
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
Federal Republic of Nigeria | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "Unity and Faith, Peace and Progress" | |
| Anthem: "Arise, O Compatriots" | |
| Capital | Abuja 9°4′N 7°29′E / 9.067°N 7.483°E |
| Largest city | Lagos |
| Official languages | English |
| National languages | |
| Regional languages[2] | Over 525 languages[1] |
| Ethnic groups (2018)[3] | |
| Demonym(s) | Nigerian |
| Government | Federal presidential republic |
| Bola Tinubu | |
| Kashim Shettima | |
| Godswill Akpabio | |
| Tajudeen Abbas | |
| Olukayode Ariwoola | |
| Legislature | National Assembly |
| Senate | |
| House of Representatives | |
| Independence from the United Kingdom | |
| 1 January 1900 | |
| 1 January 1900 | |
| 1 January 1914 | |
| 1 October 1960 | |
| 1 October 1963 | |
| 29 May 1999 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 923,769 km2 (356,669 sq mi) (31st) |
• Water (%) | 1.4 |
| Population | |
• 2023 estimate | |
• Density | 249.8/km2 (647.0/sq mi) (42nd) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2023 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2023 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| Gini (2020) | medium |
| HDI (2022) | low (161rd) |
| Currency | Naira (₦) (NGN) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (WAT) |
| Driving side | right[8] |
| Calling code | +234 |
| ISO 3166 code | NG |
| Internet TLD | .ng |
Nigeria,[a] officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa.[9] It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea to the south in the Atlantic Ocean. It covers an area of 923,769 square kilometres (356,669 sq mi), and with a population of over 230 million, it is the most populous country in Africa, and the world's sixth-most populous country. Nigeria borders Niger in the north, Chad in the northeast, Cameroon in the east, and Benin in the west. Nigeria is a federal republic comprising 36 states and the Federal Capital Territory, where the capital, Abuja, is located. The largest city in Nigeria is Lagos, one of the largest metropolitan areas in the world and the largest in Africa.
Nigeria has been home to several indigenous pre-colonial states and kingdoms since the second millennium BC, with the Nok civilization in the 15th century BC marking the first internal unification.[10] The modern state originated with British colonialization in the 19th century, taking its present territorial shape with the merging of the Southern Nigeria Protectorate and the Northern Nigeria Protectorate in 1914. The British set up administrative and legal structures while practising indirect rule through traditional chiefdoms.[11] Nigeria became a formally independent federation on 1 October 1960. It experienced a civil war from 1967 to 1970, followed by a succession of military dictatorships and democratically elected civilian governments until achieving a stable government in the 1999 Nigerian presidential election, with the election of Olusegun Obasanjo of the Peoples Democratic Party. However, the country frequently experiences electoral fraud, and corruption is significantly present in all levels of Nigerian politics.
Nigeria is a multinational state inhabited by more than 250 ethnic groups speaking 500 distinct languages, all identifying with a wide variety of cultures.[12][13][14] The three largest ethnic groups are the Hausa in the north, Yoruba in the west, and Igbo in the east, together constituting over 60% of the total population.[15] The official language is English, chosen to facilitate linguistic unity at the national level.[16] Nigeria's constitution ensures de jure freedom of religion,[17] and it is home to some of the world's largest Muslim and Christian populations.[18] Nigeria is divided roughly in half between Muslims, who live mostly in the north part of the country, and Christians, who live mostly in the south; indigenous religions, such as those native to the Igbo and Yoruba ethnicities, are in the minority.[19]
Nigeria is a regional power in Africa and a middle power in international affairs. Nigeria's economy is the second-largest in Africa, the 39th-largest in the world by nominal GDP, and 27th-largest by PPP. Nigeria is often referred to as the Giant of Africa owing to its large population and economy,[20] and is considered to be an emerging market by the World Bank. Nigeria is a founding member of the African Union and a member of many international organizations, including the United Nations, the Commonwealth of Nations, NAM,[21] the Economic Community of West African States, Organisation of Islamic Cooperation and OPEC. It is also a member of the informal MINT group of countries and is one of the Next Eleven economies.
Etymology
The name Nigeria derives from the Niger River running through the country. This name was coined on 8 January 1897, by the British journalist Flora Shaw. The neighbouring Republic of Niger takes its name from the same river. The origin of the name Niger, which originally applied to only the middle reaches of the Niger River, is uncertain. The word is likely an alteration of the Tuareg name egerew n-igerewen used by inhabitants along the middle reaches of the river around Timbuktu before 19th-century European colonialism.[22][23] Before Flora Shaw suggested the name Nigeria, other proposed names included Royal Niger Company Territories, Central Sudan, Niger Empire, Niger Sudan, and Hausa Territories.[24]
History
Prehistory
Kainji Dam excavations showed ironworking by the 2nd century BC. The transition from Neolithic times to the Iron Age was accomplished without intermediate bronze production. Some have suggested the technology moved west from the Nile Valley. But the Iron Age in the Niger River valley and the forest region appears to predate the introduction of metallurgy in the upper savanna by more than 800 years, as well as predating it in the Nile Valley. More recent research suggests that iron metallurgy was developed independently in sub-Saharan Africa.[25][26][27][28]

The Nok civilization thrived between 1,500 BC and AD 200. It produced life-sized terracotta figures that are some of the earliest known sculptures in sub-Saharan Africa[29][30][31][32][33] and smelted iron by about 550 BC and possibly a few centuries earlier.[25][26][27] Evidence of iron smelting has also been excavated at sites in the Nsukka region of southeast Nigeria: dating to 2000 BC at the site of Lejja[34] and to 750 BC and at the site of Opi.
Early history

The Kano Chronicle highlights an ancient history dating to around 999 AD of the Hausa Sahelian city-state of Kano, with other major Hausa cities (or Hausa Bakwai) of Daura, Hadeija, Kano, Katsina, Zazzau, Rano, and Gobir all having recorded histories dating back to the 10th century. With the spread of Islam from the 7th century AD, the area became known as Sudan or as Bilad Al Sudan (English: Land of the Blacks). Since the populations were partially affiliated with the Arab Muslim culture of North Africa, they began trans-Saharan trade and were referred to by the Arabic speakers as Al-Sudan (meaning "The Blacks") as they were considered an extended part of the Muslim world. There are early historical references by medieval Arab and Muslim historians and geographers which refer to the Kanem–Bornu Empire as the region's major centre for Islamic civilization.[citation needed]
The Kingdom of Nri of the Igbo people consolidated in the 10th century and continued until it lost its sovereignty to the British in 1911.[35][36] Nri was ruled by the Eze Nri, and the city of Nri is considered to be the foundation of Igbo culture. Nri and Aguleri, where the Igbo creation myth originates, are in the territory of the Umeuri clan. Members of the clan trace their lineages back to the patriarchal king-figure Eri.[37] In West Africa, the oldest bronzes made using the lost wax process were from Igbo-Ukwu, a city under Nri influence.[35]
The Yoruba kingdoms of Ife and Oyo in southwestern Nigeria became prominent in the 12th[38][39] and 14th[40] centuries, respectively. The oldest signs of human settlement at Ife's current site date back to the 9th century,[38] and its material culture includes terracotta and bronze figures.
Pre-colonial era

In the 16th century, Portuguese explorers were the first Europeans to begin important, direct trade with the peoples of southern Nigeria, at the port they named Lagos (formerly Eko) and in Calabar along the region Slave Coast. Europeans traded goods with peoples at the coast; coastal trade with Europeans also marked the beginnings of the Atlantic slave trade.[41] The port of Calabar on the historical Bight of Biafra (now commonly referred to as the Bight of Bonny) became one of the largest slave-trading posts in West Africa in this era. Other major slaving ports were located in Badagry, Lagos on the Bight of Benin, and Bonny Island on the Bight of Biafra.[41][42] The majority of those taken to these ports were captured in raids and wars.[43] Usually, the captives were taken back to the conquerors' territory as forced labour; they were sometimes gradually acculturated and absorbed into the conquerors' society. Slave routes were established throughout Nigeria linking the hinterland areas with the major coastal ports. Some of the more prolific slave-trading kingdoms who participated in the Atlantic slave trade were linked with the Edo's Benin Empire in the south, Oyo Empire in the southwest, and the Aro Confederacy in the southeast.[41][42] Benin's power lasted between the 15th and 19th centuries.[44] Oyo, at its territorial zenith in the late 17th to early 18th centuries, extended its influence from western Nigeria to modern-day Togo.
In the north, the incessant fighting amongst the Hausa city-states and the decline of the Bornu Empire allowed the Fulani people to gain headway into the region. Until this point, the Fulani, a nomadic ethnic group, primarily traversed the semi-desert Sahelian region north of Sudan with cattle and avoided trade and intermingling with the Sudanic peoples. At the beginning of the 19th century, Usman dan Fodio led a successful jihad against the Hausa Kingdoms, founding the centralised Sokoto Caliphate. This empire, with Arabic as its official language, grew rapidly under his rule and that of his descendants, who sent out invading armies in every direction. The vast landlocked empire connected the east with the western Sudan region and made inroads down south conquering parts of the Oyo Empire (modern-day Kwara), and advanced towards the Yoruba heartland of Ibadan, to reach the Atlantic Ocean. The territory controlled by the empire included much of modern-day northern and central Nigeria. The sultan sent out emirs to establish suzerainty over the conquered territories and promote Islamic civilization; the emirs in turn became increasingly rich and powerful through trade and slavery. By the 1890s, the largest slave population in the world, about two million, was concentrated in the territories of the Sokoto Caliphate. The use of slave labour was extensive, especially in agriculture.[45] By the time of its break-up in 1903 into various European colonies, the Sokoto Caliphate was one of the largest pre-colonial African states.[46]
A changing legal imperative (the outlawing of the Atlantic slave trade in 1807) and economic imperative (a desire for political and social stability) led most European powers to support the widespread cultivation of agricultural products, such as the palm, for use in European industry. The slave trade continued after the ban, as illegal smugglers purchased slaves along the coast from native slavers. Britain's West Africa Squadron sought to intercept the smugglers at sea. The rescued slaves were taken to Freetown, a colony in West Africa originally established by Lieutenant John Clarkson for the resettlement of slaves freed by Britain in North America after the American Revolutionary War.
British colonization
Britain intervened in the Lagos kingship power struggle by bombarding Lagos in 1851, deposing the slave-trade-friendly Oba Kosoko, helping to install the amenable Oba Akitoye and signing the Treaty between Great Britain and Lagos on 1 January 1852. Britain annexed Lagos as a crown colony in August 1861 with the Lagos Treaty of Cession. British missionaries expanded their operations and travelled further inland. In 1864, Samuel Ajayi Crowther became the first African bishop of the Anglican Church.[47]

In 1885, British claims to a West African sphere of influence received recognition from other European nations at the Berlin Conference. The following year, it chartered the Royal Niger Company under the leadership of Sir George Taubman Goldie. By the late 19th and early 20th centuries, the company had vastly succeeded in subjugating the independent southern kingdoms along the Niger River, the British conquered Benin in 1897, and, in the Anglo-Aro War (1901–1902), defeated other opponents. The defeat of these states opened up the Niger area to British rule. In 1900, the company's territory came under the direct control of the British government and established the Southern Nigeria Protectorate as a British protectorate and part of the British Empire.

By 1902, the British had begun plans to move north into the Sokoto Caliphate. British General Lord Frederick Lugard was tasked by the Colonial Office to implement the agenda. Lugard used rivalries between many of the emirs in the southern reach of the caliphate and the central Sokoto administration to prevent any defence as he worked towards the capital. As the British approached the city of Sokoto, Sultan Muhammadu Attahiru I organized a quick defence of the city and fought the advancing British-led forces. The British force quickly won, sending Attahiru I and thousands of followers on a Mahdist hijra. In the northeast, the decline of the Bornu Empire gave rise to the British-controlled Borno Emirate which established Abubakar Garbai of Borno as ruler.

In 1903, the British victory in the Battle of Kano gave them a logistical edge in pacifying the heartland of the Sokoto Caliphate and parts of the former Bornu Empire. On 13 March 1903, at the grand market square of Sokoto, the last vizier of the caliphate officially conceded to British rule. The British appointed Muhammadu Attahiru II as the new caliph. Lugard abolished the caliphate but retained the title sultan as a symbolic position in the newly organized Northern Nigeria Protectorate. This remnant became known as "Sokoto Sultanate Council". In June 1903, the British defeated the remaining northern forces of Attahiru. By 1906, all resistance to British rule had ended.
On 1 January 1914, the British formally united the Southern Nigeria Protectorate and the Northern Nigeria Protectorate into the Colony and Protectorate of Nigeria. Administratively, Nigeria remained divided into the Northern and Southern Protectorates and Lagos Colony. Inhabitants of the southern region sustained more interaction, economic and cultural, with the British and other Europeans owing to the coastal economy.[48] Christian missions established Western educational institutions in the protectorates. Under Britain's policy of indirect rule and validation of Islamic legitimist tradition, the Crown did not encourage the operation of Christian missions in the northern, Islamic part of the country.[49]
By the mid-20th century following World War II, a wave for independence was sweeping across Africa, in response to the growth of Nigerian nationalism and demands for independence, successive constitutions legislated by the British government moved Nigeria toward self-government on a representative and increasingly federal basis. By the eve of independence in 1960, regional differences in modern educational access were marked. The legacy, though less pronounced, continues to the present day. Imbalances between north and south were expressed in Nigeria's political life as well. For instance, northern Nigeria did not outlaw slavery until 1936 whilst in other parts of Nigeria, slavery was abolished soon after colonialism.[50][42]


Independence and federal republic
Nigeria gained a degree of self-rule in 1954, and full independence from the United Kingdom on 1 October 1960, as the Federation of Nigeria with Abubakar Tafawa Balewa as its prime minister, while retaining the British monarch, Elizabeth II, as nominal head of state and Queen of Nigeria. Azikiwe replaced the colonial governor-general in November 1960. At independence, the cultural and political differences were sharp among Nigeria's dominant ethnic groups: the Hausa in the north, Igbo in the east and Yoruba in the west.[51] The Westminster system of government was retained, and thus the President's powers were generally ceremonial.[52] The parliamentary system of government had Abubakar Tafawa Balewa as Prime Minister and Nnamdi Azikiwe as the ceremonial president. The founding government was a coalition of conservative parties: the Northern People's Congress led by Sir Ahmadu Bello, a party dominated by Muslim northerners, and the Igbo and Christian-dominated National Council of Nigeria and the Cameroons led by Nnamdi Azikiwe. The opposition consisted of the comparatively liberal Action Group, which was largely dominated by the Yoruba and led by Obafemi Awolowo. An imbalance was created in the polity as the result of the 1961 plebiscite. Southern Cameroons opted to join the Republic of Cameroon while Northern Cameroons chose to join Nigeria. The northern part of the country became larger than the southern part.

Fall of the First Republic and Civil War
The disequilibrium and perceived corruption of the electoral and political process led to two military coups in 1966. The first coup was in January 1966 and was led mostly by soldiers under Majors Emmanuel Ifeajuna (of the Igbo tribe), Chukwuma Kaduna Nzeogwu (Northerner of Eastern extraction) and Adewale Ademoyega (a Yoruba from the West). The coup plotters succeeded in assassinating Sir Ahmadu Bello and Sir Abubakar Tafawa Balewa alongside prominent leaders of the Northern Region and Premier Samuel Akintola of the Western Region, but the plotters struggled to form a central government. Senate President Nwafor Orizu handed over government control to the Army, under the command of another Igbo officer, Major General[53] Johnson Aguiyi-Ironsi. Later, the counter-coup of 1966, supported primarily by Northern military officers, facilitated the rise of Yakubu Gowon as military head of state. Tension rose between north and south; Igbos in northern cities suffered persecution and many fled to the Eastern Region.[54]

In May 1967, Governor of the Eastern Region Lt. Colonel Emeka Ojukwu declared the region independent from the federation as a state called the Republic of Biafra, as a result of the continuous and systematically planned attacks against Igbos and those of Eastern extraction popularly known as 1966 pogroms.[55][56] This declaration precipitated the Nigerian Civil War, which began as the official Nigerian government side attacked Biafra on 6 July 1967, at Garkem. The 30-month war, with a long blockade of Biafra and its isolation from trade and international relief, ended in January 1970.[57] Estimates of the number of dead in the former Eastern Region during the 30-month civil war range from one to three million.[58] Britain and the Soviet Union were the main military backers of the Nigerian government, with Nigeria utilizing air support from Egyptian pilots provided by Gamal Abdel Nasser,[59][60] while France and Israel aided the Biafrans. The Congolese government, under President Joseph-Désiré Mobutu, took an early stand on the Biafran secession, voicing strong support for the Nigerian federal government[61] and deploying thousands of troops to fight against the secessionists.[62][63]
Following the war, Nigeria enjoyed an oil boom in the 1970s, during which the country joined OPEC and received huge oil revenues. Despite these revenues, the military government did little to improve the standard of living, help small and medium businesses, or invest in infrastructure. As oil revenues fuelled the rise of federal subsidies to states, the federal government became the centre of political struggle and the threshold of power in the country. As oil production and revenue rose, the Nigerian government became increasingly dependent on oil revenues and international commodity markets for budgetary and economic concerns.[64] The coup in July 1975, led by Generals Shehu Musa Yar'Adua and Joseph Garba, ousted Gowon,[65] who fled to Britain.[66] The coup plotters wanted to replace Gowon's autocratic rule with a triumvirate of three brigadier generals whose decisions could be vetoed by a Supreme Military Council. For this triumvirate, they convinced General Murtala Muhammed to become military head of state, with General Olusegun Obasanjo as his second-in-command, and General Theophilus Danjuma as the third.[67] Together, the triumvirate introduced austerity measures to stem inflation, established a Corrupt Practices Investigation Bureau, replaced all military governors with new officers, and launched "Operation Deadwood" through which they fired 11,000 officials from the civil service.[68]
Colonel Buka Suka Dimka launched a February 1976 coup attempt,[69] during which General Murtala Muhammed was assassinated. Dimka lacked widespread support among the military, and his coup failed, forcing him to flee.[70] After the coup attempt, General Olusegun Obasanjo was appointed military head of state.[71] Obasanjo vowed to continue Murtala's policies.[72] Aware of the danger of alienating northern Nigerians, Obasanjo brought General Shehu Yar'Adua as his replacement and second-in-command as Chief of Staff, Supreme Headquarters completing the military triumvirate, with Obasanjo as head of state and General Theophilus Danjuma as Chief of Army Staff, the three went on to re-establish control over the military regime and organized the military's transfer of power programme: states creation and national delimitation, local government reforms and the constitutional drafting committee for a new republic.[73]
Second Republic and military dictatorship
The military carefully planned the return to civilian rule putting in place measures to ensure that political parties had broader support than witnessed during the first republic. In 1979, five political parties competed in a series of elections in which Alhaji Shehu Shagari of the National Party of Nigeria (NPN) was elected president. All five parties won representation in the National Assembly. On 1 October 1979, Shehu Shagari was sworn in as the first President and Commander-in-Chief of the Federal Republic of Nigeria. Obasanjo peacefully transferred power to Shagari, becoming the first head of state in Nigerian history to willingly step down.

The Shagari government became viewed as corrupt by virtually all sectors of Nigerian society. In 1983, the inspectors of the state-owned Nigerian National Petroleum Corporation began to notice "the slow poisoning of the waters of this country".[74] In August 1983, Shagari and the NPN were returned to power in a landslide victory, with a majority of seats in the National Assembly and control of 12 state governments. But the elections were marred by violence, and allegations of widespread vote-rigging and electoral malfeasance led to legal battles over the results. There were also uncertainties, such as in the first republic, that political leaders may be unable to govern properly.
The 1983 military coup d'état was coordinated by key officers of the Nigerian military and led to the overthrow of the government and the installation of Major General Muhammadu Buhari as head of state. The military coup of Muhammadu Buhari shortly after the regime's re-election in 1984 was generally viewed as a positive development.[75] In 1985, Ibrahim Babangida overthrew Buhari in a coup d'état. In 1986, Babangida established the Nigerian Political Bureau which made recommendations for the transition to the Third Nigerian Republic. In 1989, Babangida started making plans for the transition to the Third Nigerian Republic. Babangida survived the 1990 Nigerian coup d'état attempt, then postponed a promised return to democracy to 1992.[76]
12 June and the crisis of the Third Republic
Babangida legalized the formation of political parties and formed the two-party system with the Social Democratic Party and National Republican Convention ahead of the 1992 general elections. He urged all Nigerians to join either of the parties, which Chief Bola Ige referred to as "two leper hands". The 1993 presidential election held on 12 June was the first since the military coup of 1983. The results, though not officially declared by the National Electoral Commission, showed the duo of Moshood Abiola and Baba Gana Kingibe of the Social Democratic Party defeated Bashir Tofa and Sylvester Ugoh of the National Republican Convention by over 2.3 million votes. However, Babangida annulled the elections, leading to massive civilian protests that effectively shut down the country for weeks. In August 1993, Babangida finally kept his promise to relinquish power to a civilian government but not before appointing Ernest Shonekan head of an interim national government.[77] Babangida's regime has been considered the most corrupt and responsible for creating a culture of corruption in Nigeria.[78]

Shonekan's interim government, the shortest in the political history of the country, was overthrown in a coup d'état of 1993 led by General Sani Abacha, who used military force on a wide scale to suppress the continuing civilian unrest. In 1995, the government hanged environmentalist Ken Saro-Wiwa on trumped-up charges in the deaths of four Ogoni elders, which caused Nigerian's suspension from the Commonwealth. Lawsuits under the American Alien Tort Statute against Royal Dutch Shell and Brian Anderson, the head of Shell's Nigerian operation, settled out of court with Shell continuing to deny liability.[79] Several hundred million dollars in accounts traced to Abacha were discovered in 1999.[80] The regime came to an end in 1998 when the dictator died in the villa. He looted money to offshore accounts in western European banks and defeated coup plots by arresting and bribing generals and politicians. His successor, General Abdulsalami Abubakar, adopted a new constitution on 5 May 1999, which provided for multiparty elections.
Return to democracy (1999–present)

On 29 May 1999, Abubakar handed over power to the winner of the 1999 presidential election, former military ruler General Olusegun Obasanjo, as President of Nigeria. Obasanjo had been in prison under the dictatorship of Abacha. Obasanjo's inauguration heralded the beginning of the Fourth Nigerian Republic,[81] ending a 39-year period of short-lived democracies, civil war and military dictatorship. Although the elections that brought Obasanjo to power and allowed him to run for a second term in the 2003 presidential elections were condemned as unfree and unfair, Nigeria made significant progress in democratisation under Obasanjo.[82]
In the 2007 general elections, Umaru Yar'Adua of the People's Democratic Party came to power. The international community, which had observed the Nigerian elections to promote a free and fair process, condemned these elections as seriously flawed.[83] Yar'Adua died on 5 May 2010, and Vice President Goodluck Jonathan had been sworn in by the Senate three months earlier as acting president to succeed Yar'Adua.[84][85] Jonathan won the 2011 presidential election; the polls went smoothly and with relatively little violence or electoral fraud.[86] Jonathan's tenure saw an economic recovery that made Nigeria the leading economic power in Africa.[87][88] The Jonathan administration also saw an increase in unparalleled corruption, with as many as 20 billion US dollars said to have been lost to the Nigerian state through the national oil company. Above all, however, Jonathan's tenure saw the emergence of a wave of terror by the Boko Haram insurgency, such as the Gwoza massacre and Chibok schoolgirls kidnapping in 2014.[89]
Ahead of the general election of 2015, a merger of the biggest opposition parties in Nigeria – the Action Congress of Nigeria, the Congress for Progressive Change, the All Nigeria Peoples Party, a faction of the All Progressives Grand Alliance and the new PDP (a faction of serving governors of the ruling People's Democratic Party) – formed the All Progressives Congress led by current president Bola Ahmed Tinubu. At the time, it was the most expensive election ever to be held on the African continent (being surpassed only by the elections of 2019 and 2023). The new mega-opposition party chose as their candidate for the election former military dictator Muhammadu Buhari. Buhari's campaign in 2015 was popular and built around his image as a staunch anti-corruption fighter—he won the election by over two million votes. Observers generally praised the election as being fair.[90][91][92][93] The election marked the first time an incumbent president had lost re-election in Nigeria. In the 2019 presidential election, Buhari was re-elected.[94]
Four candidates vied for the presidency in the 2023 presidential election; for the first time since the return of democracy, no former military ruler ran for president, marking a strengthening of democracy and faith in the multiparty constitution. The election also saw the rise of metonymic supporters of the new candidates, the Obidient movement of Peter Obi, previously governor of Anambra State, widely appealed to young, urban voters and has his core base in the Southeast;[95] and the Kwankwassiya of Rabiu Kwankwaso, former governor of Kano State in the Northwest.[96]

Bola Tinubu, of the ruling party, won the disputed election with 36.61% of the vote,[97] but both runner-ups claimed victory and litigation is ongoing in an election tribunal.[98] Bola Tinubu's inauguration was held on 29 May 2023.[99] Problems with widespread kidnapping in Nigeria continued.[100]
Geography
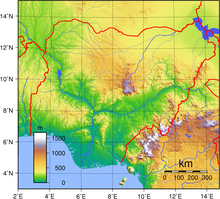
Nigeria is located in western Africa on the Gulf of Guinea and has a total area of 923,768 km2 (356,669 sq mi),[101] making it the world's 32nd-largest country. Its borders span 4,047 kilometres (2,515 mi), and it shares borders with Benin (773 km or 480 mi), Niger (1,497 km or 930 mi), Chad (87 km or 54 mi), and Cameroon (including the separatist Ambazonia) 1,690 km or 1,050 mi. Its coastline is at least 853 km (530 mi).[102] Nigeria lies between latitudes 4° and 14°N, and longitudes 2° and 15°E. The highest point in Nigeria is Chappal Waddi at 2,419 m (7,936 ft). The main rivers are the Niger and the Benue, which converge and empty into the Niger Delta. This is one of the world's largest river deltas and the location of a large area of Central African mangroves.
Nigeria's most expansive topographical region is that of the valleys of the Niger and Benue river valleys (which merge and form a Y-shape).[103] To the southwest of the Niger is a "rugged" highland. To the southeast of the Benue are hills and mountains, which form the Mambilla Plateau, the highest plateau in Nigeria. This plateau extends through the border with Cameroon, where the montane land is part of the Bamenda Highlands of Cameroon.
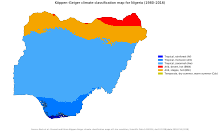
The far south is defined by its tropical rainforest climate, where annual rainfall is 1,500 to 2,000 millimetres (60 to 80 in) per year.[104] In the southeast stands the Obudu Plateau. Coastal plains are found in both the southwest and the southeast.[103] Mangrove swamps are found along the coast.[105]
The area near the border with Cameroon close to the coast is rich rainforest and part of the Cross-Sanaga-Bioko coastal forests ecoregion, an important centre for biodiversity. It is a habitat for the drill primate, which is found in the wild only in this area and across the border in Cameroon. The areas surrounding Calabar, Cross River State, also in this forest, are believed to contain the world's largest diversity of butterflies. The area of southern Nigeria between the Niger and the Cross Rivers has lost most of its forest because of development and harvesting by increased population, and has been replaced by grassland.
Everything in between the far south and the far north is savannah (insignificant tree cover, with grasses and flowers located between trees). Rainfall is more limited to between 500 and 1,500 millimetres (20 and 60 in) per year.[104] The savannah zone's three categories are Guinean forest-savanna mosaic, Sudan savannah, and Sahel savannah. Guinean forest-savanna mosaic is plains of tall grass interrupted by trees. Sudan savannah is similar but with shorter grasses and shorter trees. Sahel savannah consists of patches of grass and sand, found in the northeast.[105]

Hydrology
Nigeria is divided into two main catchment areas - that of Lake Chad and that of the Niger. The Niger catchment area covers about 63% of the country. The main tributary of the Niger is the Benue, whose tributaries extend beyond Cameroon into Cameroon into Chad and the Sharie catchment area. In the Sahel region, rain is less than 500 millimetres (20 in) per year, and the Sahara Desert is encroaching.[104] In the dry northeast corner of the country lies Lake Chad, on a shared water boundary delimitation with Niger, Chad and Cameroon.
The Chad Basin is fed from the north-eastern quarter of Nigeria. The Bauchi Plateau forms the watershed between the Niger/Benue and Komadugu Yobe river systems. The flat plains of north-eastern Nigeria are geographically part of the Chad Basin, where the course of the El Beid River forms the border with Cameroon, from the Mandara Mountains to Lake Chad. The Komadugu Yobe river system gives rise to the internationally important Hadejia-Nguru wetlands and Ox-bow lakes around Lake Nguru in the rainy season.[106][107] Other rivers of the northeast include the Ngadda and the Yedseram, both of which flow through the Sambisa swamps, thus forming a river system. The river system of the northeast is also a major river system.[108] In addition, Nigeria has numerous coastal rivers.

Over the last million years, Lake Chad in the far north-east of Nigeria has dried up several times for a few thousand years and just as often growing to many times its current size. In recent decades its surface area has been reduced considerably, which may also be due to humans taking water from the inlets to irrigate agricultural land.
Vegetation
Nigeria is covered by three types of vegetation: forests (where there is significant tree cover), savannahs (insignificant tree cover, with grasses and flowers located between trees), and montane land (least common and mainly found in the mountains near the Cameroon border). Both the forest zone and the savannah zone are divided into three parts.[109]
Some of the forest zone's most southerly portion, especially around the Niger River and Cross River deltas, is mangrove swamp. North of this is fresh water swamp, containing different vegetation from the salt water mangrove swamps, and north of that is rain forest.[109]
The savannah zone's three categories are divided into Guinean forest-savanna mosaic, made up of plains of tall grass which are interrupted by trees, the most common across the country; Sudan savannah, with short grasses and short trees; and Sahel savannah patches of grass and sand, found in the northeast.[109]

Environmental issues

Waste management including sewage treatment, the linked processes of deforestation and soil degradation, and climate change or global warming are the major environmental problems in Nigeria. Waste management presents problems in a megacity like Lagos and other major Nigerian cities which are linked with economic development, population growth and the inability of municipal councils to manage the resulting rise in industrial and domestic waste. This waste management problem is also attributable to unsustainable environmental management lifestyles of Kubwa community in the Federal Capital Territory, where there are habits of indiscriminate disposal of waste, dumping of waste along or into the canals, sewerage systems that are channels for water flows, and the like. Haphazard industrial planning, increased urbanisation, poverty and lack of competence of the municipal government are seen as the major reasons for high levels of waste pollution in major cities of the country. Some of the solutions have been disastrous to the environment, resulting in untreated waste being dumped in places where it can pollute waterways and groundwater.[111]
In 2005, Nigeria had the highest rate of deforestation in the world, according to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.[112] That year, 12.2%, the equivalent of 11,089,000 hectares, had been forested in the country. Between 1990 and 2000, Nigeria lost an average of 409,700 hectares of forest every year equal to an average annual deforestation rate of 2.4%. Between 1990 and 2005, in total Nigeria lost 35.7% of its forest cover or around 6,145,000 hectares.[113] Nigeria had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 6.2/10, ranking it 82nd globally out of 172 countries.[114]
In the year 2010, thousands of people were inadvertently exposed to lead-containing soil from informal gold mining within the northern state of Zamfara. While estimates vary, it is thought that upwards of 400 children died of acute lead poisoning, making this perhaps the largest lead poisoning fatality outbreak ever encountered.[115]
Nigeria's Delta region is one of the most polluted regions in the world due to serious oil spills and other environmental problems caused by its oil industry.[116][117] The heavy contamination of the air, ground and water with toxic pollutants is often used as an example of ecocide.[118][119][120][121][122] In additional to the environmental damage it has caused conflict in the Delta region.
Illegal oil refineries, in which local operators convert stolen crude oil into petrol and diesel, are considered particularly "dirty, dangerous and lucrative".[123] Safety and environmental aspects are usually ignored. Refining petroleum also inevitably produces heavy oil, which is "cracked" into lighter fuel components in regular plants at great technical expense. Illegal refineries do not have these technical possibilities and "dispose" of the heavy oil where it accumulates. The lighter components of crude oil (methane to butane, isobutane) create a certain risk of explosion, which often leads to disasters at illegal plants.[124] In 2022, Nigeria suffered 125 deaths from explosions at local, illegal refineries.[125]
Politics
Government

Nigeria is a federal republic modelled after the United States,[126] with 36 states and capital Abuja as an independent unit. The executive power is exercised by the President. The president is both head of state and head of the federal government; the president is elected by popular vote to a maximum of two four-year terms.[127] State governors, like the president, are elected for four years and may serve a maximum of two terms. The president's power is checked by a Senate and a House of Representatives, which are combined in a bicameral body called the National Assembly. The Senate is a 109-seat body with three members from each state and one from the capital region of Abuja; members are elected by popular vote to four-year terms. The House contains 360 seats, with the number of seats per state determined by population.[127]
The Nigerian president is elected in a modified two-round system. To be elected in the first round, a candidate must receive a relative majority of the votes and more than 25% of the votes in at least 24 of the 36 states.[128] If no candidate reaches this hurdle, a second round of voting takes place between the leading candidate and the next candidate who received the majority of votes in the highest number of states. By convention, presidential candidates take a running mate (candidate for the vice-presidency) who is both ethnically and religiously the opposite of themselves. There is no law prescribing this, yet all presidential candidates since the existence of the Fourth Republic until 2023 adhered to this rule.
However, this principle of religious and ethnic diversity in leadership was ignored in the 2023 General Elections, where the candidate for the All Progressives Congress, Bola Ahmed Tinubu, a Muslim, selected another Muslim, Senator Kashim Shettima, as running mate.
Administrative divisions

Nigeria is divided into thirty-six states and one Federal Capital Territory, which are further sub-divided into 774 local government areas. In some contexts, the states are aggregated into six geopolitical zones: North West, North East, North Central, South West, South East, and South South.[129][130]
Nigeria has five cities with a population of over a million (from largest to smallest): Lagos, Kano, Ibadan, Benin City and Port Harcourt. Lagos is the largest city in Africa, with a population of over 12 million in its urban area.[131]
The south of the country in particular is characterised by very strong urbanisation and a relatively large number of cities. According to an estimate from 2015,[132] there are 20 cities in Nigeria with more than 500,000 inhabitants, including ten cities with a population of one million.
Law
The Constitution of Nigeria is the supreme law of the country. There are four distinct legal systems in Nigeria, which include English law, common law, customary law, and Sharia law:
- English law in Nigeria consists of the collection of British laws from colonial times.
- Common law is the collection of authoritative judicial decisions in the field of civil law (so-called precedents) that have been handed down in the country concerned - in this case Nigeria. (This system is mainly found in Anglo-Saxon countries; in continental Europe, on the other hand, codified and, as far as possible, abstracted civil law predominates, as in the Napoleonic Code in France).[133]
- Customary law is derived from indigenous traditional norms and practices, including the dispute resolution meetings of pre-colonial Yoruba land secret societies and the Èkpè and Okónkò of Igboland and Ibibioland.[134]
- Sharia law (also known as Islamic Law) used to be used only in Northern Nigeria, where Islam is the predominant religion. It is also being used in Lagos State, Oyo State, Kwara State, Ogun State, and Osun State by Muslims. Muslim penal codes are not the same in every state and they differentiate in punishment and offences according to religious affiliation (for example, alcohol consumption and distribution).
The country has a judicial branch, the highest court of which is the Supreme Court of Nigeria.[135]
Foreign relations

Upon gaining independence in 1960, Nigeria made African unity the centrepiece of its foreign policy.[136] One exception to the African focus was Nigeria's close relationship developed with Israel throughout the 1960s. Israel sponsored and oversaw the construction of Nigeria's parliament buildings.[137]
Nigeria's foreign policy was put to the test in the 1970s after the country emerged united from its civil war. It supported movements against white minority governments in Southern Africa. Nigeria backed the African National Congress by taking a committed tough line about the South African government. Nigeria was a founding member of the Organisation for African Unity (now the African Union) and has tremendous influence in West Africa and Africa on the whole. Nigeria founded regional cooperative efforts in West Africa, functioning as the standard-bearer for the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) and ECOMOG (especially during the Liberia and Sierra Leone civil wars).
With this Africa-centred stance, Nigeria readily sent troops to the Congo at the behest of the United Nations shortly after independence (and has maintained membership since that time). Nigeria also supported several Pan-African and pro-self government causes in the 1970s, including garnering support for Angola's MPLA, SWAPO in Namibia, and aiding opposition to the minority governments of Portuguese Mozambique, and Rhodesia. Nigeria retains membership in the Non-Aligned Movement. In late November 2006, it organized an Africa-South America Summit in Abuja to promote what some attendees termed "South-South" linkages on a variety of fronts.[138] Nigeria is also a member of the International Criminal Court and the Commonwealth of Nations. It was temporarily expelled from the latter in 1995 when ruled by the Abacha regime.
Nigeria has remained a key player in the international oil industry since the 1970s and maintains membership in OPEC, which it joined in July 1971. Its status as a major petroleum producer figures prominently in its sometimes volatile international relations with developed countries, notably the United States, and with developing countries.[139]
Since 2000, Chinese–Nigerian trade relations have risen exponentially. There has been an increase in total trade of over 10.3 billion dollars between the two nations from 2000 to 2016.[140] However, the structure of the Chinese–Nigerian trade relationship has become a major political issue for the Nigerian state. Chinese exports account for around 80 per cent of total bilateral trade volumes.[141] This has resulted in a serious trade imbalance, with Nigeria importing ten times more than it exports to China.[142] Subsequently, Nigeria's economy is becoming over-reliant on cheap imports to sustain itself, resulting in a clear decline in Nigerian industry under such arrangements.[143]
Continuing its Africa-centred foreign policy, Nigeria introduced the idea of a single currency for West Africa known as the Eco under the presumption that it would be led by the naira. But on 21 December 2019, Ivorian President Alassane Ouattara, Emmanuel Macron, and multiple other UEMOA states announced that they would merely rename the CFA franc instead of replacing the currency as originally intended. As of 2020, the Eco currency has been delayed to 2025.[144]
Military

The Nigerian Armed Forces are the combined military forces of Nigeria. It consists of three uniformed service branches: the Nigerian Army, Nigerian Navy, and Nigerian Air Force. The President of Nigeria functions as the commander-in-chief of the armed forces, exercising his constitutional authority through the Ministry of Defence, which is responsible for the management of the military and its personnel. The operational head of the AFN is the Chief of the Defence Staff, who is subordinate to the Nigerian Defence Minister. With a force of more than 223,000 active personnel, the Nigerian military is one of the largest uniformed combat services in Africa.[145]

Nigeria has 143,000 troops in the armed forces (army 100,000, navy 25,000, air force 18,000) and another 80,000 personnel for "gendarmerie & paramilitary" in 2020, according to the International Institute for Strategic Studies.[146] Nigeria spent just under 0.4 per cent of its economic output, or US$1.6 billion, on its armed forces in 2017.[147][148] For 2022, US$2.26 billion has been budgeted for the Nigerian armed forces, which is just over a third of Belgium's defence budget (US$5.99 billion).[146]
Regional conflicts

Boko Haram and the bandit conflict have been responsible for numerous serious attacks with thousands of casualties since mid-2010. Since then, according to the Council on Foreign Relations' Nigeria Security Tracker, over 41,600 lives have been lost to this conflict (as of October 2022).[149] The United Nations refugee agency UNHCR counts about 1.8 million internally displaced persons and about 200,000 Nigerian refugees in neighbouring countries.
The Boko Haram-affected states agreed in February 2015 to establish an 8,700-strong Multinational Joint Task Force to jointly fight Boko Haram. By October 2015, Boko Haram had been driven out of all the cities it controlled and almost all the counties in northeastern Nigeria. In 2016, Boko Haram split and in 2022, 40,000 fighters surrendered.[150] The splinter group ISWAP (Islamic State in West Africa) remains active.
The fight against Boko Haram, other sectarians and criminals has been accompanied by increasing police attacks. The Council on Foreign Relations' Nigeria Security Tracker counted 1,086 deaths from Boko Haram attacks and 290 deaths from police violence in the first 12 months of its establishment in May 2011. In the 12 months after October 2021, 2,193 people died from police violence and 498 from Boko Haram and ISWAP,[149] according to the NST. The Nigerian police are notorious for vigilante justice.[149]
The Niger Delta saw intense attacks on oil infrastructure in 2016 by militant groups such as the Movement for the Emancipation of the Niger Delta (MEND), the Niger Delta People's Volunteer Force (NDPVF), the Ijaw National Congress (INC) and the Pan Niger Delta Forum (PANDEF). In response, the new Buhari government pursued a dual strategy of repression and negotiation.
In late 2016, the Nigerian federal government resorted to the gambit of offering the militant groups a 4.5 billion naira (US$144 million) contract to guard oil infrastructure. Most accepted. The contract was renewed in August 2022, but led to fierce disputes among the above-mentioned groups over the distribution of the funds. Representatives speak of "war"[151] - against each other. The high propensity for violence and the pettiness of the leaders, as well as the complete absence of social and environmental arguments in this dispute[151] give rise to fears that the militant groups, despite their lofty names, have discarded responsibility for their region and ethnic groups and have moved into the realm of protection rackets and self-enrichment. In any case, the pipelines in the Niger Delta are not very effectively "guarded" - the pollution of the Niger Delta with stolen crude oil and illegally produced heavy fuel oil continued unhindered after 2016.[152]
In central Nigeria, conflicts between Muslim Hausa-Fulani herders and indigenous Christian farmers flared up again, especially in Kaduna, Plateau, Taraba and Benue states. In individual cases, these clashes have claimed several hundred lives. Conflict over land and resources is increasing due to the ongoing desertification in northern Nigeria, population growth and the generally tense economic situation.
In June 2022, a massacre took place in the St. Francis Xavier Church, in Owo. The Government blamed ISWAP for the murder of over 50 parishioners, but locals suspect Fulani herdsmen involvement.[153]
Economy

Nigeria's economy is the largest in Africa, the 31st-largest in the world by nominal GDP, and 30th-largest by PPP. GDP (PPP) per capita is US$9,148[155] (as of 2022), which is less than South Africa, Egypt or Morocco, but a little more than Ghana or Ivory Coast.
Nigeria is a leader in Africa as an energy power, financial market, in pharmaceuticals and in the entertainment industry. Next to petroleum, the second-largest source of foreign exchange earnings for Nigeria are remittances sent home by Nigerians living abroad.[156]
Nigeria has a highly developed financial services sector, with a mix of local and international banks, asset management companies, brokerage houses, insurance companies and brokers, private equity funds and investment banks.[157]
Nigeria has a lower-middle-income economy[158] with an abundant supply of natural resources. Its wide array of underexploited mineral resources include coal, bauxite, tantalite, gold, tin, iron ore, limestone, niobium, lead and zinc.[159] Despite huge deposits of these natural resources, the mining industry in Nigeria is still in its infancy.
Before 1999, economic development has been hindered by years of military rule, corruption, and mismanagement. The restoration of democracy and subsequent economic reforms have supported economic potential.
After 2015, the Nigerian economy was able to diversify somewhat. Apart from oil and gas, Nigeria exports fertilisers and cement/cement board, moulded polypropylene (plastic) products, personal care products, paint, malt beverages and armoured vehicles.
Agriculture

In 2021, about 23.4% of Nigeria's GDP is contributed by agriculture, forestry and fishing combined.[160] Nigeria is the world's largest producer of cassava.[161] Further major crops include maize, rice, millet, yam beans, and guinea corn (sorghum).[162] Cocoa is the principal agricultural export, and one of the country's most significant non-petroleum products.[163][164] Nigeria is also one of the world's top twenty exporters of natural rubber, generating $20.9 million in 2019.[165]
Before the Nigerian Civil War and the oil boom, Nigeria was self-sufficient in food.[166][167][168] Agriculture used to be the principal foreign exchange earner of Nigeria.[169] Agriculture has failed to keep pace with Nigeria's rapid population growth, and Nigeria now relies upon food imports to sustain itself.[167][170] It spends US$6.7 billion yearly for food imports, four times more than revenues from food export.[161] The Nigerian government promoted the use of inorganic fertilizers in the 1970s.[171]
Nigeria's rice production increased by 10% from 2017/18 to 2021/22 to 5 million tonnes a year,[172] but could hardly keep up with the increased demand. Rice imports therefore remained constant at 2 million tonnes per year. In August 2019, Nigeria closed its border with Benin and other neighbouring countries to stop rice smuggling into the country as part of efforts to boost local production.[173]
Until now, Nigeria exported unhusked rice but had to import husked rice, the country's staple food. - The rice mill in Imota, near Lagos, is intended to handle the corresponding processing at home, improve the balance of trade and the labour market, and save unnecessary costs for transport and middlemen. When fully operational at the end of 2022, the plant, the largest south of the Sahara, is expected to employ 250,000 people and produce 2.5 million 50-kg bags of rice annually.[174]
Oil and natural gas

Nigeria is the 15th largest producer of petroleum in the world, the 6th largest exporter, and has the 9th largest proven reserves. Petroleum plays a large role in the Nigerian economy and politics, accounting for about 80% of government earnings. Nigeria also has the 9th largest proven natural gas reserves estimated by OPEC; the government's value of its about 206.53 trillion cubic feet has been valued at $803.4 trillion.[175] Natural gas is seen as having the potential to unlock an economic miracle on the Niger River.[176] Nigeria each year loses to gas flaring an estimate of US$2.5 billion,[177] and over 120,000 barrels of oil per day to crude theft in the Niger Delta, its main oil-producing region.[178][179] This has led to piracy and conflict for control in the region and has led to disruptions in production preventing the country from meeting its OPEC quota and exporting petroleum at full capability.[180]

Nigeria has a total of 159 oil fields and 1,481 wells in operation according to the Department of Petroleum Resources.[181] The most productive region of the nation is the coastal Niger Delta Basin in the Niger Delta or "south-south" region which encompasses 78 of the 159 oil fields. Most of Nigeria's oil fields are small and scattered, and as of 1990, these small fields accounted for 62.1% of all Nigerian production. This contrasts with the sixteen largest fields which produced 37.9% of Nigeria's petroleum at that time.[182] Petrol was Nigeria's main import commodity until 2021, accounting for 24% of import volume.[183]
The Niger Delta Nembe Creek oil field was discovered in 1973 and produces from middle Miocene deltaic sandstone-shale in an anticline structural trap at a depth of 2 to 4 kilometres (7,000 to 13,000 feet).[184] In June 2013, Shell announced a strategic review of its operations in Nigeria, hinting that assets could be divested. While many international oil companies have operated there for decades, by 2014 most were making moves to divest their interests, citing a range of issues including oil theft. In August 2014, Shell said it was finalising its interests in four Nigerian oil fields.[185]
The supply of natural gas to Europe, threatened by the Ukraine war, is pushing projects to transport Nigerian natural gas via pipelines to Morocco or Algeria.[186][187][188] As of May 2022, however, there are no results on this yet.
Energy

Nigeria's energy consumption is much more than its generation capacity. Most of the energy comes from traditional fossil fuel, which account for 73% of total primary production. The rest is from hydropower (27%). Since independence, Nigeria has tried to develop a domestic nuclear industry for energy. Nigeria opened in 2004 a Chinese-origin research reactor at Ahmadu Bello University and has sought the support of the International Atomic Energy Agency to develop plans for up to 4,000 MWe of nuclear capacity by 2027 according to the National Program for the Deployment of Nuclear Power for Generation of Electricity. In 2007, President Umaru Yar'Adua urged the country to embrace nuclear power to meet its growing energy needs. In 2017, Nigeria signed the UN Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons.[189] In April 2015, Nigeria began talks with Russia's state-owned Rosatom to collaborate on the design, construction and operation of four nuclear power plants by 2035, the first of which will be in operation by 2025. In June 2015, Nigeria selected two sites for the planned construction of the nuclear plants. Neither the Nigerian government nor Rosatom would disclose the specific locations of the sites, but it is believed that the nuclear plants will be sited in Akwa Ibom State and Kogi State. The sites are planned to house two plants each. In 2017 agreements were signed for the construction of the Itu nuclear power plant.
Electricity
94% of Nigerians are connected to the national grid, according to the survey, but only 57% have their electricity consumption recorded by an electricity meter.[190] Only 1% of Nigerians surveyed reported having electricity 24 hours a day. 68% have electricity 1 to 9 hours a day, according to the NIO. 66% of Nigerians pay up to 10,000 Naira (US$13) a month for electricity, which is almost 3% of the average income in Nigeria.[190] 67% of respondents were willing to pay more for uninterrupted electricity supply. 21% own a power generator, 14% of Nigerians use solar energy.[190]
Manufacturing and technology

Nigeria has a manufacturing industry that includes leather and textiles (centred in Kano, Abeokuta, Onitsha, and Lagos), plastics and processed food. Ogun is considered to be Nigeria's current industrial hub, as most factories are located in Ogun and more companies are moving there, followed by Lagos.[191][192][193] The city of Aba in the south-eastern part of the country is well known for handicrafts and shoes, known as "Aba made".[194] Nigeria has a market of 720,000 cars per year, but less than 20% of these are produced domestically.[195]
In 2016, Nigeria was the leading cement producer south of the Sahara, ahead of South Africa.[196] Aliko Dangote, Nigeria's richest inhabitant, based his wealth on cement production, as well as agricultural commodities.[197] According to its own information, the Ajaokuta Steel Company Limited produces 1.3 million tonnes of steel per year.[198] This would be equivalent to one-sixth of the United Kingdom's steel production in 2021.[199] However, steel plants in Katsina, Jos and Osogbo no longer appear to be active.[200]
In June 2019, Nigeria EduSat-1 was deployed from the International Space Station. It is the first satellite that was built in Nigeria, which followed many other Nigerian satellites that were built by other countries.[b][201] In 2021, Nigeria hosts about 60 percent of the pharmaceutical production capacity in Africa,[202] the larger pharmaceutical companies are located in Lagos.[203] The pharmaceutical producer with the most employees in Nigeria is Emzor Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.[204] Nigeria has a few electronic manufacturers like Zinox, the first branded Nigerian computer, and manufacturers of electronic gadgets such as tablet PCs.[205] As of January 2022, Nigeria is the host to 5 out of the 7 unicorn companies in Africa.[206]
Internet and telecommunications

Nigerian telecommunications market is one of the fastest-growing in the world, with major emerging market operators (like MTN, 9mobile, Airtel and Globacom) basing their largest and most profitable centres in the country.[207] Nigeria's ICT sector has experienced a lot of growth, representing 10% of the nation's GDP in 2018 as compared to just 1% in 2001.[208] Lagos is regarded as one of the largest technology hubs in Africa with its thriving tech ecosystem.[209] According to a survey by the GSM Association, 92% of adult Nigerian men and 88% of women owned a mobile phone.[210] Using various measures including but not limited to Illegal arrest, taking down of websites, passport seizures, and restricted access to bank accounts, the Nigerian government is punishing citizens for expressing themselves on the internet and working to stifle internet freedom.[211]
Tourism

Tourism in Nigeria centres largely on events, because of the country's ample amount of ethnic groups, but also includes rain forests, savannah, waterfalls, and other natural attractions.[212] Abuja is home to several parks and green areas. The largest, Millennium Park, was designed by architect Manfredi Nicoletti and officially opened in December 2003. After the re-modernization project achieved by the administration of Governor Raji Babatunde Fashola, Lagos is gradually becoming a major tourist destination. Lagos is currently taking steps to become a global city. The 2009 Eyo carnival (a yearly festival originating from Iperu Remo, Ogun State) was a step toward world city status. Currently, Lagos is primarily known as a business-oriented and fast-paced community.[213] Lagos has become an important location for African and black cultural identity.[214]
Lagos has sandy beaches by the Atlantic Ocean, including Elegushi Beach and Alpha Beach. Lagos also has many private beach resorts including Inagbe Grand Beach Resort and several others in the outskirts. Lagos has a variety of hotels ranging from three-star to five-star hotels, with a mixture of local hotels such as Eko Hotels and Suites, Federal Palace Hotel and franchises of multinational chains such as Intercontinental Hotel, Sheraton, and Four Points by Sheraton. Other places of interest include the Tafawa Balewa Square, Festac town, The Nike Art Gallery, Freedom Park, and the Cathedral Church of Christ.
Infrastructure
Due to Nigeria's location in the centre of West Africa, transport plays a major role in the national service sector. The government investments has seen an increase in extensive road repairs and new construction have been carried out gradually as states in particular spend their share of increased government allocations. Representative of these improvements is the Second Niger Bridge near Onitsha, which was largely completed in 2022.[215] A 2017 World Bank report on logistics hubs in Africa placed the country in fourth place, behind Côte d'Ivoire, Senegal, and Sao Tome,[216] but in 2021, Nigeria joined the World Logistics Passport, a private sector group working to increase the effiency of global trade.[217]
Roads
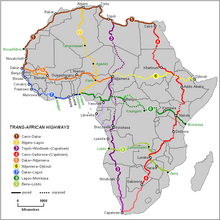

Four trans-African automobile routes pass through Nigeria:
Nigeria has the largest road network in West Africa. It covers about 200,000 km, of which 60,000 km are asphalted. Nigeria's roads and highways handle 90% of all passenger and freight traffic. It contributes N2.4trn ($6.4bn) to GDP in 2020. 35,000 km of the road network fall under the jurisdiction of the federal government. The motorway links of important economic centres such as Lagos-Ibadan, Lagos-Badagry and Enugu-Onitsha have been renovated.[218]
The rest of the road network is a state matter and therefore in very different shape, depending on which state you are in. Economically strong states such as Lagos, Anambra and Rivers receive particularly poor evaluations.[219] Most roads were built in the 1980s and early 1990s. Poor maintenance and inferior materials have worsened the condition of the roads. Travelling is very difficult. Especially during the rainy season, the use of secondary roads is sometimes almost impossible due to potholes.[220] Road bandits often take advantage of this situation for their criminal purposes.[221][222]

Rail transport
Railways have undergone a massive revamping with projects such as the Lagos-Kano Standard Gauge Railway being completed connecting northern cities of Kano, Kaduna, Abuja, Ibadan and Lagos.
Zdroj:https://en.wikipedia.org?pojem=Nigeria
Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších podmienok. Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky použitia.
Abomey
Adjassou-Linguetor
Adya Houn'tò
African-American religion
African diaspora in the Americas
African diaspora religions
African divination
African philosophy
Agassou
Agwé
Aja people
Akan religion
Alfred Burdon Ellis
Anaisa Pye
Androgyny
Angel
Arará religion
Autoritní kontrola
Ayida-Weddo
Ayizan
Azaka-Tonnerre
Baluba mythology
Bandiagara Escarpment
Bantu religion
Baron Criminel
Baron Samedi
Belie Belcan
Benin
Benin City
Bossou Ashadeh
Boum'ba Maza
Bugid Y Aiba
Bushongo mythology
Bwiti
Candomblé
Candomblé Jejé
Captain Debas
Christianity
Clermeil
Colonisation of Africa
Cosmogony
Creator deity
Cuban Vodú
Dahomean religion
Dahomey
Damballa
Dan Petro
Diable Tonnere
Diejuste
Digital object identifier
Dinclinsin
Dingir (časopis)
Dini Ya Msambwa
Dinka religion
Divination
Dogon religion
Doi (identifier)
Dominican Vudú
Domorodá náboženství
Eclecticism
Efik mythology
Erzulie
Ewe language
Ewe people
Fatick
Fetishism
File:Akodessawa Fetish Market 2005.jpg
File:Akodessawa Fetish Market 2008.jpg
File:Akodessawa Fetish Market 2016.jpg
File:Booth at Akodessawa Fetish Market 2008.jpg
File:Booth at Akodessawa Fetish Market 2016.jpg
File:Brooklyn Museum 1989.51.39 Nommo Figure with Raised Arms.jpg
File:COLLECTIE TROPENMUSEUM Houten masker TMnr 6372-2.jpg
File:Preparation of a bat at Akodessawa Fetish Market for Voodoo rituals.jpg
File:Skulls at Akodessawa Fetish Market 2008.jpg
File:Skulls at Akodessawa Fetish Market 2016.jpg
File:Voodo-altar.jpg
File:Voodo-fetischmarkt-Lomé.jpg
File:Voodoo.jpg
Filomez
Fon language
Fon people
Gemeinsame Normdatei
Ghana
Gran Maître
Gris-gris (talisman)
Guédé-Double
Guédé-Linto
Guede
Guede L'Orage
Guede Nibo
Gun language
Haiti
Haitian mythology
Haitian Vodou
Haitian Vodou art
Hausa animism
Help:Authority control
Help:CS1 errors#periodical ignored
Help:IPA
Heviosso
High priestess
Hogon
Hoodoo (folk magic)
Hoodoo (spirituality)
Houngan
Ifá
Ifẹ
Igbo-Ukwu
Intercession of saints
International Standard Book Number
Internet Archive
ISBN (identifier)
Islam
ISO 3166-2:BJ
ISSN (identifier)
Jorubové
Joseph Danger
JSTOR (identifier)
Juju
Kabiye
Kalfu
Kanem–Bornu Empire
Kingdom of Sine
Kongo religion
Kushite religion
L’Aube Nouvelle
Legba
Library of Congress Control Number
LIBRIS
List of African mythological figures
Loa
Lomé
Lotuko mythology
Louisiana Voodoo
Lozi mythology
Lugbara mythology
Maîtresse Délai
Maîtresse Hounon'gon
Maasai mythology
Mademoiselle Charlotte
Maman Brigitte
Mambo (Vodou)
Marassa Jumeaux
Marinette (loa)
Mawu
Mbuti mythology
Mombu
Mounanchou
Mount Hombori
Multiple religious belonging
Národní knihovna České republiky
Národní knihovna Izraele
Nana Buluku
Nasal vowel
Ndut initiation rite
Nebeská cirkev Kristova
New World
Nigeria
Nommo
Nri-Igbo
Nsukka
Odinala
Ogun
Okuyi
Ondřej Havelka (cestovatel)
Ouidah
Oyo, Oyo
Papa Legba
Persecution of traditional African religions
Phallus
Pie (loa)
Point of Sangomar
Polytematický strukturovaný heslář
Portal:Traditional African religion
Portal:Traditional African religions
Porto Novo
Priestly caste
Q177764#identifiers
Q177764#identifiers|Editovat na Wikidatech
Queen mothers in Africa
Religious cosmology
Religious persecution#Persecution of Dogons
Religious persecution#Persecution of Serers
Roman Catholic
S2CID (identifier)
Saltigue
Sangha, Mali
Sangha Ogol Leye
Santería
San religion
Serer religion
Shango
Simbi
Sine River
Sirius#Dogon
Sirius#Serer spirituality
Sobo (deity)
Somb
Soubor:Vodun statue in Benin.jpg
Soubor:Voodo-altar.jpg
Sousson-Pannan
Speciální:Zdroje knih/978-80-87580-24-0
Syncretic religion
Syncretism
Tambor de Mina
Tattaguine
Template:Cite book
Template:Traditional African religions
Template:Voodoo sidebar
Template talk:Traditional African religions
Template talk:Voodoo sidebar
The Journal of Negro History/Volume 7/Number 1/Slave Society on the Southern Plantation
Ti Jean Petro
Ti Jean Quinto
Ti Malice and Bouki
Togo
Tone (linguistics)
Traditional African religions
Traditional African religion and other religions
Trinidadian Vodunu
Tukar
Tumbuka mythology
Vúdú
Veneration of the dead
Veve
Vlajka Beninu
Vodun
Vodun art
Voodoo (disambiguation)
Waaqeffanna
Wayback Machine
West Africa
West African mythology
Wikimedia Commons
Wikipedia:Contents/Portals
Winti
Witchcraft
Witch doctor
Yaboyabo
Yoruba religion
Youga Dogorou
Zangbeto
Zulu traditional religion
Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative
Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších
podmienok.
Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky
použitia.
www.astronomia.sk | www.biologia.sk | www.botanika.sk | www.dejiny.sk | www.economy.sk | www.elektrotechnika.sk | www.estetika.sk | www.farmakologia.sk | www.filozofia.sk | Fyzika | www.futurologia.sk | www.genetika.sk | www.chemia.sk | www.lingvistika.sk | www.politologia.sk | www.psychologia.sk | www.sexuologia.sk | www.sociologia.sk | www.veda.sk I www.zoologia.sk




