
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
Federal Republic of Germany Bundesrepublik Deutschland (German) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1949–1990(g) | |||||||||||||
| Motto: Gott mit uns "God with us" (1949–1962) Einigkeit und Recht und Freiheit "Unity and Justice and Freedom" (since 1962) | |||||||||||||
| Anthem: Ich hab mich ergeben "I have surrendered myself" (unofficial, 1949–1952)[1] | |||||||||||||
 Location of West Germany (dark green) in Europe (dark grey)  Location of West Germany (dark green) in Europe (dark grey)  Territory of West Germany Lands of pre-1937 Germany that were annexed by Poland and the Soviet Union after World War II, claimed by West Germany until 1972 | |||||||||||||
| Capital | Bonn(f) | ||||||||||||
| Largest city | Hamburg | ||||||||||||
| Official languages | German | ||||||||||||
| Religion | See Religion in West Germany | ||||||||||||
| Demonym(s) |
| ||||||||||||
| Government | Federal parliamentary constitutional republic | ||||||||||||
| President | |||||||||||||
• 1949–1959 (first) | Theodor Heuss | ||||||||||||
• 1984–1990 (last) | Richard von Weizsäcker(b) | ||||||||||||
| Chancellor | |||||||||||||
• 1949–1963 (first) | Konrad Adenauer | ||||||||||||
• 1982–1990 (last) | Helmut Kohlc | ||||||||||||
| Legislature | Bicameralism | ||||||||||||
| Bundesrat | |||||||||||||
| Bundestag | |||||||||||||
| Historical era | Cold War | ||||||||||||
| 23 May 1949 | |||||||||||||
| 5 May 1955 | |||||||||||||
• Member of NATO | 9 May 1955 | ||||||||||||
| 1 January 1957 | |||||||||||||
• Creation of EEC | 25 March 1957 | ||||||||||||
• Basic Treaty with the GDR | 21 December 1972 | ||||||||||||
| 18 September 1973 | |||||||||||||
| 12 September 1990 | |||||||||||||
| 3 October 1990(g) | |||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||
• Total | 248,717 km2 (96,030 sq mi) | ||||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||||
• 1950(d) | 50,958,000 | ||||||||||||
• 1970 | 61,001,000 | ||||||||||||
• 1990 | 63,254,000 | ||||||||||||
• Density | 254/km2 (657.9/sq mi) | ||||||||||||
| GDP (PPP) | 1990 estimate | ||||||||||||
• Total | ~$1.0 trillion (4th) | ||||||||||||
| Currency | Deutsche Mark(e) (DM) (DEM) | ||||||||||||
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) | ||||||||||||
• Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) | ||||||||||||
| Calling code | +49 | ||||||||||||
| Internet TLD | .de | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Today part of | Germany | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
West Germany (German: Westdeutschland, pronounced [ˈvɛstˌdɔɪ̯t͡ʃlant] ⓘ) is the colloquial English term used to describe the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG; German: Bundesrepublik Deutschland [ˈbʊndəsʁepuˌbliːk ˈdɔʏtʃlant] ⓘ) from its formation on 23 May 1949 until the reunification of Germany through the accession of East Germany on 3 October 1990. During the Cold War, the western portion of Germany and the associated territory of West Berlin were parts of the Western Bloc. West Germany was formed as a political entity during the Allied occupation of Germany after World War II, established from 12 states formed in the three Allied zones of occupation held by the United States, the United Kingdom, and France. The FRG's provisional capital was the city of Bonn, and the Cold War–era country is retrospectively designated as the Bonn Republic (Bonner Republik).[4]
At the onset of the Cold War, Europe was divided between the Western and Eastern blocs. Germany was divided into the two countries. Initially, West Germany claimed an exclusive mandate for all of Germany, representing itself as the sole democratically reorganised continuation of the 1871–1945 German Reich.[5]
Three southwestern states of West Germany merged to form Baden-Württemberg in 1952, and the Saarland joined West Germany as a state in 1957 after it had been separated as the Saar Protectorate from Allied-occupied Germany by France (the separation had been not fully legal as it had been opposed by the Soviet Union). In addition to the resulting ten states, West Berlin was considered an unofficial de facto eleventh state. While de jure not part of West Germany, for Berlin was under the control of the Allied Control Council (ACC), West Berlin politically aligned itself with West Germany and was directly or indirectly represented in its federal institutions.
The foundation for the influential position held by Germany today was laid during the economic miracle of the 1950s (Wirtschaftswunder), when West Germany rose from the enormous destruction wrought by World War II to become the world's second-largest economy. The first chancellor Konrad Adenauer, who remained in office until 1963, worked for a full alignment with the NATO rather than neutrality, and secured membership in the military alliance. Adenauer was also a proponent of agreements that developed into the present-day European Union. When the G6 was established in 1975, there was no serious debate as to whether West Germany would become a member.
Following the collapse of the Eastern Bloc, symbolised by the opening of the Berlin Wall, both states took action to achieve German reunification. East Germany voted to dissolve and accede to the Federal Republic of Germany in 1990. The five post-war states (Länder) were reconstituted, along with the reunited Berlin, which ended its special status and formed an additional Land. They formally joined the federal republic on 3 October 1990, raising the total number of states from ten to sixteen, and ending the division of Germany. The reunited Germany is the direct continuation of the state previously informally called West Germany and not a new state, as the process was essentially a voluntary act of accession: the Federal Republic of Germany was enlarged to include the additional six states of the German Democratic Republic. The expanded Federal Republic retained West Germany's political culture and continued its existing memberships in international organisations, as well as its Western foreign policy alignment and affiliation to Western alliances such as the United Nations, NATO, OECD, and the European Economic Community.
Naming conventions
Before reunification, Germany was divided between the Bundesrepublik Deutschland (Federal Republic of Germany; commonly known as West Germany) and the Deutsche Demokratische Republik (DDR; German Democratic Republic; commonly known as East Germany). Reunification was achieved by accession (Beitritt) of the German Democratic Republic to the Federal Republic of Germany, so Bundesrepublik Deutschland became the official name of reunified Germany.
In East Germany, the terms Westdeutschland (West Germany) or westdeutsche Bundesrepublik (West German Federal Republic) were preferred during the 1950s and 1960s. This changed under its constitutional amendment in 1974, when the idea of a single German nation was abandoned by East Germany. As a result, it officially considered West Germans and West Berliners as foreigners. The initialism BRD (FRG in English) began to prevail in East German usage in the early 1970s, beginning in the newspaper Neues Deutschland. Other Eastern Bloc nations soon followed suit.
In 1965, the West German Federal Minister of All-German Affairs, Erich Mende, had issued the "Directives for the Appellation of Germany", recommending avoiding the initialism BRD. On 31 May 1974, the heads of West German federal and state governments recommended always using the full name in official publications. From then on, West German sources avoided the abbreviated form, with the exception of left-leaning organizations which embraced it. In November 1979, the federal government informed the Bundestag that the West German public broadcasters ARD and ZDF had agreed to refuse to use the initialism.[6]
The ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 country code of West Germany was DE (for Deutschland, Germany), which has remained the country code of Germany after reunification. ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 codes are the most widely used country codes, and the DE code is notably used as a country identifier, extending the postal code and as the Internet's country code top-level domain .de. The less widely used ISO 3166-1 alpha-3 country code of West Germany was DEU, which has remained the country code of reunified Germany. The now deleted codes for East Germany, on the other hand, were DD in ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 and DDR in ISO 3166-1 alpha-3.
The colloquial term West Germany or its equivalent was used in many languages. Westdeutschland was also a widespread colloquial form used in German-speaking countries, usually without political overtones.
History
| History of Germany |
|---|
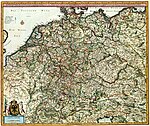 |
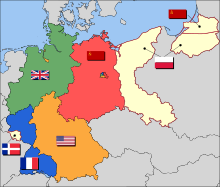
On 4–11 February 1945 leaders from the United States, the United Kingdom, and the Soviet Union held the Yalta Conference where future arrangements regarding post-war Europe and Allied strategy against Japan in the Pacific were negotiated. They agreed that the boundaries of Germany as at 31 December 1937 would be chosen as demarcating German national territory from German-occupied territory; all German annexations after 1937 were automatically null. Subsequently, and into the 1970s, the West German state was to maintain that these 1937 boundaries continued to be 'valid in international law'; although the Allies had already agreed amongst themselves that the territories east of Oder-Neisse line must be transferred to Poland and the Soviet Union in any peace agreement. The conference agreed that post-war Germany, minus these transfers, would be divided into four occupation zones: a French Zone in the far west; a British Zone in the northwest; an American Zone in the south; and a Soviet Zone in the East. Berlin was separately divided into four zones. These divisions were not intended to dismember Germany, only to designate zones of administration.

By the subsequent Potsdam Agreement, the four Allied Powers asserted joint sovereignty over "Germany as a whole", defined as the totality of the territory within the occupation zones. Former German areas east of the rivers Oder and Neisse and outside of 'Germany as a whole' were officially separated from German sovereignty in August 1945 and transferred from Soviet military occupation to Polish and Soviet (in the case of the territory of Kaliningrad) civil administration, their Polish and Soviet status to be confirmed at a final Peace Treaty. Following wartime commitments by the Allies to the governments-in-exile of Czechoslovakia and Poland, the Potsdam Protocols also agreed to the 'orderly and humane' transfer to Germany as a whole of the ethnic German populations in Poland, Czechoslovakia and Hungary. Eight million German expellees and refugees eventually settled in West Germany. Between 1946 and 1949, three of the occupation zones began to merge. First, the British and American zones were combined into the quasi-state of Bizonia. Soon afterwards, the French zone was included into Trizonia. Conversely, the Soviet zone became East Germany. At the same time, new federal states (Länder) were formed in the Allied zones; replacing the geography of pre-Nazi German states such as the Free State of Prussia and the Republic of Baden, which had derived ultimately from former independent German kingdoms and principalities.
In the dominant post-war narrative of West Germany, the Nazi regime was characterised as having been a 'criminal' state,[7] illegal and illegitimate from the outset; while the Weimar Republic was characterised as having been a 'failed' state,[8] whose inherent institutional and constitutional flaws had been exploited by Hitler in his illegal seizure of dictatorial powers. Consequently, following the death of Hitler in 1945 and the subsequent capitulation of the German Armed Forces, the national political, judicial, administrative, and constitutional instruments of both Nazi Germany and the Weimar Republic were understood as entirely defunct, such that a new West Germany could be established in a condition of constitutional nullity.[9] Nevertheless, the new West Germany asserted its fundamental continuity with the 'overall' German state that was held to have embodied the unified German people since the Frankfurt Parliament of 1848, and which from 1871 had been represented within the German Reich; albeit that this overall state had become effectively dormant long before 8 May 1945.
In 1949 with the continuation and aggravation of the Cold War (for example, the Berlin Airlift of 1948–49), the two German states that were originated in the Western Allied and the Soviet Zones became known internationally as West Germany and East Germany. Commonly known in English as East Germany, the former Soviet occupation zone in Germany, eventually became the German Democratic Republic or GDR. In 1990 West Germany and East Germany jointly signed the Treaty on the Final Settlement with Respect to Germany (also known as the "Two-plus-Four Agreement"); by which transitional status of Germany following World War II was definitively ended and the Four Allied powers relinquished their joint residual sovereign authority for Germany as a whole including the area of West Berlin which had officially remained under Allied occupation for the purposes of international and GDR law (a status that the Western countries applied to Berlin as a whole despite the Soviets declaring the end of occupation of East Berlin unilaterally many decades before). The Two-plus-Four Agreement also saw the two parts of Germany confirm their post-war external boundaries as final and irreversible (including the 1945 transfer of former German lands east of the Oder–Neisse line), and the Allied Powers confirmed their consent to German Reunification. From 3 October 1990, after the reformation of the GDR's Länder, the East German states and East Berlin joined the Federal Republic.
NATO membership

With territories and frontiers that coincided largely with the ones of old Middle Ages East Francia and the 19th-century Napoleonic Confederation of the Rhine, the Federal Republic of Germany was founded on 23 May 1949 under the terms of the Bonn–Paris conventions, whereby it obtained "the full authority of a sovereign state" on 5 May 1955 (although "full sovereignty" was not obtained until the Two Plus Four Agreement in 1990).[a] The former occupying Western troops remained on the ground, now as part of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), which West Germany joined on 9 May 1955, promising to rearm itself soon.[11]
West Germany became a focus of the Cold War with its juxtaposition to East Germany, a member of the subsequently founded Warsaw Pact. The former capital, Berlin, had been divided into four sectors, with the Western Allies joining their sectors to form West Berlin, while the Soviets held East Berlin. West Berlin was completely surrounded by East German territory and had suffered a Soviet blockade in 1948–49, which was overcome by the Berlin airlift.

The outbreak of the Korean War in June 1950 led to U.S. calls to rearm West Germany to help defend Western Europe from the perceived Soviet threat. Germany's partners in the European Coal and Steel Community proposed to establish a European Defence Community (EDC), with an integrated army, navy and air force, composed of the armed forces of its member states. The West German military would be subject to complete EDC control, but the other EDC member states (Belgium, France, Italy, Luxembourg and the Netherlands) would cooperate in the EDC while maintaining independent control of their own armed forces.
Though the EDC treaty was signed (May 1952), it never entered into force. France's Gaullists rejected it on the grounds that it threatened national sovereignty, and when the French National Assembly refused to ratify it (August 1954), the treaty died. The French Gaullists and communists had killed the French government's proposal. Then other means had to be found to allow West German rearmament. In response, at the London and Paris Conferences, the Brussels Treaty was modified to include West Germany, and to form the Western European Union (WEU). West Germany was to be permitted to rearm (an idea many Germans rejected), and have full sovereign control of its military, called the Bundeswehr. The WEU, however, would regulate the size of the armed forces permitted to each of its member states. Also, the German constitution prohibited any military action, except in the case of an external attack against Germany or its allies (Bündnisfall). Also, Germans could reject military service on grounds of conscience, and serve for civil purposes instead.[12]
The three Western Allies retained occupation powers in Berlin and certain responsibilities for Germany as a whole. Under the new arrangements, the Allies stationed troops within West Germany for NATO defense, pursuant to stationing and status-of-forces agreements. With the exception of 55,000 French troops, Allied forces were under NATO's joint defense command. (France withdrew from the collective military command structure of NATO in 1966.)
Reforms during the 1960s
Konrad Adenauer was 73 years old when he became chancellor in 1949, and for this reason he was initially reckoned as a caretaker. However, he stayed in power for 14 years. The grand old man of German postwar politics had to be dragged—almost literally—out of office in 1963.[13]
In October 1962 the weekly news magazine Der Spiegel published an analysis of the West German military defence. The conclusion was that there were several weaknesses in the system. Ten days after publication, the offices of Der Spiegel in Hamburg were raided by the police and quantities of documents were seized. Chancellor Adenauer proclaimed in the Bundestag that the article was tantamount to high treason and that the authors would be prosecuted. The editor/owner of the magazine, Rudolf Augstein spent some time in jail before the public outcry over the breaking of laws on freedom of the press became too loud to be ignored. The FDP members of Adenauer's cabinet resigned from the government, demanding the resignation of Franz Josef Strauss, Defence Minister, who had decidedly overstepped his competence during the crisis. Adenauer was still wounded by his brief run for president, and this episode damaged his reputation even further. He announced that he would step down in the fall of 1963. His successor was to be Ludwig Erhard.[14]
In the early 1960s, the rate of economic growth slowed down significantly. In 1962 growth rate was 4.7% and the following year, 2.0%. After a brief recovery, the growth rate slowed again into a recession, with no growth in 1967.
A new coalition was formed to deal with this problem. Erhard stepped down in 1966 and was succeeded by Kurt Georg Kiesinger. He led a grand coalition between West Germany's two largest parties, the CDU/CSU and the Social Democratic Party (SPD). This was important for the introduction of new emergency acts: the grand coalition gave the ruling parties the two-thirds majority of votes required for their ratification. These controversial acts allowed basic constitutional rights such as freedom of movement to be limited in case of a state of emergency.

During the time leading up to the passing of the laws, there was fierce opposition to them, above all by the Free Democratic Party, the rising West German student movement, a group calling itself Notstand der Demokratie ("Democracy in Crisis") and members of the Campaign against Nuclear Armament. A key event in the development of open democratic debate occurred in 1967, when the Shah of Iran, Mohammad Reza Pahlavi, visited West Berlin. Several thousand demonstrators gathered outside the Opera House where he was to attend a special performance. Supporters of the Shah (later known as Jubelperser), armed with staves and bricks attacked the protesters while the police stood by and watched. A demonstration in the centre was being forcibly dispersed when a bystander named Benno Ohnesorg was shot in the head and killed by a plainclothes policeman. (It has now been established that the policeman, Kurras, was a paid spy of the East German security forces.) Protest demonstrations continued, and calls for more active opposition by some groups of students were made, which was declared by the press, especially the tabloid Bild-Zeitung newspaper, as a massive disruption to life in Berlin, in a massive campaign against the protesters. Protests against the US intervention in Vietnam, mingled with anger over the vigour with which demonstrations were repressed led to mounting militance among the students at the universities in Berlin. One of the most prominent campaigners was a young man from East Germany called Rudi Dutschke who also criticised the forms of capitalism that were to be seen in West Berlin. Just before Easter 1968, a young man tried to kill Dutschke as he bicycled to the student union, seriously injuring him. All over West Germany, thousands demonstrated against the Springer newspapers which were seen as the prime cause of the violence against students. Trucks carrying newspapers were set on fire and windows in office buildings broken.[15]
In the wakes of these demonstrations, in which the question of America's role in Vietnam began to play a bigger role, came a desire among the students to find out more about the role of the parent-generation in the Nazi era. The proceedings of the War Crimes Tribunal at Nuremberg had been widely publicised in Germany but until a new generation of teachers, educated with the findings of historical studies, could begin to reveal the truth about the war and the crimes committed in the name of the German people, one courageous attorney, Fritz Bauer patiently gathered evidence on the guards of the Auschwitz concentration camp and about twenty were put on trial in Frankfurt in 1963. Daily newspaper reports and visits by school classes to the proceedings revealed to the German public the nature of the concentration camp system and it became evident that the Shoah was of vastly greater dimensions than the German population had believed. (The term "Holocaust" for the systematic mass-murder of Jews first came into use in 1979, when a 1978 American mini-series with that name was shown on West German television.) The processes set in motion by the Auschwitz trial reverberated decades later.
The calling in question of the actions and policies of government led to a new climate of debate. The issues of emancipation, colonialism, environmentalism and grass roots democracy were discussed at all levels of society. In 1979 the environmental party, the Greens, reached the 5% limit required to obtain parliamentary seats in the Free Hanseatic City of Bremen provincial election. Also of great significance was the steady growth of a feminist movement in which women demonstrated for equal rights. Until 1977, a married woman had to have the permission of her husband if she wanted to take on a job or open a bank account.[16] Further reforms in 1979 to parental rights law gave equal legal rights to the mother and the father, abolishing the legal authority of the father.[17] Parallel to this, a gay movement began to grow in the larger cities, especially in West Berlin, where homosexuality had been widely accepted during the twenties in the Weimar Republic.

Anger over the treatment of demonstrators following the death of Benno Ohnesorg and the attack on Rudi Dutschke, coupled with growing frustration over the lack of success in achieving their aims led to growing militance among students and their supporters. In May 1968, three young people set fire to two department stores in Frankfurt; they were brought to trial and made very clear to the court that they regarded their action as a legitimate act in what they described as the "struggle against imperialism".[15] The student movement began to split into different factions, ranging from the unattached liberals to the Maoists and supporters of direct action in every form—the anarchists. Several groups set as their objective the aim of radicalising the industrial workers and taking an example from activities in Italy of the Red Brigades (Brigate Rosse), many students went to work in the factories, but with little or no success. The most notorious of the underground groups was the Red Army Faction which began by making bank raids to finance their activities and eventually went underground having killed a number of policemen, several bystanders and eventually two prominent West Germans, whom they had taken captive in order to force the release of prisoners sympathetic to their ideas. In the 1990s attacks were still being committed under the name "RAF". The last action took place in 1993 and the group announced it was giving up its activities in 1998. Evidence that the groups had been infiltrated by German Intelligence undercover agents has since emerged, partly through the insistence of the son of one of their prominent victims, the State Counsel Buback.[18]
Willy Brandt
In October 1969 Willy Brandt became chancellor. He maintained West Germany's close alignment with the United States and focused on strengthening European integration in western Europe, while launching the new policy of Ostpolitik aimed at improving relations with Eastern Europe. Brandt was controversial on both the right wing, for his Ostpolitik, and on the left wing, for his support of American policies, including the Vietnam War, and right-wing authoritarian regimes. The Brandt Report became a recognised measure for describing the general North-South divide in world economics and politics between an affluent North and a poor South. Brandt was also known for his fierce anti-communist policies at the domestic level, culminating in the Radikalenerlass (Anti-Radical Decree) in 1972. In 1970, while visiting a memorial to the Warsaw Ghetto Uprising crushed by the Germans, Brandt unexpectedly knelt and meditated in silence, a moment remembered as the Kniefall von Warschau.
Brandt resigned as chancellor in 1974, after Günter Guillaume, one of his closest aides, was exposed as an agent of the Stasi, the East German secret service.
Helmut Schmidt
Finance Minister Helmut Schmidt (SPD) formed a coalition and he served as Chancellor from 1974 to 1982. Hans-Dietrich Genscher, a leading FDP official, became Vice Chancellor and Foreign Minister. Schmidt, a strong supporter of the European Community (EC) and the Atlantic alliance, emphasized his commitment to "the political unification of Europe in partnership with the USA".[19] Mounting external problems forced Schmidt to concentrate on foreign policy and limited the domestic reforms that he could carry out. The USSR upgraded its intermediate-range missiles, which Schmidt complained was an unacceptable threat to the balance of nuclear power, because it increased the likelihood of political coercion and required a western response. NATO respond in the form of its twin-track policy. The domestic reverberations were serious inside the SPD, and undermined its coalition with the FDP.[20] One of his major successes, in collaboration with French President Valéry Giscard d'Estaing, was the launching of the European Monetary System (EMS) in April 1978.[21]
Helmut Kohl
In October 1982 the SPD–FDP coalition fell apart when the FDP joined forces with the CDU/CSU to elect CDU Chairman Helmut Kohl as Chancellor in a constructive vote of no confidence. Following national elections in March 1983, Kohl emerged in firm control of both the government and the CDU. The CDU/CSU fell just short of an absolute majority, due to the entry into the Bundestag of the Greens, who received 5.6% of the vote.
In January 1987 the Kohl–Genscher government was returned to office, but the FDP and the Greens gained at the expense of the larger parties. Kohl's CDU and its Bavarian sister party, the CSU, slipped from 48.8% of the vote in 1983 to 44.3%. The SPD fell to 37%; long-time SPD Chairman Brandt subsequently resigned in April 1987 and was succeeded by Hans-Jochen Vogel. The FDP's share rose from 7% to 9.1%, its best showing since 1980. The Greens' share rose to 8.3% from their 1983 share of 5.6%.
Reunification
With the collapse of eastern bloc in 1989, symbolised by the opening of the Berlin Wall, there was a rapid move towards German reunification; and a final settlement of the post-war special status of Germany. Following democratic elections, East Germany declared its accession to the Federal Republic subject to the terms of the Unification Treaty between the two states; and then both West Germany and East Germany radically amended their respective constitutions in accordance with that Treaty's provisions. East Germany then dissolved itself, and its five post-war states (Länder) were reconstituted, along with the reunited Berlin which ended its special status and formed an additional Land. They formally joined the Federal Republic on 3 October 1990, raising the number of states from 10 to 16, ending the division of Germany. The expanded Federal Republic retained West Germany's political culture and continued its existing memberships in international organisations, as well as its Western foreign policy alignment and affiliation to Western alliances like NATO and the European Union.
The official German reunification ceremony on 3 October 1990 was held at the Reichstag building, including Chancellor Helmut Kohl, President Richard von Weizsäcker, former Chancellor Willy Brandt and many others. One day later, the parliament of the united Germany would assemble in an act of symbolism in the Reichstag building.
However, at that time, the role of Berlin had not yet been decided upon. Only after a fierce debate, considered by many as one of the most memorable sessions of parliament, the Bundestag concluded on 20 June 1991, with quite a slim majority, that both government and parliament should move to Berlin from Bonn.
Economic miracle
The West German Wirtschaftswunder ("economic miracle", coined by The Times) began in 1950. This improvement was sustained by the currency reform of 1948 which replaced the Reichsmark with the Deutsche Mark and halted rampant inflation. The Allied dismantling of the West German coal and steel industry finally ended in 1950.

As demand for consumer goods increased after World War II, the resulting shortage helped overcome lingering resistance to the purchase of German products. At the time Germany had a large pool of skilled and cheap labour, partly as a result of the flight and expulsion of Germans from Central and Eastern Europe, which affected up to 16.5 million Germans. This helped Germany to more than double the value of its exports during the war. Apart from these factors, hard work and long hours at full capacity among the population and in the late 1950s and 1960s extra labour supplied by thousands of Gastarbeiter ("guest workers") provided a vital base for the economic upturn. This would have implications later on for successive German governments as they tried to assimilate this group of workers.[22]
With the dropping of Allied reparations, the freeing of German intellectual property and the impact of the Marshall Plan stimulus, West Germany developed one of the strongest economies in the world, almost as strong as before the Second World War. The East German economy showed a certain growth, but not as much as in West Germany, partly because of continued reparations to the USSR.[23]
In 1952, West Germany became part of the European Coal and Steel Community, which would later evolve into the European Union. On 5 May 1955 West Germany was declared to have the "authority of a sovereign state".[a] The British, French and U.S. militaries remained in the country, just as the Soviet Army remained in East Germany. Four days after obtaining the "authority of a sovereign state" in 1955, West Germany joined NATO. The UK and the USA retained an especially strong presence in West Germany, acting as a deterrent in case of a Soviet invasion. In 1976 West Germany became one of the founding nations of the Group of Six (G6). In 1973, West Germany—home to roughly 1.26% of the world's population—featured the world's fourth largest GDP of 944 billion (5.9% of the world total). In 1987 the FRG held a 7.4% share of total world production.
Demographics
Population and vital statistics
Total population of West Germany from 1950 to 1990, as collected by the Statistisches Bundesamt.[3]
| Average population (x 1000)[25] | Live births | Deaths | Natural change | Crude birth rate (per 1000) | Crude death rate (per 1000) | Natural change (per 1000) | TFR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1946 | 732 998 | 588 331 | 144 667 | 15.9 | 12.7 | 3.2 | 1.89 | |
| 1947 | 781 421 | 574 628 | 206 793 | 16.6 | 12.2 | 4.4 | 2.01 | |
| 1948 | 806 074 | 515 092 | 290 982 | 16.7 | 10.6 | 6.0 | 2.07 | |
| 1949 | 832 803 | 517 194 | 315 609 | 16.9 | 10.5 | 6.4 | 2.14 | |
| 1950 | 50 958 | 812 835 | 528 747 | 284 088 | 16.3 | 10.6 | 5.7 | 2.10 |
| 1951 | 51 435 | 795 608 | 543 897 | 251 711 | 15.7 | 10.8 | 4.9 | 2.06 |
| 1952 | 51 864 | 799 080 | 545 963 | 253 117 | 15.7 | 10.7 | 5.0 | 2.08 |
| 1953 | 52 454 | 796 096 | 578 027 | 218 069 | 15.5 | 11.3 | 4.2 | 2.07 |
| 1954 | 52 943 | 816 028 | 555 459 | 260 569 | 15.7 | 10.7 | 5.0 | 2.12 |
| 1955 | 53 518 | 820 128 | 581 872 | 238 256 | 15.7 | 11.1 | 4.6 | 2.11 |
| 1956 | 53 340 | 855 887 | 599 413 | 256 474 | 16.1 | 11.3 | 4.8 | 2.19 |
| 1957 | 54 064 | 892 228 | 615 016 | 277 212 | 16.6 | 11.5 | 5.2 | 2.28 |
| 1958 | 54 719 | 904 465 | 597 305 | 307 160 | 16.7 | 11.0 | 5.7 | 2.29 |
| 1959 | 55 257 | 951 942 | 605 504 | 346 438 | 17.3 | 11.0 | 6.3 | 2.34 |
| 1960 | 55 958 | 968 629 | 642 962 | 325 667 | 17.4 | 11.6 | 5.9 | 2.37 |
| 1961 | 56 589 | 1 012 687 | 627 561 | 385 126 | 18.0 | 11.2 | 6.9 | 2.47 |
| 1962 | 57 247 | 1 018 552 | 644 819 | 373 733 | 17.9 | 11.3 | 6.6 | 2.45 |
| 1963 | 57 865 | 1 054 123 | 673 069 | 381 054 | 18.4 | 11.7 | 6.7 | 2.52 |
| 1964 | 58 587 | 1 065 437 | 644 128 | 421 309 | 18.3 | 11.1 | 7.2 | 2.55 |
| 1965 | 59 297 | 1 044 328 | 677 628 | 366 700 | 17.8 | 11.6 | 6.3 | 2.51 |
| 1966 | 59 793 | 1 050 345 | 686 321 | 364 024 | 17.8 | 11.6 | 6.2 | 2.54 |
| 1967 | Zdroj:https://en.wikipedia.org?pojem=West_Germany


