
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9

| Part of a series on |
| Biochemistry |
|---|
 |
Enzymes (/ˈɛnzaɪmz/) are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life.[1]: 8.1 Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called enzymology and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties.[2][3]
Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types.[4] Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. An enzyme's specificity comes from its unique three-dimensional structure.

Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction rate by lowering its activation energy. Some enzymes can make their conversion of substrate to product occur many millions of times faster. An extreme example is orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase, which allows a reaction that would otherwise take millions of years to occur in milliseconds.[5][6] Chemically, enzymes are like any catalyst and are not consumed in chemical reactions, nor do they alter the equilibrium of a reaction. Enzymes differ from most other catalysts by being much more specific. Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules: inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity, and activators are molecules that increase activity. Many therapeutic drugs and poisons are enzyme inhibitors. An enzyme's activity decreases markedly outside its optimal temperature and pH, and many enzymes are (permanently) denatured when exposed to excessive heat, losing their structure and catalytic properties.
Some enzymes are used commercially, for example, in the synthesis of antibiotics. Some household products use enzymes to speed up chemical reactions: enzymes in biological washing powders break down protein, starch or fat stains on clothes, and enzymes in meat tenderizer break down proteins into smaller molecules, making the meat easier to chew.
Etymology and history

By the late 17th and early 18th centuries, the digestion of meat by stomach secretions[7] and the conversion of starch to sugars by plant extracts and saliva were known but the mechanisms by which these occurred had not been identified.[8]
French chemist Anselme Payen was the first to discover an enzyme, diastase, in 1833.[9] A few decades later, when studying the fermentation of sugar to alcohol by yeast, Louis Pasteur concluded that this fermentation was caused by a vital force contained within the yeast cells called "ferments", which were thought to function only within living organisms. He wrote that "alcoholic fermentation is an act correlated with the life and organization of the yeast cells, not with the death or putrefaction of the cells."[10]
In 1877, German physiologist Wilhelm Kühne (1837–1900) first used the term enzyme, which comes from Ancient Greek ἔνζυμον (énzymon) 'leavened, in yeast', to describe this process.[11] The word enzyme was used later to refer to nonliving substances such as pepsin, and the word ferment was used to refer to chemical activity produced by living organisms.[12]
Eduard Buchner submitted his first paper on the study of yeast extracts in 1897. In a series of experiments at the University of Berlin, he found that sugar was fermented by yeast extracts even when there were no living yeast cells in the mixture.[13] He named the enzyme that brought about the fermentation of sucrose "zymase".[14] In 1907, he received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for "his discovery of cell-free fermentation". Following Buchner's example, enzymes are usually named according to the reaction they carry out: the suffix -ase is combined with the name of the substrate (e.g., lactase is the enzyme that cleaves lactose) or to the type of reaction (e.g., DNA polymerase forms DNA polymers).[15]
The biochemical identity of enzymes was still unknown in the early 1900s. Many scientists observed that enzymatic activity was associated with proteins, but others (such as Nobel laureate Richard Willstätter) argued that proteins were merely carriers for the true enzymes and that proteins per se were incapable of catalysis.[16] In 1926, James B. Sumner showed that the enzyme urease was a pure protein and crystallized it; he did likewise for the enzyme catalase in 1937. The conclusion that pure proteins can be enzymes was definitively demonstrated by John Howard Northrop and Wendell Meredith Stanley, who worked on the digestive enzymes pepsin (1930), trypsin and chymotrypsin. These three scientists were awarded the 1946 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.[17]
The discovery that enzymes could be crystallized eventually allowed their structures to be solved by x-ray crystallography. This was first done for lysozyme, an enzyme found in tears, saliva and egg whites that digests the coating of some bacteria; the structure was solved by a group led by David Chilton Phillips and published in 1965.[18] This high-resolution structure of lysozyme marked the beginning of the field of structural biology and the effort to understand how enzymes work at an atomic level of detail.[19]
Classification and nomenclature
Enzymes can be classified by two main criteria: either amino acid sequence similarity (and thus evolutionary relationship) or enzymatic activity.
Enzyme activity. An enzyme's name is often derived from its substrate or the chemical reaction it catalyzes, with the word ending in -ase.[1]: 8.1.3 Examples are lactase, alcohol dehydrogenase and DNA polymerase. Different enzymes that catalyze the same chemical reaction are called isozymes.[1]: 10.3
The International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology have developed a nomenclature for enzymes, the EC numbers (for "Enzyme Commission"). Each enzyme is described by "EC" followed by a sequence of four numbers which represent the hierarchy of enzymatic activity (from very general to very specific). That is, the first number broadly classifies the enzyme based on its mechanism while the other digits add more and more specificity.[20]
The top-level classification is:
- EC 1, Oxidoreductases: catalyze oxidation/reduction reactions
- EC 2, Transferases: transfer a functional group (e.g. a methyl or phosphate group)
- EC 3, Hydrolases: catalyze the hydrolysis of various bonds
- EC 4, Lyases: cleave various bonds by means other than hydrolysis and oxidation
- EC 5, Isomerases: catalyze isomerization changes within a single molecule
- EC 6, Ligases: join two molecules with covalent bonds.
- EC 7, Translocases: catalyze the movement of ions or molecules across membranes, or their separation within membranes.
These sections are subdivided by other features such as the substrate, products, and chemical mechanism. An enzyme is fully specified by four numerical designations. For example, hexokinase (EC 2.7.1.1) is a transferase (EC 2) that adds a phosphate group (EC 2.7) to a hexose sugar, a molecule containing an alcohol group (EC 2.7.1).[21]
Sequence similarity. EC categories do not reflect sequence similarity. For instance, two ligases of the same EC number that catalyze exactly the same reaction can have completely different sequences. Independent of their function, enzymes, like any other proteins, have been classified by their sequence similarity into numerous families. These families have been documented in dozens of different protein and protein family databases such as Pfam.[22]
Non-homologous isofunctional enzymes. Unrelated enzymes that have the same enzymatic activity have been called non-homologous isofunctional enzymes.[23] Horizontal gene transfer may spread these genes to unrelated species, especially bacteria where they can replace endogenous genes of the same function, leading to hon-homologous gene displacement.
Structure

Enzymes are generally globular proteins, acting alone or in larger complexes. The sequence of the amino acids specifies the structure which in turn determines the catalytic activity of the enzyme.[24] Although structure determines function, a novel enzymatic activity cannot yet be predicted from structure alone.[25] Enzyme structures unfold (denature) when heated or exposed to chemical denaturants and this disruption to the structure typically causes a loss of activity.[26] Enzyme denaturation is normally linked to temperatures above a species' normal level; as a result, enzymes from bacteria living in volcanic environments such as hot springs are prized by industrial users for their ability to function at high temperatures, allowing enzyme-catalysed reactions to be operated at a very high rate.
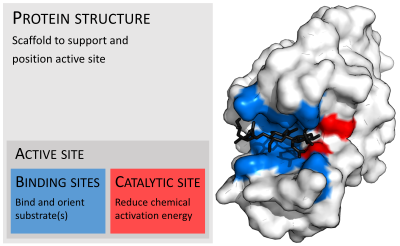
Enzymes are usually much larger than their substrates. Sizes range from just 62 amino acid residues, for the monomer of 4-oxalocrotonate tautomerase,[27] to over 2,500 residues in the animal fatty acid synthase.[28] Only a small portion of their structure (around 2–4 amino acids) is directly involved in catalysis: the catalytic site.[29] This catalytic site is located next to one or more binding sites where residues orient the substrates. The catalytic site and binding site together compose the enzyme's active site. The remaining majority of the enzyme structure serves to maintain the precise orientation and dynamics of the active site.[30]
In some enzymes, no amino acids are directly involved in catalysis; instead, the enzyme contains sites to bind and orient catalytic cofactors.[30] Enzyme structures may also contain allosteric sites where the binding of a small molecule causes a conformational change that increases or decreases activity.[31]
A small number of RNA-based biological catalysts called ribozymes exist, which again can act alone or in complex with proteins. The most common of these is the ribosome which is a complex of protein and catalytic RNA components.[1]: 2.2
Mechanism
Substrate binding
Enzymes must bind their substrates before they can catalyse any chemical reaction. Enzymes are usually very specific as to what substrates they bind and then the chemical reaction catalysed. Specificity is achieved by binding pockets with complementary shape, charge and hydrophilic/hydrophobic characteristics to the substrates. Enzymes can therefore distinguish between very similar substrate molecules to be chemoselective, regioselective and stereospecific.[32]
Some of the enzymes showing the highest specificity and accuracy are involved in the copying and expression of the genome. Some of these enzymes have "proof-reading" mechanisms. Here, an enzyme such as DNA polymerase catalyzes a reaction in a first step and then checks that the product is correct in a second step.[33] This two-step process results in average error rates of less than 1 error in 100 million reactions in high-fidelity mammalian polymerases.[1]: 5.3.1 Similar proofreading mechanisms are also found in RNA polymerase,[34] aminoacyl tRNA synthetases[35] and ribosomes.[36]
Conversely, some enzymes display enzyme promiscuity, having broad specificity and acting on a range of different physiologically relevant substrates. Many enzymes possess small side activities which arose fortuitously (i.e. neutrally), which may be the starting point for the evolutionary selection of a new function.[37][38]
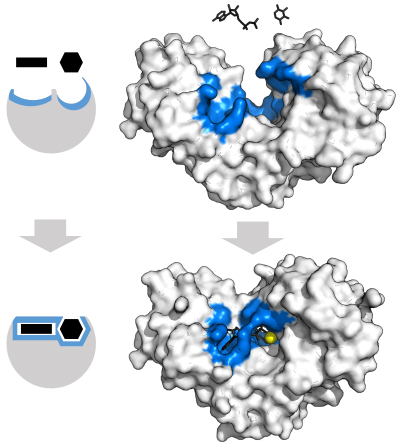
"Lock and key" model
To explain the observed specificity of enzymes, in 1894 Emil Fischer proposed that both the enzyme and the substrate possess specific complementary geometric shapes that fit exactly into one another.[39] This is often referred to as "the lock and key" model.[1]: 8.3.2 This early model explains enzyme specificity, but fails to explain the stabilization of the transition state that enzymes achieve.[40]
Induced fit model
In 1958, Daniel Koshland suggested a modification to the lock and key model: since enzymes are rather flexible structures, the active site is continuously reshaped by interactions with the substrate as the substrate interacts with the enzyme.[41] As a result, the substrate does not simply bind to a rigid active site; the amino acid side-chains that make up the active site are molded into the precise positions that enable the enzyme to perform its catalytic function. In some cases, such as glycosidases, the substrate molecule also changes shape slightly as it enters the active site.[42] The active site continues to change until the substrate is completely bound, at which point the final shape and charge distribution is determined.[43] Induced fit may enhance the fidelity of molecular recognition in the presence of competition and noise via the conformational proofreading mechanism.[44]
Catalysis
Enzymes can accelerate reactions in several ways, all of which lower the activation energy (ΔG‡, Gibbs free energy)[45]
- By stabilizing the transition state:
- Creating an environment with a charge distribution complementary to that of the transition state to lower its energy[46]
- By providing an alternative reaction pathway:
- Temporarily reacting with the substrate, forming a covalent intermediate to provide a lower energy transition state[47]
- By destabilising the substrate ground state:
- Distorting bound substrate(s) into their transition state form to reduce the energy required to reach the transition state[48]
- By orienting the substrates into a productive arrangement to reduce the reaction entropy change[49] (the contribution of this mechanism to catalysis is relatively small)[50]
Enzymes may use several of these mechanisms simultaneously. For example, proteases such as trypsin perform covalent catalysis using a catalytic triad, stabilise charge build-up on the transition states using an oxyanion hole, complete hydrolysis using an oriented water substrate.[51]
Dynamics
Enzymes are not rigid, static structures; instead they have complex internal dynamic motions – that is, movements of parts of the enzyme's structure such as individual amino acid residues, groups of residues forming a protein loop or unit of secondary structure, or even an entire protein domain. These motions give rise to a conformational ensemble of slightly different structures that interconvert with one another at equilibrium. Different states within this ensemble may be associated with different aspects of an enzyme's function. For example, different conformations of the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase are associated with the substrate binding, catalysis, cofactor release, and product release steps of the catalytic cycle,[52] consistent with catalytic resonance theory.
Substrate presentation
This section needs additional citations for verification. (October 2023) |
Substrate presentation is a process where the enzyme is sequestered away from its substrate. Enzymes can be sequestered to the plasma membrane away from a substrate in the nucleus or cytosol. Or within the membrane, an enzyme can be sequestered into lipid rafts away from its substrate in the disordered region. When the enzyme is released it mixes with its substrate. Alternatively, the enzyme can be sequestered near its substrate to activate the enzyme. For example, the enzyme can be soluble and upon activation bind to a lipid in the plasma membrane and then act upon molecules in the plasma membrane.
Allosteric modulation
Allosteric sites are pockets on the enzyme, distinct from the active site, that bind to molecules in the cellular environment. These molecules then cause a change in the conformation or dynamics of the enzyme that is transduced to the active site and thus affects the reaction rate of the enzyme.[53] In this way, allosteric interactions can either inhibit or activate enzymes. Allosteric interactions with metabolites upstream or downstream in an enzyme's metabolic pathway cause feedback regulation, altering the activity of the enzyme according to the flux through the rest of the pathway.[54]
Cofactors

Some enzymes do not need additional components to show full activity. Others require non-protein molecules called cofactors to be bound for activity.[55] Cofactors can be either inorganic (e.g., metal ions and iron–sulfur clusters) or organic compounds (e.g., flavin and heme). These cofactors serve many purposes; for instance, metal ions can help in stabilizing nucleophilic species within the active site.[56] Organic cofactors can be either coenzymes, which are released from the enzyme's active site during the reaction, or prosthetic groups, which are tightly bound to an enzyme. Organic prosthetic groups can be covalently bound (e.g., biotin in enzymes such as pyruvate carboxylase).[57]
An example of an enzyme that contains a cofactor is carbonic anhydrase, which uses a zinc cofactor bound as part of its active site.[58] These tightly bound ions or molecules are usually found in the active site and are involved in catalysis.[1]: 8.1.1 For example, flavin and heme cofactors are often involved in redox reactions.[1]: 17
Enzymes that require a cofactor but do not have one bound are called apoenzymes or apoproteins. An enzyme together with the cofactor(s) required for activity is called a holoenzyme (or haloenzyme). The term holoenzyme can also be applied to enzymes that contain multiple protein subunits, such as the DNA polymerases; here the holoenzyme is the complete complex containing all the subunits needed for activity.[1]: 8.1.1
Coenzymes
Coenzymes are small organic molecules that can be loosely or tightly bound to an enzyme. Coenzymes transport chemical groups from one enzyme to another.[59] Examples include NADH, NADPH and adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Some coenzymes, such as flavin mononucleotide (FMN), flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP), and tetrahydrofolate (THF), are derived from vitamins. These coenzymes cannot be synthesized by the body de novo and closely related compounds (vitamins) must be acquired from the diet. The chemical groups carried include:
- the hydride ion (H−), carried by NAD or NADP+
- the phosphate group, carried by adenosine triphosphate
- the acetyl group, carried by coenzyme A
- formyl, methenyl or methyl groups, carried by folic acid and
- the methyl group, carried by S-adenosylmethionine[59]
Since coenzymes are chemically changed as a consequence of enzyme action, it is useful to consider coenzymes to be a special class of substrates, or second substrates, which are common to many different enzymes. For example, about 1000 enzymes are known to use the coenzyme NADH.[60]
Coenzymes are usually continuously regenerated and their concentrations maintained at a steady level inside the cell. For example, NADPH is regenerated through the pentose phosphate pathway and S-adenosylmethionine by methionine adenosyltransferase. This continuous regeneration means that small amounts of coenzymes can be used very intensively. For example, the human body turns over its own weight in ATP each day.[61]
Thermodynamics
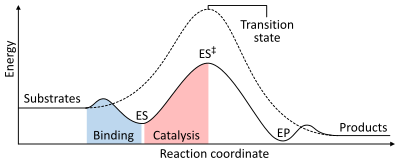
As with all catalysts, enzymes do not alter the position of the chemical equilibrium of the reaction. In the presence of an enzyme, the reaction runs in the same direction as it would without the enzyme, just more quickly.[1]: 8.2.3 For example, carbonic anhydrase catalyzes its reaction in either direction depending on the concentration of its reactants:[62]
-
(in tissues; high CO2 concentration)(1)
-
(in lungs; low CO2 concentration)(2)
The rate of a reaction is dependent on the activation energy needed to form the transition state which then decays into products. Enzymes increase reaction rates by lowering the energy of the transition state. First, binding forms a low energy enzyme-substrate complex (ES). Second, the enzyme stabilises the transition state such that it requires less energy to achieve compared to the uncatalyzed reaction (ES‡). Finally the enzyme-product complex (EP) dissociates to release the products.[1]: 8.3
Enzymes can couple two or more reactions, so that a thermodynamically favorable reaction can be used to "drive" a thermodynamically unfavourable one so that the combined energy of the products is lower than the substrates. For example, the hydrolysis of ATP is often used to drive other chemical reactions.[63]
Kinetics
Enzyme kinetics is the investigation of how enzymes bind substrates and turn them into products.[64] The rate data used in kinetic analyses are commonly obtained from enzyme assays. In 1913 Leonor Michaelis and Maud Leonora Menten proposed a quantitative theory of enzyme kinetics, which is referred to as Michaelis–Menten kinetics.[65] The major contribution of Michaelis and Menten was to think of enzyme reactions in two stages. In the first, the substrate binds reversibly to the enzyme, forming the enzyme-substrate complex. This is sometimes called the Michaelis–Menten complex in their honor. The enzyme then catalyzes the chemical step in the reaction and releases the product. This work was further developed by G. E. Briggs and J. B. S. Haldane, who derived kinetic equations that are still widely used today.[66]
Enzyme rates depend on solution conditions and substrate concentration. To find the maximum speed of an enzymatic reaction, the substrate concentration is increased until a constant rate of product formation is seen. This is shown in the saturation curve on the right. Saturation happens because, as substrate concentration increases, more and more of the free enzyme is converted into the substrate-bound ES complex. At the maximum reaction rate (Vmax) of the enzyme, all the enzyme active sites are bound to substrate, and the amount of ES complex is the same as the total amount of enzyme.[1]: 8.4
Vmax is only one of several important kinetic parameters. The amount of substrate needed to achieve a given rate of reaction is also important. This is given by the Michaelis–Menten constant (Km), which is the substrate concentration required for an enzyme to reach one-half its maximum reaction rate; generally, each enzyme has a characteristic KM for a given substrate. Another useful constant is kcat, also called the turnover number, which is the number of substrate molecules handled by one active site per second.[1]: 8.4
The efficiency of an enzyme can be expressed in terms of kcat/Km. This is also called the specificity constant and incorporates the rate constants for all steps in the reaction up to and including the first irreversible step. Because the specificity constant reflects both affinity and catalytic ability, it is useful for comparing different enzymes against each other, or the same enzyme with different substrates. The theoretical maximum for the specificity constant is called the diffusion limit and is about 108 to 109 (M−1 s−1). At this point every collision of the enzyme with its substrate will result in catalysis, and the rate of product formation is not limited by the reaction rate but by the diffusion rate. Enzymes with this property are called catalytically perfect or kinetically perfect. Example of such enzymes are triose-phosphate isomerase, carbonic anhydrase, acetylcholinesterase, catalase, fumarase, β-lactamase, and superoxide dismutase.[1]: 8.4.2 The turnover of such enzymes can reach several million reactions per second.[1]: 9.2 But most enzymes are far from perfect: the average values of and are about
Antropológia
Aplikované vedy
Bibliometria
Dejiny vedy
Encyklopédie
Filozofia vedy
Forenzné vedy
Humanitné vedy
Knižničná veda
Kryogenika
Kryptológia
Kulturológia
Literárna veda
Medzidisciplinárne oblasti
Metódy kvantitatívnej analýzy
Metavedy
Metodika
Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative
Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších
podmienok.
Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky
použitia.
www.astronomia.sk | www.biologia.sk | www.botanika.sk | www.dejiny.sk | www.economy.sk | www.elektrotechnika.sk | www.estetika.sk | www.farmakologia.sk | www.filozofia.sk | Fyzika | www.futurologia.sk | www.genetika.sk | www.chemia.sk | www.lingvistika.sk | www.politologia.sk | www.psychologia.sk | www.sexuologia.sk | www.sociologia.sk | www.veda.sk I www.zoologia.sk






