacting a new constitution in 1869,[80] without consulting the Porte, Serbian diplomats confirmed the de facto independence of the country. In 1876, Serbia declared war on the Ottoman Empire, siding with the ongoing Christian uprisings in Bosnia-Herzegovina and Bulgaria.[81][82]
The formal independence of the country was internationally recognised at the Congress of Berlin in 1878, which ended the Russo-Turkish War; this treaty, however, prohibited Serbia from uniting with other Serbian regions by placing Bosnia and Herzegovina under Austro-Hungarian occupation, alongside the occupation of the region of Raška.[83] From 1815 to 1903, the principality was ruled by the House of Obrenović, save for the rule of Prince Aleksandar Karađorđević between 1842 and 1858. In 1882, Principality of Serbia became the Kingdom of Serbia, ruled by King Milan I.[84] The House of Karađorđević, descendants of the revolutionary leader Karađorđe Petrović, assumed power in 1903 following the May Overthrow.[85] The 1848 revolution in Austria led to the establishment of the autonomous territory of Serbian Vojvodina; by 1849, the region was transformed into the Voivodeship of Serbia and Banat of Temeschwar.[86]
Balkan Wars and World War I
In the First Balkan War in 1912, the Balkan League defeated the Ottoman Empire and captured its European territories, which enabled territorial expansion of the Kingdom of Serbia into regions of Raška, Kosovo, Metohija, and Vardarian Macedonia. The Second Balkan War soon ensued when Bulgaria turned on its former allies, but was defeated, resulting in the Treaty of Bucharest. In two years, Serbia enlarged its territory by 80% and its population by 50%,[87] it also suffered high casualties on the eve of World War I, with more than 36,000 dead.[88] Austria-Hungary became wary of the rising regional power on its borders and its potential to become an anchor for unification of Serbs and other South Slavs, and the relationship between the two countries became tense.
The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria on 28 June 1914 in Sarajevo by Gavrilo Princip, a member of the Young Bosnia organisation, led to Austria-Hungary declaring war on Serbia, on 28 July 1914, setting off World War I.[90]
Serbia won the first major battles of the war, including the Battle of Cer,[91] and the Battle of Kolubara.[92] Despite initial success, it was eventually overpowered by the Central Powers in 1915 and Austro-Hungarian occupation of Serbia followed. Most of its army and some people retreated to Greece and Corfu, suffering immense losses on the way. After the Central Powers' military situation on other fronts worsened, the remains of the Serb army returned east and led a final breakthrough through enemy lines on 15 September 1918, liberating Serbia and defeating Bulgaria and Austria-Hungary.[93] Serbia, with its campaign, was a major Balkan Entente Power[94] which contributed significantly to the Allied victory in the Balkans in November 1918, especially by helping France force Bulgaria's capitulation.[95] Serbia's casualties accounted for 8% of the total Entente military deaths; 58% (243,600) soldiers of the Serbian army perished in the war.[96] The total number of casualties is placed around 700,000,[97] more than 16% of Serbia's prewar size,[98] and a majority (57%) of its overall male population.[99][100][101] Serbia suffered the biggest casualty rate in World War I.[102]
Kingdom of Yugoslavia
The Corfu Declaration was a formal agreement between the government-in-exile of the Kingdom of Serbia and the Yugoslav Committee (anti-Habsburg South Slav émigrés) that pledged to unify Kingdom of Serbia and Kingdom of Montenegro with Austria-Hungary's South Slav autonomous crown lands: Kingdom of Croatia-Slavonia, Kingdom of Dalmatia, Slovenia, Vojvodina (then part of the Kingdom of Hungary) and Bosnia and Herzegovina in a post-war Yugoslav state. It was signed on 20 July 1917 on Corfu.

As the Austro-Hungarian Empire collapsed, the territory of Syrmia united with Serbia on 24 November 1918.[87] Just a day later, the Great People's Assembly of Serbs, Bunjevci and other Slavs in Banat, Bačka and Baranja declared the unification of these regions (Banat, Bačka, and Baranja) with Serbia.[103]
On 26 November 1918, the Podgorica Assembly deposed the House of Petrović-Njegoš and united Montenegro with Serbia.[104] On 1 December 1918, in Belgrade, Serbian Prince Regent Alexander Karađorđević proclaimed the Kingdom of the Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes, under King Peter I of Serbia.[105][106] King Peter was succeeded by his son, Alexander, in August 1921. Serb centralists and Croat autonomists clashed in the parliament, and most governments were fragile and short-lived. Nikola Pašić, a conservative prime minister, headed or dominated most governments until his death. King Alexander established a dictatorship in 1929 with the aim of establishing the Yugoslav ideology and single Yugoslav nation, changed the name of the country to Yugoslavia. The effect of Alexander's dictatorship was to further alienate the non-Serbs living in Yugoslavia from the idea of unity.[107]
Alexander was assassinated in Marseille, during an official visit in 1934 by Vlado Chernozemski, member of the IMRO. Alexander was succeeded by his eleven-year-old son Peter II. In August 1939 the Cvetković–Maček Agreement established an autonomous Banate of Croatia as a solution to Croatian concerns.
World War II
In 1941, in spite of Yugoslav attempts to remain neutral, the Axis powers invaded Yugoslavia. The territory of modern Serbia was divided between Hungary, Bulgaria, the Independent State of Croatia, Greater Albania and Montenegro, while the remainder was placed under the military administration of Nazi Germany, with Serbian puppet governments led by Milan Aćimović and Milan Nedić assisted by Dimitrije Ljotić's fascist organization Yugoslav National Movement (Zbor).
The Yugoslav territory was the scene of a civil war between royalist Chetniks commanded by Draža Mihailović and communist partisans commanded by Josip Broz Tito. Axis auxiliary units of the Serbian Volunteer Corps and the Serbian State Guard fought against both of these forces. The siege of Kraljevo was a major battle of the uprising in Serbia, led by Chetnik forces against the Nazis. Several days after the battle began the German forces committed a massacre of approximately 2,000 civilians in an event known as the Kraljevo massacre, in a reprisal for the attack.
Draginac and Loznica massacre of 2,950 villagers in Western Serbia in 1941 was the first large execution of civilians in occupied Serbia by Germans, with Kragujevac massacre and Novi Sad Raid of Jews and Serbs by Hungarian fascists being the most notorious, with over 3,000 victims in each case.[108][109] After one year of occupation, around 16,000 Serbian Jews were murdered in the area, or around 90% of its pre-war Jewish population during The Holocaust in Serbia. Many concentration camps were established across the area. Banjica concentration camp was the largest concentration camp and jointly run by the German army and Nedić's regime,[110] with primary victims being Serbian Jews, Roma, and Serb political prisoners.[111]
Hundreds of thousands of ethnic Serbs fled the Axis puppet state known as the Independent State of Croatia and sought refuge in German-occupied Serbia, seeking to escape the large-scale persecution and Genocide of Serbs, Jews, and Roma being committed by the Ustaše regime.[112] The number of Serb victims was approximately 300,000 to 350,000.[113][114][115] According to Tito himself, Serbs made up the vast majority of anti-fascist fighters and Yugoslav Partisans for the whole course of World War II.[116]
The Republic of Užice was a short-lived liberated territory established by the Partisans and the first liberated territory in World War II Europe, organised as a military mini-state that existed in the autumn of 1941 in the west of occupied Serbia. By late 1944, the Belgrade Offensive swung in favour of the partisans in the civil war; the partisans subsequently gained control of Yugoslavia.[117] Following the Belgrade Offensive, the Syrmian Front was the last major military action of World War II in Serbia. A study by Vladimir Žerjavić estimates total war-related deaths in Yugoslavia at 1,027,000, including 273,000 in Serbia.[118]
Socialist Yugoslavia

The victory of the Communist Partisans resulted in the abolition of the monarchy and a subsequent constitutional referendum. A one-party state was soon established in Yugoslavia by the Communist Party of Yugoslavia. It is claimed between 60,000 and 70,000 people died in Serbia during the 1944–45 communist purge.[119] Serbia became a constituent republic within the Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia known as the People's Republic of Serbia, and had a republic-branch of the federal communist party, the League of Communists of Serbia. Serbia's most powerful and influential politician in Tito-era Yugoslavia was Aleksandar Ranković, one of the "big four" Yugoslav leaders. Ranković was later removed from the office because of the disagreements regarding Kosovo's nomenklatura and the unity of Serbia. Ranković's dismissal was highly unpopular among Serbs. Pro-decentralisation reformers in Yugoslavia succeeded in the late 1960s in attaining substantial decentralisation of powers, creating substantial autonomy in Kosovo and Vojvodina, and recognising a distinctive "Muslim" nationality. As a result of these reforms, there was a massive overhaul of Kosovo's nomenklatura and police, that shifted from being Serb-dominated to ethnic Albanian-dominated through firing Serbs on a large scale. Further concessions were made to the ethnic Albanians of Kosovo in response to unrest, including the creation of the University of Pristina as an Albanian language institution. These changes created widespread fear among Serbs of being treated as second-class citizens.[120]
Belgrade, the capital of FPR Yugoslavia and PR Serbia, hosted the first Non-Aligned Movement Summit in September 1961, as well as the first major gathering of the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) with the aim of implementing the Helsinki Accords from October 1977 to March 1978.[121][122] The 1972 smallpox outbreak in SAP Kosovo and other parts of SR Serbia was the last major outbreak of smallpox in Europe since World War II.[123]
Breakup of Yugoslavia and political transition

In 1989, Slobodan Milošević rose to power in Serbia. Milošević promised a reduction of powers for the autonomous provinces of Kosovo and Vojvodina, where his allies subsequently took over power, during the Anti-bureaucratic revolution.[124] This ignited tensions between the communist leadership of the other republics of Yugoslavia and awoke ethnic nationalism across Yugoslavia that eventually resulted in its breakup, with Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Macedonia declaring independence during 1991 and 1992.[125][better source needed] Serbia and Montenegro remained together as the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (FRY).[11] However, according to the Badinter Commission, the country was not legally considered a continuation of the former SFRY, but a new state.
Fueled by ethnic tensions, the Yugoslav Wars (1991–2001) erupted, with the most severe conflicts taking place in Croatia and Bosnia, where the large ethnic Serb communities opposed independence from Yugoslavia. The FRY remained outside the conflicts, but provided logistic, military and financial support to Serb forces in the wars. In response, the UN imposed sanctions against Yugoslavia which led to political isolation and the collapse of the economy (GDP decreased from $24 billion in 1990 to under $10 billion in 1993). Serbia was in the 2000s sued on the charges of alleged genocide by neighbouring Bosnia and Herzegovina and Croatia but in both cases the main charges against Serbia were dismissed.[126][127]
Multi-party democracy was introduced in Serbia in 1990, officially dismantling the one-party system. Despite constitutional changes, Milošević maintained strong political influence over the state media and security apparatus.[128][129] When the ruling Socialist Party of Serbia refused to accept its defeat in municipal elections in 1996, Serbians engaged in large protests against the government.

In 1998, continued clashes between the Albanian guerilla Kosovo Liberation Army and Yugoslav security forces led to the short Kosovo War (1998–99), in which NATO intervened, leading to the withdrawal of Serbian forces and the establishment of UN administration in the province.[130] After the Yugoslav Wars, Serbia became home to highest number of refugees and internally displaced persons in Europe.[131][132][133]
After presidential elections in September 2000, opposition parties accused Milošević of electoral fraud.[134][135] A campaign of civil resistance followed, led by the Democratic Opposition of Serbia (DOS), a broad coalition of anti-Milošević parties. This culminated on 5 October when half a million people from all over the country congregated in Belgrade, compelling Milošević to concede defeat.[136] The fall of Milošević ended Yugoslavia's international isolation. Milošević was sent to the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia. The DOS announced that FR Yugoslavia would seek to join the European Union. In 2003, the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia was renamed Serbia and Montenegro;[137] the EU opened negotiations with the country for the Stabilisation and Association Agreement.

Serbia's political climate remained tense and in 2003, Prime Minister Zoran Đinđić was assassinated as result of a plot originating from organised crime and former security officials. In 2004 unrest in Kosovo took place, leaving 19 people dead and a number of Serbian Orthodox churches and monasteries destroyed or damaged.[138][139]
Contemporary period
On 21 May 2006, Montenegro held a referendum which showed 55.4% of voters in favour of independence, just above the 55% required by the referendum. This was followed on 5 June 2006 by Serbia's declaration of independence, marking the re-emergence of Serbia as an independent state. The National Assembly of Serbia declared Serbia to be the legal successor to the former state union.[140]
The Assembly of Kosovo unilaterally declared independence from Serbia on 17 February 2008. Serbia immediately condemned the declaration and continues to deny any statehood to Kosovo. The declaration has sparked varied responses from the international community.[141] Status-neutral talks between Serbia and Kosovo-Albanian authorities are held in Brussels, mediated by the EU.
Serbia officially applied for membership in the European Union on 22 December 2009,[142] and received candidate status on 1 March 2012, following a delay in December 2011.[143][144] Following a positive recommendation of the European Commission and European Council in June 2013, negotiations to join the EU commenced in January 2014.[145]
Since Aleksandar Vučić and his Serbian Progressive Party came to power in 2012,[146][147] Serbia has suffered from democratic backsliding into authoritarianism,[148][149][150] followed by a decline in media freedom and civil liberties.[151][152] After the COVID-19 pandemic spread to Serbia in March 2020, a state of emergency was declared and a curfew was introduced for the first time in Serbia since World War II.[153] In April 2022, President Aleksandar Vučić was re-elected.[154] Serbia drew western criticism for not joining EU sanctions against Russia and maintaining bilateral relations after the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine. However, Serbia condemned Russia at the United Nations General Assembly and Human Rights Council.[155] In December 2023, President Vučić won a snap parliamentary election.[156] The election resulted in protests, with opposition supporters claiming that the election result was fraudulent.[157][158][159][160]
Geography

A landlocked country situated at the crossroads between Central[161][162] and Southeastern Europe, Serbia is located in the Balkan peninsula and the Pannonian Plain. Serbia lies between latitudes 41° and 47° N, and longitudes 18° and 23° E. The country covers a total of 88,499 km2 (34,170 sq mi) (including Kosovo); with Kosovo excluded, the total area is 77,474 km2 (29,913 sq mi).[3][2] Its total border length amounts to 2,027 km (1,260 mi): Albania 115 km (71 mi), Bosnia and Herzegovina 302 km (188 mi), Bulgaria 318 km (198 mi), Croatia 241 km (150 mi), Hungary 151 km (94 mi), North Macedonia 221 km (137 mi), Montenegro 203 km (126 mi) and Romania 476 km (296 mi).[3] All of Kosovo's border with Albania (115 km (71 mi)), North Macedonia (159 km (99 mi)) and Montenegro (79 km (49 mi))[163] are under control of the Kosovo border police.[164] Serbia treats the 352 km (219 mi) border with Kosovo as an "administrative line"; it is under shared control of Kosovo border police and Serbian police forces.[165] The Pannonian Plain covers the northern third of the country (Vojvodina and Mačva[166]) while the easternmost tip of Serbia extends into the Wallachian Plain. The terrain of the central part of the country consists chiefly of hills traversed by rivers. Mountains dominate the southern third of Serbia. Dinaric Alps stretch in the west and the southwest, following the flow of the rivers Drina and Ibar. The Carpathian Mountains and Balkan Mountains stretch in a north–south direction in eastern Serbia.[167]
Ancient mountains in the southeast corner of the country belong to the Rilo-Rhodope Mountain system. Elevation ranges from the Midžor peak of the Balkan Mountains at 2,169 metres (7,116 feet) (the highest peak in Serbia, excluding Kosovo) to the lowest point of just 17 metres (56 feet) near the Danube river at Prahovo.[168] The largest lake is Đerdap Lake (163 square kilometres (63 sq mi)) and the longest river passing through Serbia is the Danube (587.35 kilometres (364.96 mi)).
Climate

The climate of Serbia is under the influences of the landmass of Eurasia and the Atlantic Ocean and Mediterranean Sea. With mean January temperatures around 0 °C (32 °F), and mean July temperatures of 22 °C (72 °F), it can be classified as a warm-humid continental or humid subtropical climate.[169] In the north, the climate is more continental, with cold winters, and hot, humid summers along with well-distributed rainfall patterns. In the south, summers and autumns are drier, and winters are relatively cold, with heavy inland snowfall in the mountains.
Differences in elevation, proximity to the Adriatic Sea and large river basins, as well as exposure to the winds account for climate variations.[170] Southern Serbia is subject to Mediterranean influences.[171] The Dinaric Alps and other mountain ranges contribute to the cooling of most of the warm air masses. Winters are quite harsh in the Pešter plateau, because of the mountains which encircle it.[172] One of the climatic features of Serbia is Košava, a cold and very squally southeastern wind which starts in the Carpathian Mountains and follows the Danube northwest through the Iron Gate where it gains a jet effect and continues to Belgrade and can spread as far south as Niš.[173]
The average annual air temperature for the period 1961–1990 for the area with an elevation of up to 300 m (984 ft) is 10.9 °C (51.6 °F). The areas with an elevation of 300 to 500 m (984 to 1,640 ft) have an average annual temperature of around 10.0 °C (50.0 °F), and over 1,000 m (3,281 ft) of elevation around 6.0 °C (42.8 °F).[174] The lowest recorded temperature in Serbia was −39.5 °C (−39.1 °F) on 13 January 1985, Karajukića Bunari in Pešter, and the highest was 44.9 °C (112.8 °F), on 24 July 2007, recorded in Smederevska Palanka.[175]
Serbia is one of few European countries with very high risk of natural hazards (earthquakes, storms, floods, droughts).[176] It is estimated that potential floods, particularly in areas of Central Serbia, threaten over 500 larger settlements and an area of 16,000 square kilometres.[177] The most disastrous were the floods in May 2014, when 57 people died and a damage of over 1.5 billion euros was inflicted.[178]
Hydrology
Almost all of Serbia's rivers drain to the Black Sea, by way of the Danube river. The Danube, the second largest European river, passes through Serbia with 588 kilometres[179] (21% of its overall length) and represents the major source of fresh water.[180][181] It is joined by its biggest tributaries, the Great Morava (longest river entirely in Serbia with 493 km (306 mi) of length[182]), Sava and Tisza rivers.[183] One notable exception is the Pčinja which flows into the Aegean. Drina river forms the natural border between Bosnia and Herzegovina and Serbia, and represents the main kayaking and rafting attraction in both countries.
Due to configuration of the terrain, natural lakes are sparse and small; most of them are located in the lowlands of Vojvodina, like the aeolian lake Palić or numerous oxbow lakes along river flows (like Zasavica and Carska Bara). However, there are numerous artificial lakes, mostly due to hydroelectric dams, the biggest being Đerdap (Iron Gates) on the Danube with 163 km2 (63 sq mi) on the Serbian side[184] (a total area of 253 km2 (98 sq mi) is shared with Romania); Perućac on the Drina, and Vlasina. The largest waterfall, Jelovarnik, located in Kopaonik, is 71 m high.[185] Abundance of relatively unpolluted surface waters and numerous underground natural and mineral water sources of high water quality presents a chance for export and economy improvement; however, more extensive exploitation and production of bottled water began only recently.[citation needed]
Environment
Serbia is a country of rich ecosystem and species diversity—covering only 1.9% of the whole European territory, Serbia is home to 39% of European vascular flora, 51% of European fish fauna, 40% of European reptiles and amphibian fauna, 74% of European bird fauna, and 67% European mammal fauna.[186] Its abundance of mountains and rivers make it an ideal environment for a variety of animals, many of which are protected including wolves, lynx, bears, foxes, and stags. There are 17 snake species living all over the country; 8 of them are venomous.[187]
Mountain of Tara in western Serbia is one of the last regions in Europe where bears can still live in absolute freedom.[188][better source needed] Serbia is home to about 380 species of birds. In Carska Bara, there are over 300 bird species on just a few square kilometres.[189] Uvac Gorge is considered one of the last habitats of the Griffon vulture in Europe.[190] In area around the city of Kikinda, in the northernmost part of the country, some 145 endangered long-eared owls are noted, making it the world's biggest settlement of these species.[191] The country is considerably rich with threatened species of bats and butterflies as well.[192]
There are 380 protected areas of Serbia, encompassing 4,947 square kilometres or 6.4% of the country.[186] Those protected areas include 5 national parks (Đerdap, Tara, Kopaonik, Fruška Gora and Šar Mountain), 15 nature parks, 15 "landscapes of outstanding features", 61 nature reserves, and 281 natural monuments.[185] With 29.1% of its territory covered by forest, Serbia is considered to be a middle-forested country, compared on a global scale to world forest coverage at 30%, and European average of 35%. The total forest area in Serbia is 2,252,000 ha (1,194,000 ha or 53% are state-owned, and 1,058,387 ha or 47% are privately owned) or 0.3 ha per inhabitant.[193] It had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 5.29/10, ranking it 105th globally out of 172 countries.[194] The most common trees are oak, beech, pines, and firs.
Air pollution is a significant problem in Bor area, due to work of large copper mining and smelting complex, and Pančevo where oil and petrochemical industry is based.[195] Some cities suffer from water supply problems, due to mismanagement and low investments in the past, as well as water pollution (like the pollution of the Ibar River from the Trepča zinc-lead combinate,[196] affecting the city of Kraljevo, or the presence of natural arsenic in underground waters in Zrenjanin).[197]
Poor waste management has been identified as one of the most important environmental problems in Serbia and the recycling is a fledgling activity, with only 15% of its waste being turned back for reuse.[198] The 1999 NATO bombing caused serious damage to the environment, with several thousand tonnes of toxic chemicals stored in targeted factories and refineries released into the soil and water basins.[199]
Politics
Serbia is a parliamentary republic, with the government divided into legislative, executive, and judiciary branches. The current constitution was adopted in 2006 in the aftermath of the Montenegro independence referendum.[200] The Constitutional Court rules on matters regarding the Constitution.
The President of the Republic (Predsednik Republike) is the head of state, is elected by popular vote to a five-year term and is limited by the Constitution to a maximum of two terms. In addition to being the commander in chief of the armed forces, the president has the procedural duty of appointing the prime minister with the consent of the parliament, and has some influence on foreign policy.[201] Aleksandar Vučić of the Serbian Progressive Party is the current president following the 2017 presidential election.[202] Seat of the presidency is Novi Dvor.
The Government (Vlada) is composed of the prime minister and cabinet ministers. The Government is responsible for proposing legislation and a budget, executing the laws, and guiding the foreign and internal policies. The current prime minister is Ana Brnabić, nominated by the Serbian Progressive Party.[203]
The National Assembly (Narodna skupština) is a unicameral legislative body. The National Assembly has the power to enact laws, approve the budget, schedule presidential elections, select and dismiss the Prime Minister and other ministers, declare war, and ratify international treaties and agreements.[204] It is composed of 250 proportionally elected members who serve four-year terms. Following the 2020 parliamentary election, the largest political parties in the National Assembly are the populist Serbian Progressive Party and Socialist Party of Serbia, that with its partners, hold more than a supermajority number of seats.[205]
In 2021, Serbia was the 5th country in Europe by the number of women holding high-ranking public functions.[206][better source needed]
Law and criminal justice
Serbia has a three-tiered judicial system, made up of the Supreme Court of Cassation as the court of the last resort, Courts of Appeal as the appellate instance, and Basic and High courts as the general jurisdictions at first instance.[207][208]
Courts of special jurisdictions are the Administrative Court, commercial courts (including the Commercial Court of Appeal at second instance) and misdemeanor courts (including High Misdemeanor Court at second instance).[209] The judiciary is overseen by the Ministry of Justice. Serbia has a typical civil law legal system.
Law enforcement is the responsibility of the Serbian Police, which is subordinate to the Ministry of the Interior. Serbian Police fields 27,363 uniformed officers.[210] National security and counterintelligence are the responsibility of the Security Intelligence Agency (BIA).[211]
Foreign relations
Serbia has established diplomatic relations with 191 UN member states, the Holy See, the Sovereign Military Order of Malta and the European Union.[212] Foreign relations are conducted through the Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Serbia has a network of 74 embassies and 25 consulates internationally.[213] There are 69 foreign embassies, 5 consulates and 4 liaison offices in Serbia.[214][215] Serbian foreign policy is focused on achieving the strategic goal of becoming a member state of the European Union (EU). Serbia officially applied for membership in the European Union on 22 December 2009.[216] It received a full candidate status on 1 March 2012 and started accession talks on 21 January 2014.[217][218] The European Commission considers accession possible by 2025.[219]
On 17 February 2008, Kosovo unilaterally declared independence from Serbia. In protest, Serbia initially recalled its ambassadors from countries that recognised Kosovo's independence.[220] The resolution of 26 December 2007 by the National Assembly stated that both the Kosovo declaration of independence and recognition thereof by any state would be gross violation of international law.[221]
Serbia began cooperation and dialogue with NATO in 2006, when the country joined the Partnership for Peace programme and the Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council. The country's military neutrality was formally proclaimed by a resolution adopted by Serbia's parliament in December 2007, which makes joining any military alliance contingent on a popular referendum,[222][223] a stance acknowledged by NATO.[224][225][226] On the other hand, Serbia's relations with Russia are habitually described by mass media as a "centuries-old religious, ethnic and political alliance"[227] and Russia is said to have sought to solidify its relations with Serbia since the imposition of sanctions against Russia in 2014.[228] During the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, Serbia voted to condemn the invasion, supporting the adoption of the United Nations draft resolution demanding Russia to withdraw its military forces from Ukraine.[229] However, Serbia is one of the only countries in Europe not to sanction Russia after the invasion.[230]
Military
 Special forces brigade 4th Army Brigade |
 Serbian Air Force and Air Defence Eurocopter EC145 |
The Serbian Armed Forces are subordinate to the Ministry of Defence, and are composed of the Army and the Air Force. Although a landlocked country, Serbia operates a River Flotilla which patrols on the Danube, Sava and Tisa rivers. The Serbian Chief of the General Staff reports to the Defence Minister. The Chief of Staff is appointed by the president, who is the commander-in-chief.[201] As of 2019[update], Serbian defence budget amounts to $804 million.[231]
Traditionally having relied on a large number of conscripts, Serbian Armed Forces went through a period of downsizing, restructuring and professionalisation. Conscription was abolished in 2011.[232] Serbian Armed Forces have 28,000 active troops,[233] supplemented by the "active reserve" which numbers 20,000 members and "passive reserve" with about 170,000.[234][235]
Serbia participates in the NATO Individual Partnership Action Plan programme,[224] but has no intention of joining NATO, due to significant popular rejection, largely a legacy of the NATO bombing of Yugoslavia in 1999.[236] It is an observer member of the Collective Security Treaty Organisation (CSTO) as of 2013.[237] The country also signed the Stability Pact for South Eastern Europe. The Serbian Armed Forces take part in several multinational peacekeeping missions, including deployments in Lebanon, Cyprus, Ivory Coast, and Liberia.[238]
Serbia is a major producer and exporter of military equipment in the region. Defence exports totaled around $600 million in 2018.[239] The defence industry has seen significant growth over the years and it continues to grow on a yearly basis.[240][241]
Serbia is one of the countries with the largest number of firearms in the civilian population in the world.[242]
Administrative divisions

Serbia is a unitary state[243] composed of municipalities/cities, districts, and two autonomous provinces. In Serbia, excluding Kosovo, there are 145 municipalities (opštine) and 29 cities (gradovi), which form the basic units of local self-government.[244] Apart from municipalities/cities, there are 24 districts (okruzi, 10 most populated listed below), with the City of Belgrade constituting an additional district. Except for Belgrade, which has an elected local government, districts are regional centres of state authority, but have no powers of their own; they present purely administrative divisions.[244] The Constitution of Serbia recognizes two autonomous provinces, Vojvodina in the north, and the disputed territory of Kosovo and Metohija in the south,[244] while the remaining area of Central Serbia has never had its own regional authority. Following the Kosovo War, UN peacekeepers entered Kosovo and Metohija, as per UNSC Resolution 1244. The government of Serbia does not recognise Kosovo's February 2008 declaration of independence, considering it illegal and illegitimate.[245]
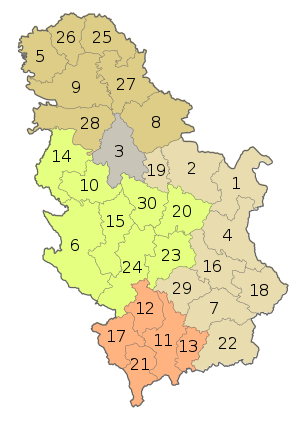 |
Demographics
As of the 2022 census, Serbia (excluding Kosovo) has a total population of 6,647,003 and the overall population density is medium as it stands at 85.8 inhabitants per square kilometre.[4] The census was not conducted in Kosovo which held its own census that numbered their total population at 1,739,825.[246] Serbia has been enduring a demographic crisis since the beginning of the 1990s, with a death rate that has continuously exceeded its birth rate.[247][248] It is estimated that 500,000 people left Serbia during the 1990s, 20% of whom had a higher education.[249][250] Serbia has one of the oldest populations in the world, with the average age of 43.3 years,[251] and its population is shrinking at one of the fastest rates in the world.[252] A fifth of all households consist of only one person, and just one-fourth of four and more persons.[253] The average life expectancy in Serbia is 76.1 years.[254]
During the 1990s, Serbia had the largest refugee population in Europe.[255] Refugees and internally displaced persons (IDPs) in Serbia formed between 7% and 7.5% of its population at the time – about half a million refugees sought refuge in the country following the series of Yugoslav wars, mainly from Croatia (and to a lesser extent from Bosnia and Herzegovina) and the IDPs from Kosovo.[256]
Serbs with 5,360,239 are the largest ethnic group in Serbia, representing 81% of the total population (excluding Kosovo). Serbia is one of the European countries with the highest number of registered national minorities, while the province of Vojvodina is recognizable for its multi-ethnic and multi-cultural identity.[257][258][259] Despite a decline in recent years, with a population of 184,442, Hungarians remain the largest ethnic minority in Serbia, concentrated predominantly in northern Vojvodina and representing 2.8% of the country's population (10.5% in Vojvodina). Romani population stands at 131,936 according to the 2022 census but unofficial estimates place their actual number between 400,000 and 500,000.[260] Bosniaks with 153,801 and Muslims by nationality with 13,011 are concentrated in Raška (Sandžak), in the southwest. Other minority groups include Albanians, Croats and Bunjevci, Slovaks, Yugoslavs, Montenegrins, Romanians and Vlachs, Macedonians and Bulgarians. Chinese, estimated at 15,000, are the only significant non-European immigrant minority.[261][262] Most recently, tens of thousands of Russians and Ukrainians have immigrated to Serbia following the Russian Invasion of Ukraine.[263]
The majority of the population, or 59.4%, reside in urban areas and some 16.1% in Belgrade alone. Belgrade is the only city with more than a million inhabitants and there are four more with over 100,000 inhabitants.[264]
| Rank | Name | District | Pop. | Rank | Name | District | Pop. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Belgrade  Novi Sad |
1 | Belgrade | City of Belgrade | 1,197,714 | 11 | Kraljevo | Raška District | 61,490 |  Niš  Kragujevac |
| 2 | Novi Sad | South Bačka | 306,702 | 12 | Smederevo | Podunavlje District | 59,261 | ||
| 3 | Niš | Nišava District | 260,237 | 13 | Leskovac | Jablanica District | 58,338 | ||
| 4 | Kragujevac | Šumadija District | 146,315 | 14 | Valjevo | Kolubara District | 56,059 | ||
| 5 | Subotica | North Bačka | 94,228 | 15 | Vranje | Pčinja District | 55,214 | ||
| 6 | Pančevo | South Banat | 86,408 | 16 | Užice | Zlatibor District | 54,965 | ||
| 7 | Novi Pazar | Raška District | 71,462 | 17 | Požarevac | Braničevo District | 51,271 | ||
| 8 | Čačak | Moravica District | 69,598 | 18 | Šabac | Mačva District | 51,163 | ||
| 9 | Kruševac | Rasina District | 68,119 | 19 | Sombor | West Bačka | 41,814 | ||
| 10 | Zrenjanin | Central Banat | 67,129 | 20 | Sremska Mitrovica | Srem District | 40,144 | ||
Religion

The Constitution of Serbia defines it as a secular state with guaranteed religious freedom. Orthodox Christians with 6,079,396 comprise 84.5% of country's population. The Serbian Orthodox Church is the largest and traditional church of the country, adherents of which are overwhelmingly Serbs. Other Orthodox Christian communities in Serbia include Montenegrins, Romanians, Vlachs, Macedonians and Bulgarians.
In 2011, Roman Catholics numbered 356,957 in Serbia, or roughly 6% of the population, mostly in northern Vojvodina which is home to ethnic minority groups such as Hungarians, Croats, and Bunjevci, as well as to some Slovaks and Czechs.[266] Greek Catholic Church is adhered by around 25,000 citizens (0.37% of the population), mostly Rusyns in Vojvodina.[267]
Protestantism accounts for about 1% of the country's population, chiefly Lutheranism among Slovaks in Vojvodina as well as Calvinism among Reformed Hungarians.
Muslims, with 222,282 or 3% of the population, form the third largest religious group. Islam has a strong historic following in the southern regions of Serbia, primarily in southern Raška. Bosniaks are the largest Islamic community in Serbia, followed by Albanians; estimates are that around a third of the country's Roma people are Muslim.[citation needed]
In 2011, there were only 578 Jews in Serbia,[268] compared to over 30,000 prior to World War II. Atheists numbered 80,053, or 1.1% of the population, and an additional 4,070 declared themselves to be agnostics.[268]
Zdroj:https://en.wikipedia.org?pojem=Serbia
Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších podmienok. Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky použitia.
Antropológia
Aplikované vedy
Bibliometria
Dejiny vedy
Encyklopédie
Filozofia vedy
Forenzné vedy
Humanitné vedy
Knižničná veda
Kryogenika
Kryptológia
Kulturológia
Literárna veda
Medzidisciplinárne oblasti
Metódy kvantitatívnej analýzy
Metavedy
Metodika
Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative
Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších
podmienok.
Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky
použitia.
www.astronomia.sk | www.biologia.sk | www.botanika.sk | www.dejiny.sk | www.economy.sk | www.elektrotechnika.sk | www.estetika.sk | www.farmakologia.sk | www.filozofia.sk | Fyzika | www.futurologia.sk | www.genetika.sk | www.chemia.sk | www.lingvistika.sk | www.politologia.sk | www.psychologia.sk | www.sexuologia.sk | www.sociologia.sk | www.veda.sk I www.zoologia.sk