
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
Conscription is the state-mandated enlistment of people in a national service, mainly a military service.[1] Conscription dates back to antiquity and it continues in some countries to the present day under various names. The modern system of near-universal national conscription for young men dates to the French Revolution in the 1790s, where it became the basis of a very large and powerful military. Most European nations later copied the system in peacetime, so that men at a certain age would serve 1 to 8 years on active duty and then transfer to the reserve force.
Conscription is controversial for a range of reasons, including conscientious objection to military engagements on religious or philosophical grounds; political objection, for example to service for a disliked government or unpopular war; sexism, in that historically men have been subject to the draft in the most cases; and ideological objection, for example, to a perceived violation of individual rights. Those conscripted may evade service, sometimes by leaving the country,[2] and seeking asylum in another country. Some selection systems accommodate these attitudes by providing alternative service outside combat-operations roles or even outside the military, such as siviilipalvelus (alternative civil service) in Finland and Zivildienst (compulsory community service) in Austria and Switzerland. Several countries conscript male soldiers not only for armed forces, but also for paramilitary agencies, which are dedicated to police-like domestic-only service like internal troops, border guards or non-combat rescue duties like civil defence.
As of 2023, many states no longer conscript their citizens, relying instead upon professional militaries with volunteers. The ability to rely on such an arrangement, however, presupposes some degree of predictability with regard to both war-fighting requirements and the scope of hostilities. Many states that have abolished conscription still, therefore, reserve the power to resume conscription during wartime or times of crisis.[3] States involved in wars or interstate rivalries are most likely to implement conscription, and democracies are less likely than autocracies to implement conscription.[4] With a few exceptions, such as Singapore and Egypt, former British colonies are less likely to have conscription, as they are influenced by British anti-conscription norms that can be traced back to the English Civil War; the United Kingdom abolished conscription in 1960.[4]
History
In pre-modern times
Ilkum
Around the reign of Hammurabi (1791–1750 BC), the Babylonian Empire used a system of conscription called Ilkum. Under that system those eligible were required to serve in the royal army in time of war. During times of peace they were instead required to provide labour for other activities of the state. In return for this service, people subject to it gained the right to hold land. It is possible that this right was not to hold land per se but specific land supplied by the state.[5]
Various forms of avoiding military service are recorded. While it was outlawed by the Code of Hammurabi, the hiring of substitutes appears to have been practiced both before and after the creation of the code. Later records show that Ilkum commitments could become regularly traded. In other places, people simply left their towns to avoid their Ilkum service. Another option was to sell Ilkum lands and the commitments along with them. With the exception of a few exempted classes, this was forbidden by the Code of Hammurabi.[6]
Medieval period
Medieval levies
Under the feudal laws on the European continent, landowners in the medieval period enforced a system whereby all peasants, freemen commoners and noblemen aged 15 to 60 living in the countryside or in urban centers, were summoned for military duty when required by either the king or the local lord, bringing along the weapons and armor according to their wealth. These levies fought as footmen, sergeants, and men at arms under local superiors appointed by the king or the local lord such as the arrière-ban in France. Arrière-ban denoted a general levy, where all able-bodied males age 15 to 60 living in the Kingdom of France were summoned to go to war by the King (or the constable and the marshals). Men were summoned by the bailiff (or the sénéchal in the south). Bailiffs were military and political administrators installed by the King to steward and govern a specific area of a province following the king's commands and orders. The men summoned in this way were then summoned by the lieutenant who was the King's representative and military governor over an entire province comprising many bailiwicks, seneschalties and castellanies. All men from the richest noble to the poorest commoner were summoned under the arrière-ban and they were supposed to present themselves to the King or his officials.[7][8][9][10]
In medieval Scandinavia the leiðangr (Old Norse), leidang (Norwegian), leding, (Danish), ledung (Swedish), lichting (Dutch), expeditio (Latin) or sometimes leþing (Old English), was a levy of free farmers conscripted into coastal fleets for seasonal excursions and in defence of the realm.[11]
The bulk of the Anglo-Saxon English army, called the fyrd, was composed of part-time English soldiers drawn from the freemen of each county. In the 690s laws of Ine of Wessex, three levels of fines are imposed on different social classes for neglecting military service.[12]
Some modern writers claim military service in Europe was restricted to the landowning minor nobility. These thegns were the land-holding aristocracy of the time and were required to serve with their own armour and weapons for a certain number of days each year. The historian David Sturdy has cautioned about regarding the fyrd as a precursor to a modern national army composed of all ranks of society, describing it as a "ridiculous fantasy":
The persistent old belief that peasants and small farmers gathered to form a national army or fyrd is a strange delusion dreamt up by antiquarians in the late eighteenth or early nineteenth centuries to justify universal military conscription.[13]

In feudal Japan the shogun decree of 1393 exempted money lenders from religious or military levies, in return for a yearly tax. The Ōnin War weakened the shogun and levies were imposed again on money lenders. This overlordism was arbitrary and unpredictable for commoners. While the money lenders were not poor, several overlords tapped them for income. Levies became necessary for the survival of the overlord, allowing the lord to impose taxes at will. These levies included tansen tax on agricultural land for ceremonial expenses. Yakubu takumai tax was raised on all land to rebuild the Ise Grand Shrine, and munabechisen tax was imposed on all houses. At the time, land in Kyoto was acquired by commoners through usury and in 1422 the shogun threatened to repossess the land of those commoners who failed to pay their levies.[14]
Military slavery

The system of military slaves was widely used in the Middle East, beginning with the creation of the corps of Turkic slave-soldiers (ghulams or mamluks) by the Abbasid caliph al-Mu'tasim in the 820s and 830s. The Turkish troops soon came to dominate the government, establishing a pattern throughout the Islamic world of a ruling military class, often separated by ethnicity, culture and even religion by the mass of the population, a paradigm that found its apogee in the Mamluks of Egypt and the Janissary corps of the Ottoman Empire, institutions that survived until the early 19th century.
In the middle of the 14th century, Ottoman Sultan Murad I developed personal troops to be loyal to him, with a slave army called the Kapıkulu. The new force was built by taking Christian children from newly conquered lands, especially from the far areas of his empire, in a system known as the devşirme (translated "gathering" or "converting"). The captive children were forced to convert to Islam. The Sultans had the young boys trained over several years. Those who showed special promise in fighting skills were trained in advanced warrior skills, put into the sultan's personal service, and turned into the Janissaries, the elite branch of the Kapıkulu. A number of distinguished military commanders of the Ottomans, and most of the imperial administrators and upper-level officials of the Empire, such as Pargalı İbrahim Pasha and Sokollu Mehmet Paşa, were recruited in this way.[15] By 1609, the Sultan's Kapıkulu forces increased to about 100,000.[16]
In later years, Sultans turned to the Barbary Pirates to supply their Jannissaries corps. Their attacks on ships off the coast of Africa or in the Mediterranean, and subsequent capture of able-bodied men for ransom or sale provided some captives for the Sultan's system. Starting in the 17th century, Christian families living under the Ottoman rule began to submit their sons into the Kapikulu system willingly, as they saw this as a potentially invaluable career opportunity for their children. Eventually the Sultan turned to foreign volunteers from the warrior clans of Circassians in southern Russia to fill his Janissary armies. As a whole the system began to break down, the loyalty of the Jannissaries became increasingly suspect. Mahmud II forcibly disbanded the Janissary corps in 1826.[17]
Similar to the Janissaries in origin and means of development were the Mamluks of Egypt in the Middle Ages. The Mamluks were usually captive non-Muslim Iranian and Turkish children who had been kidnapped or bought as slaves from the Barbary coasts. The Egyptians assimilated and trained the boys and young men to become Islamic soldiers who served the Muslim caliphs and the Ayyubid sultans during the Middle Ages. The first mamluks served the Abbasid caliphs in 9th-century Baghdad. Over time they became a powerful military caste. On more than one occasion, they seized power, for example, ruling Egypt from 1250 to 1517.
From 1250 Egypt had been ruled by the Bahri dynasty of Kipchak origin. Slaves from the Caucasus served in the army and formed an elite corps of troops. They eventually revolted in Egypt to form the Burgi dynasty. The Mamluks' excellent fighting abilities, massed Islamic armies, and overwhelming numbers succeeded in overcoming the Christian Crusader fortresses in the Holy Land. The Mamluks were the most successful defence against the Mongol Ilkhanate of Persia and Iraq from entering Egypt.[18]
On the western coast of Africa, Berber Muslims captured non-Muslims to put to work as laborers. They generally converted the younger people to Islam and many became quite assimilated. In Morocco, the Berber looked south rather than north. The Moroccan Sultan Moulay Ismail, called "the Bloodthirsty" (1672–1727), employed a corps of 150,000 black slaves, called his Black Guard. He used them to coerce the country into submission.[19]
In modern times

Modern conscription, the massed military enlistment of national citizens (levée en masse), was devised during the French Revolution, to enable the Republic to defend itself from the attacks of European monarchies. Deputy Jean-Baptiste Jourdan gave its name to the 5 September 1798 Act, whose first article stated: "Any Frenchman is a soldier and owes himself to the defense of the nation." It enabled the creation of the Grande Armée, what Napoleon Bonaparte called "the nation in arms", which overwhelmed European professional armies that often numbered only into the low tens of thousands. More than 2.6 million men were inducted into the French military in this way between the years 1800 and 1813.[20]
The defeat of the Prussian Army in particular shocked the Prussian establishment, which had believed it was invincible after the victories of Frederick the Great. The Prussians were used to relying on superior organization and tactical factors such as order of battle to focus superior troops against inferior ones. Given approximately equivalent forces, as was generally the case with professional armies, these factors showed considerable importance. However, they became considerably less important when the Prussian armies faced Napoleon's forces that outnumbered their own in some cases by more than ten to one. Scharnhorst advocated adopting the levée en masse, the military conscription used by France. The Krümpersystem was the beginning of short-term compulsory service in Prussia, as opposed to the long-term conscription previously used.[21]

In the Russian Empire, the military service time "owed" by serfs was 25 years at the beginning of the 19th century. In 1834 it was decreased to 20 years. The recruits were to be not younger than 17 and not older than 35.[22] In 1874 Russia introduced universal conscription in the modern pattern, an innovation only made possible by the abolition of serfdom in 1861. New military law decreed that all male Russian subjects, when they reached the age of 20, were eligible to serve in the military for six years.[23]
In the decades prior to World War I universal conscription along broadly Prussian lines became the norm for European armies, and those modeled on them. By 1914 the only substantial armies still completely dependent on voluntary enlistment were those of Britain and the United States. Some colonial powers such as France reserved their conscript armies for home service while maintaining professional units for overseas duties.[24]
World Wars

The range of eligible ages for conscripting was expanded to meet national demand during the World Wars. In the United States, the Selective Service System drafted men for World War I initially in an age range from 21 to 30 but expanded its eligibility in 1918 to an age range of 18 to 45.[25] In the case of a widespread mobilization of forces where service includes homefront defense, ages of conscripts may range much higher, with the oldest conscripts serving in roles requiring lesser mobility.[citation needed]
Expanded-age conscription was common during the Second World War: in Britain, it was commonly known as "call-up" and extended to age 51. Nazi Germany termed it Volkssturm ("People's Storm") and included children as young as 16 and men as old as 60.[26] During the Second World War, both Britain and the Soviet Union conscripted women. The United States was on the verge of drafting women into the Nurse Corps because it anticipated it would need the extra personnel for its planned invasion of Japan. However, the Japanese surrendered and the idea was abandoned.[27]

During the Great Patriotic War, the Red Army conscripted nearly 30 million men.[28]
Arguments against conscription
Sexism
Men's rights activists,[29][30] feminists,[31][32][33] and opponents of discrimination against men[34][35]: 102 have criticized military conscription, or compulsory military service, as sexist. The National Coalition for Men, a men's rights group, sued the US Selective Service System in 2019, leading to it being declared unconstitutional by a US Federal Judge.[36][37] The federal district judge's opinion was unanimously overturned on appeal to the U.S. Court of Appeals for the 5th Circuit.[38] In September 2021, the House of Representatives passed the annual Defense Authorization Act, which included an amendment that states that "all Americans between the ages of 18 and 25 must register for selective service." This amendment omitted the word "male", which would have extended a potential draft to women; however, the amendment was removed before the National Defense Authorization Act was passed.[39][40][41]
Feminists have argued, first, that military conscription is sexist because wars serve the interests of what they view as the patriarchy; second, that the military is a sexist institution and that conscripts are therefore indoctrinated into sexism; and third, that conscription of men normalizes violence by men as socially acceptable.[42][43] Feminists have been organizers and participants in resistance to conscription in several countries.[44][45][46][47]
Conscription has also been criticized on the ground that, historically, only men have been subjected to conscription.[35][48][49][50][51] Men who opt out or are deemed unfit for military service must often perform alternative service, such as Zivildienst in Austria, Germany and Switzerland, or pay extra taxes,[52] whereas women do not have these obligations. In the US, men who do not register with the Selective Service cannot apply for citizenship, receive federal financial aid, grants or loans, be employed by the federal government, be admitted to public colleges or universities, or, in some states, obtain a driver's license.[53][54]
Involuntary servitude

Many American libertarians oppose conscription and call for the abolition of the Selective Service System, arguing that impressment of individuals into the armed forces amounts to involuntary servitude.[55] For example, Ron Paul, a former U.S. Libertarian Party presidential nominee, has said that conscription "is wrongly associated with patriotism, when it really represents slavery and involuntary servitude".[56] The philosopher Ayn Rand opposed conscription, opining that "of all the statist violations of individual rights in a mixed economy, the military draft is the worst. It is an abrogation of rights. It negates man's fundamental right—the right to life—and establishes the fundamental principle of statism: that a man's life belongs to the state, and the state may claim it by compelling him to sacrifice it in battle."[57]
In 1917, a number of radicals[who?] and anarchists, including Emma Goldman, challenged the new draft law in federal court, arguing that it was a violation of the Thirteenth Amendment's prohibition against slavery and involuntary servitude. However, the Supreme Court unanimously upheld the constitutionality of the draft act in the case of Arver v. United States on 7 January 1918, on the ground that the Constitution gives Congress the power to declare war and to raise and support armies. The Court also relied on the principle of the reciprocal rights and duties of citizens. "It may not be doubted that the very conception of a just government in its duty to the citizen includes the reciprocal obligation of the citizen to render military service in case of need and the right to compel."[58]
Economic
It can be argued that in a cost-to-benefit ratio, conscription during peacetime is not worthwhile.[59] Months or years of service performed by the most fit and capable subtract from the productivity of the economy; add to this the cost of training them, and in some countries paying them. Compared to these extensive costs, some would argue there is very little benefit; if there ever was a war then conscription and basic training could be completed quickly, and in any case there is little threat of a war in most countries with conscription. In the United States, every male resident is required by law to register with the Selective Service System within 30 days following his 18th birthday and be available for a draft; this is often accomplished automatically by a motor vehicle department during licensing or by voter registration.[60]
According to Milton Friedman the cost of conscription can be related to the parable of the broken window in anti-draft arguments. The cost of the work, military service, does not disappear even if no salary is paid. The work effort of the conscripts is effectively wasted, as an unwilling workforce is extremely inefficient. The impact is especially severe in wartime, when civilian professionals are forced to fight as amateur soldiers. Not only is the work effort of the conscripts wasted and productivity lost, but professionally skilled conscripts are also difficult to replace in the civilian workforce. Every soldier conscripted in the army is taken away from his civilian work, and away from contributing to the economy which funds the military. This may be less a problem in an agrarian or pre-industrialized state where the level of education is generally low, and where a worker is easily replaced by another. However, this is potentially more costly in a post-industrial society where educational levels are high and where the workforce is sophisticated and a replacement for a conscripted specialist is difficult to find. Even more dire economic consequences result if the professional conscripted as an amateur soldier is killed or maimed for life; his work effort and productivity are lost.[61]
Arguments for conscription
Political and moral motives

Jean Jacques Rousseau argued vehemently against professional armies since he believed that it was the right and privilege of every citizen to participate to the defense of the whole society and that it was a mark of moral decline to leave the business to professionals. He based his belief upon the development of the Roman Republic, which came to an end at the same time as the Roman Army changed from a conscript to a professional force.[62] Similarly, Aristotle linked the division of armed service among the populace intimately with the political order of the state.[63] Niccolò Machiavelli argued strongly for conscription[64] and saw the professional armies, made up of mercenary units, as the cause of the failure of societal unity in Italy.[65]
Other proponents, such as William James, consider both mandatory military and national service as ways of instilling maturity in young adults.[66] Some proponents, such as Jonathan Alter and Mickey Kaus, support a draft in order to reinforce social equality, create social consciousness, break down class divisions and allow young adults to immerse themselves in public enterprise.[67][68][69] Charles Rangel called for the reinstatement of the draft during the Iraq War not because he seriously expected it to be adopted but to stress how the socioeconomic restratification meant that very few children of upper-class Americans served in the all-volunteer American armed forces.[70]
Economic and resource efficiency
It is estimated by the British military that in a professional military, a company deployed for active duty in peacekeeping corresponds to three inactive companies at home. Salaries for each are paid from the military budget. In contrast, volunteers from a trained reserve are in their civilian jobs when they are not deployed.[71]
It was more financially beneficial for less-educated young Portuguese men born in 1967 to participate in conscription than to participate in the highly competitive job market with men of the same age who continued to higher education.[72]
Drafting of women

Throughout history, women have only been conscripted to join armed forces in a few countries, in contrast to the universal practice of conscription from among the male population. The traditional view has been that military service is a test of manhood and a rite of passage from boyhood into manhood.[73][74] In recent years, this position has been challenged on the basis that it violates gender equality, and some countries, especially in Europe, have extended conscription obligations to women.
Nations that in present-day actively draft women into military service are Bolivia,[75] Chad,[76] Eritrea,[77][78][79] Israel,[77][78][80] Mozambique,[81] Norway,[82] North Korea,[83] Myanmar,[84] and Sweden.[85]
Norway introduced female conscription in 2015, making it the first NATO member to have a legally compulsory national service for both men and women.[82] In practice only motivated volunteers are selected to join the army in Norway.[86]
Sweden introduced female conscription in 2010, but it was not activated until 2017. This made Sweden the second nation in Europe to draft women, and the second in the world to draft women on the same formal terms as men.[85]
Israel has universal female conscription, although it is possible to avoid service by claiming a religious exemption and over a third of Israeli women do so.[77][78][87]
Finland introduced voluntary female conscription in 1995, giving women between the ages of 18 and 29 an option to complete their military service alongside men.[88][89]
Denmark will extend conscription to women from 2026.[90]
Sudanese law allows for conscription of women, but this is not implemented in practice.[91] In the United Kingdom during World War II, beginning in 1941, women were brought into the scope of conscription but, as all women with dependent children were exempt and many women were informally left in occupations such as nursing or teaching, the number conscripted was relatively few.[92]
In the Soviet Union, there was never conscription of women for the armed forces, but the severe disruption of normal life and the high proportion of civilians affected by World War II after the German invasion attracted many volunteers for "The Great Patriotic War".[93] Medical doctors of both sexes could and would be conscripted (as officers). Also, the Soviet university education system required Department of Chemistry students of both sexes to complete an ROTC course in NBC defense, and such female reservist officers could be conscripted in times of war. The United States came close to drafting women into the Nurse Corps in preparation for a planned invasion of Japan.[94][95]
In 1981 in the United States, several men filed lawsuit in the case Rostker v. Goldberg, alleging that the Selective Service Act of 1948 violates the Due Process Clause of the Fifth Amendment by requiring that only men register with the Selective Service System (SSS). The Supreme Court eventually upheld the Act, stating that "the argument for registering women was based on considerations of equity, but Congress was entitled, in the exercise of its constitutional powers, to focus on the question of military need, rather than 'equity.'"[96] In 2013, Judge Gray H. Miller of the United States District Court for the Southern District of Texas ruled that the Service's men-only requirement was unconstitutional, as while at the time Rostker was decided, women were banned from serving in combat, the situation had since changed with the 2013 and 2015 restriction removals.[97] Miller's opinion was reversed by the Fifth Circuit, stating that only the Supreme Court could overturn the Supreme Court precedence from Rostker. The Supreme Court considered but declined to review the Fifth Circuit's ruling in June 2021.[98] In an opinion authored by Justice Sonia Sotomayor and joined by Justices Stephen Breyer and Brett Kavanaugh, the three justices agreed that the male-only draft was likely unconstitutional given the changes in the military's stance on the roles, but because Congress had been reviewing and evaluating legislation to eliminate its male-only draft requirement via the National Commission on Military, National, and Public Service (NCMNPS) since 2016, it would have been inappropriate for the Court to act at that time.[99]
On 1 October 1999, in Taiwan, the Judicial Yuan of the Republic of China in its Interpretation 490 considered that the physical differences between males and females and the derived role differentiation in their respective social functions and lives would not make drafting only males a violation of the Constitution of the Republic of China.[100][(see discussion) verification needed] Though women are not conscripted in Taiwan, transsexual persons are exempt.[101]
In 2018, the Netherlands started including women in its draft registration system, although conscription is not currently enforced for either sex.[102] France and Portugal, where conscription was abolished, extended their symbolic, mandatory day of information on the armed forces for young people - called Defence and Citizenship Day in France and Day of National Defence in Portugal - to women in 1997 and 2008, respectively; at the same time, the military registry of both countries and obligation of military service in case of war was extended to women.[103][104]
Conscientious objection
A conscientious objector is an individual whose personal beliefs are incompatible with military service, or, more often, with any role in the armed forces.[105][106] In some countries, conscientious objectors have special legal status, which augments their conscription duties. For example, Sweden allows conscientious objectors to choose a service in the weapons-free civil defense.[107][108]
The reasons for refusing to serve in the military are varied. Some people are conscientious objectors for religious reasons. In particular, the members of the historic peace churches are pacifist by doctrine, and Jehovah's Witnesses, while not strictly pacifists, refuse to participate in the armed forces on the ground that they believe that Christians should be neutral in international conflicts.[109]
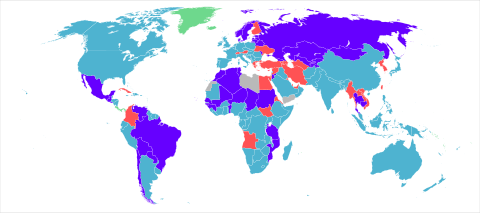
By country
Table
| Country | Conscription[110] | Conscription sex |
|---|---|---|
| No (abolished in 1992) | N/A | |
| No (abolished in 2010)[111] | N/A | |
| Yes | Male | |
| Yes | Male | |
| No. Voluntary; conscription may be required for specified reasons per Article 19 of Public Law No.24.429 promulgated on 5 January 1995.[112] | N/A | |
| Yes | Male | |
| No (abolished by parliament in 1972)[113] | N/A | |
| Yes (alternative service available)[114] | Male | |
| Yes | Male | |
| No | N/A | |
| No (but can volunteer for service in Bangladesh Ansar) | N/A | |
| No | N/A | |
| No (suspended in 1992; service not required of draftees inducted for 1994 military classes or any thereafter)[115] | N/A | |
| No | N/A | |
| No[116] | N/A | |
| Yes (whenever annual number of volunteers falls short of government's goal)[117] | Male and Female | |
| No (abolished on 1 January 2006)[118] | N/A | |
| Yes, but almost all recruits have been volunteers in recent years.[119] (Alternative service is cited in Brazilian law,[120] but a system has not been implemented.[119]) | Male | |
| No (abolished by law on 1 January 2008)[121] | N/A | |
| No (in force only in 1917–1918 and during the general mobilization of 1940–1945) | N/A | |
| Yes | Male | |
| No, however Male citizens 18 years of age and over are required to register for military service in People's Liberation Army recruiting offices. (Registration exempted for residents of |
N/A | |
| Yes | Male | |
| No (abolished by law in 2008)[126] | N/A | |
| Yes | Male | |
| Yes (alternative service available) | Male | |
| No (abolished in 2005)[127] | N/A | |
| Yes (alternative service available).[128][129] In practice, however, a great majority of recruits have been volunteers over the past few years.[130] | Male until 2026; male and female from 2026.[131] | |
| No | N/A | |
| No (suspended in 2008) | N/A | |
| Yes (alternative service available) | Male | |
| No. Legal, not practiced.
Zdroj:https://en.wikipedia.org?pojem=Conscription Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších podmienok. Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky použitia.
Analytika
Antropológia Aplikované vedy Bibliometria Dejiny vedy Encyklopédie Filozofia vedy Forenzné vedy Humanitné vedy Knižničná veda Kryogenika Kryptológia Kulturológia Literárna veda Medzidisciplinárne oblasti Metódy kvantitatívnej analýzy Metavedy Metodika Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative
Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších
podmienok. www.astronomia.sk | www.biologia.sk | www.botanika.sk | www.dejiny.sk | www.economy.sk | www.elektrotechnika.sk | www.estetika.sk | www.farmakologia.sk | www.filozofia.sk | Fyzika | www.futurologia.sk | www.genetika.sk | www.chemia.sk | www.lingvistika.sk | www.politologia.sk | www.psychologia.sk | www.sexuologia.sk | www.sociologia.sk | www.veda.sk I www.zoologia.sk |

