
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
| Twenty-third census of the United States | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
 Seal of the U.S. Census Bureau | ||
 2010 U.S. census logo | ||
| General information | ||
| Country | United States | |
| Results | ||
| Total population | 308,745,538 ( | |
| Most populous | California (37,253,956) | |
| Least populous | Wyoming (563,826) | |
The 2010 United States census was the 23rd United States census. National Census Day, the reference day used for the census, was April 1, 2010.[1] The census was taken via mail-in citizen self-reporting, with enumerators serving to spot-check randomly selected neighborhoods and communities. As part of a drive to increase the count's accuracy, 635,000 temporary enumerators were hired.[2][3] The population of the United States was counted as 308,745,538,[4] a 9.7% increase from the 2000 United States Census. This was the first census in which all states recorded a population of over 500,000 people as well as the first in which all 100 largest cities recorded populations of over 200,000.
It was the first census since 1930 that California did not record the largest population growth in absolute number. Texas surpassed California's growth by 4.3 million to 3.4 million.
Introduction
As required by the United States Constitution, the U.S. Census has been conducted every 10 years since 1790. The 2000 U.S. Census was the previous census completed. Participation in the U.S. Census is required by law of people living in the United States in Title 13 of the United States Code.[5]
On January 25, 2010, Census Bureau Director Robert Groves personally inaugurated the 2010 census enumeration by counting World War II veteran Clifton Jackson, a resident of Noorvik, Alaska.[6] More than 120 million census forms were delivered by the U.S. Post Office beginning March 15, 2010.[7] The number of forms mailed out or hand-delivered by the Census Bureau was approximately 134 million on April 1, 2010.[8] Although the questionnaire used April 1, 2010, as the reference date as to where a person was living, an insert dated March 15, 2010, included the following printed in bold type: "Please complete and mail back the enclosed census form today."
The 2010 census national mail participation rate was 74%.[9] From April through July 2010, census takers visited households that didn't return a form, an operation called "non-response follow-up" (NRFU).
In December 2010, the U.S. Census Bureau delivered population information to the U.S. president for apportionment, and later in March 2011, complete redistricting data was delivered to states.[1]
Personally identifiable information will be available in 2082.[10]
Major changes
The Census Bureau did not use a long form for the 2010 census.[11] In several previous censuses, one in six households received this long form, which asked for detailed social and economic information. The 2010 census used only a short form asking ten basic questions:[11]
- How many people were living or staying in this house, apartment, or mobile home on April 1, 2010?
- Were there any additional people staying here on April 1, 2010, that you did not include in Question 1? Mark all that apply: (checkboxes for: children; relatives; non-relatives; people staying temporarily; none)
- Is this house, apartment, or mobile home –
- What is your telephone number?
- What is Person 1's name? (last, first)
- What is Person 1's sex? (male, female)
- What is Person 1's age and Person 1's date of birth?
- Is Person 1 of Hispanic, Latino, or Spanish origin? (checkboxes for: "No", and several for "Yes" which specify groups of countries)
- What is Person 1's race? (checkboxes for 14 including "other". One possibility was "Black, African Am., or Negro")
- Does Person 1 sometimes live or stay somewhere else? (checkboxes for "No", and several locations for "Yes")
The form included space to repeat some or all of these questions for up to twelve residents total.
In contrast to the 2000 census, an Internet response option was not offered, nor was the form available for download.[11][12]
Detailed socioeconomic information collected during past censuses will continue to be collected through the American Community Survey.[12] The survey provides data about communities in the United States on a 1-year or 3-year cycle, depending on the size of the community, rather than once every 10 years. A small percentage of the population on a rotating basis will receive the survey each year, and no household will receive it more than once every five years.[13]
In June 2009, the U.S. Census Bureau announced that it would count same-sex married couples. However, the final form did not contain a separate "same-sex married couple" option. When noting the relationship between household members, same-sex couples who are married could mark their spouses as being "Husband or wife", the same response given by opposite-sex married couples. An "unmarried partner" option was available for couples (whether same-sex or opposite-sex) who were not married.[14]
The Census 2010 Language Program was significantly expanded. Language assistance in 49 languages in the 2000 Census was increased to 59 languages in Census 2000. In addition to English, Census questionnaire was available in five non-English languages: Spanish, Chinese (simplified), Korean, Vietnamese, and Russian.[15][16]
Cost
The 2010 census cost $13 billion, approximately $42 per capita; by comparison, the 2010 census per-capita cost for China was about US$1 and for India was US$0.40.[17] Operational costs were $5.4 billion, significantly under the $7 billion budget.[18] In December 2010 the Government Accountability Office (GAO) noted that the cost of conducting the census has approximately doubled each decade since 1970.[17] In a detailed 2004 report to Congress, the GAO called on the Census Bureau to address cost and design issues, and at that time, had estimated the 2010 census cost to be $11 billion.[19]
In August 2010, Commerce Secretary Gary Locke announced that the census operational costs came in significantly under budget; of an almost $7 billion operational budget:[18]
- $650 million was saved in the budget for the door-to-door questioning (NRFU) phase because 72% of households returned mailed questionnaires;
- $150 million was saved because of lower-than-planned costs in areas including Alaska and tribal lands; and
- the $800 million emergency fund was not needed.
Locke credited the management practices of Census Bureau director Robert Groves, citing in particular the decision to buy additional advertising in locations where responses lagged, which improved the overall response rate. The agency also has begun to rely more on questioning neighbors or other reliable third parties when a person could not be immediately reached at home, which reduced the cost of follow-up visits. Census data for about 22% of U.S. households that did not reply by mail were based on such outside interviews, Groves said.[18]
Technology
In 2005, Lockheed Martin won a six-year, $500 million contract to capture and standardize data for the census. The contract included systems, facilities, and staffing.[20] The final value of that contract was in excess of one billion dollars.[21] Information technology was about a quarter of the projected $11.3 billion cost of the decennial census.[22] The use of high-speed document scanning technology, such as ImageTrac scanners developed by IBML, helped Lockheed Martin complete the project on schedule and under budget.[23]
Due to the rise in social media and cell-phone usage in the U.S., the Census Bureau used research gathered through a cell-phone study in order to target media and adds to populations that were nonrespondents and promote census participation. This study also helped gauge the mindset of those who fail to respond, trying to figure out why.[24]
This was the first census to use hand-held computing devices with GPS capability, although they were only used for the address canvassing operation. Enumerators (information gatherers) that had operational problems with the device understandably made negative reports. During the 2009 Senate confirmation hearings for Robert Groves, President Obama's Census Director appointee, there was much mention of contracting problems but very little criticism of the units themselves.[25] The Census Bureau chose to conduct the primary operation, Non-Response Follow Up (NRFU), without using the handheld computing devices.[26][27]
Marketing and undercounts
Due to allegations surrounding previous censuses that poor people and non-whites are routinely undercounted, for the 2010 census, the Census Bureau tried to avoid that bias by enlisting tens of thousands of intermediaries, such as churches, charities and firms, to explain to people the importance of being counted.[8]
There was a penalty of $100 for not completing some or all of the 2010 U.S. Census. Census Bureau director Robert Grove, however, wrote "the Census Bureau has rarely prosecuted failure to respond. While the rationale for the mandatory nature of the census still applies today, our message for the 2010 Census is about the common good benefits of participation".[28] The fine for non-participation is much lower than that for reporting false information. In 2010, that penalty was $500.[29]
There was a one hundred dollar fine for not answering part or all of the 2010 U.S. census. The census director Robert Grove wrote in 2010 "the Census Bureau has rarely prosecuted failure to respond. While the rationale for the mandatory nature of the census still applies today, our message for the 2010 Census is about the common good benefits of participation."The Association of Community Organizations for Reform Now (ACORN) was given a contract to help publicize the importance of the census count and to encourage individuals to fill out their forms. In September 2009, after controversial undercover videos showing four ACORN staffers giving tax advice to a man and a woman posing as a prostitute, the bureau canceled ACORN's contract.[30] Various American celebrities, including Demi Lovato and Eva Longoria,[31] were used in public service announcements targeting younger people to fill out census forms. Wilmer Valderrama and Rosario Dawson have helped spread census awareness among young Hispanics, a historically low participating ethnicity in the U.S. census.[32] Rapper Ludacris also participated in efforts to spread awareness of the 2010 census.[33]
The Census Bureau hired about 635,000 people to find those U.S. residents who had not returned their forms by mail; as of May 28, 2010, 113 census workers had been victims of crime while conducting the census.[3][needs update] As of June 29, there were 436 incidents involving assaults or threats against enumerators, more than double the 181 incidents in 2000; one enumerator, attempting to hand-deliver the census forms to a Hawaii County police officer, was arrested for trespassing – the officer's fellow policemen made the arrest.[2]
Some political conservatives and libertarians questioned the validity of the questions and even encouraged people to refuse to answer questions for privacy and constitutional reasons.[34] Michele Bachmann, a former conservative Republican Representative from Minnesota, stated that she would not fill out her census form other than to indicate the number of people living in her household because "the Constitution doesn't require any information beyond that."[35] Former Republican representative and Libertarian presidential candidate Bob Barr stated that the census has become too intrusive, going beyond the mere enumeration (i.e., count) intended by the framers of the U.S. Constitution.[36] According to political commentator Juan Williams, "Census participation rates have been declining since 1970, and if conservatives don't participate, doubts about its accuracy and credibility may become fatal."[34]
As a result, the Census Bureau undertook an unprecedented advertising campaign targeted at encouraging white political conservatives to fill out their forms, in the hope of avoiding an undercount of this group. The 2010 U.S. census was the primary sponsor at NASCAR races in Atlanta, Bristol, and Martinsville, and sponsored the No. 16 Ford Fusion driven by Greg Biffle for part of the season, because of a marketing survey that indicated most NASCAR fans lean politically conservative.[34] It also ran an advertisement during the 2010 Super Bowl, and hired singer Marie Osmond, who is thought to have many conservative fans, to publicize the census.[34]
Reapportionment
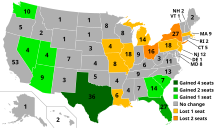

The results of the 2010 census determined the number of seats that each state received in the United States House of Representatives starting with the 2012 elections. Consequently, this affected the number of votes each state had in the Electoral College for the 2012 presidential election.
Because of population changes, eighteen states had changes in their number of seats. Eight states gained at least one seat, and ten states lost at least one seat. The final result involved 12 seats being switched.[37]
| Gained four seats | Gained two seats | Gained one seat | Lost one seat | Lost two seats |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Texas | Florida | Arizona Georgia Nevada South Carolina Utah Washington |
Illinois Iowa Louisiana Massachusetts Michigan Missouri New Jersey Pennsylvania |
New York Ohio |
Controversies
Some objected to the counting of persons who are in the United States illegally.[38][39] Senators David Vitter (R-LA) and Bob Bennett (R-UT) tried unsuccessfully to add questions on immigration status to the census form.[8]
Organizations such as the Prison Policy Initiative argued that the census counts of incarcerated men and women as residents of prisons, rather than of their pre-incarceration addresses, skewed political clout and resulted in misleading demographic and population data.[40] Many residents of prisons counted on the 2010 census were those who identify as Black and Hispanic. This could lead to the loss of resources for underserved minority communities.[41]
The term "Negro" was used in the questionnaire as one of the options for African Americans (Question 9. What is Person (number)'s race? ... Black, African Am., or Negro) as a choice to describe one's race. Census Bureau spokesman Jack Martin explained that "many older African-Americans identified themselves that way, and many still do. Those who identify themselves as Negroes need to be included."[42][43] The word was also used in the 2000 census, with over 56,000 people identifying themselves as "Negro".[44] In response to complaints over the word's inclusion on the 2010 census, the Census Bureau announced in 2013 that it would stop using "Negro" going forward, with the 2014 American Community Survey census form being the first without the word.[45]
Perhaps not a controversy, but yet, another challenge for the Census Bureau in 2010 was that almost three million people selected that their race was Black and in combination with another race. This reflects societal changes in the first decade of the 21st century as hospitals had begun recognizing multiple races at the birth of a child. Thus, when parents are reporting their child's race on the census, they selected multiple races.[46]
The 2010 census contained ten questions about age, gender, ethnicity, home ownership, and household relationships. Six of the ten questions were to be answered for each individual in the household. Federal law has provisions for fining those who refuse to complete the census form.[47]
Detroit Mayor Dave Bing held a press conference on March 22, 2011, to announce that the city would challenge its census results.[48] The challenge, being led by the city's planning department, cited an inconsistency as an example showing a downtown census tract which lost only 60 housing units, but 1,400 people, implying that a downtown jail or dormitory was missed in canvassing.[49]
NYC Mayor Michael Bloomberg held a conference on March 27, 2011, to announce that the city would also challenge his city's census results, specifically the apparent undercounting in the boroughs of Queens and Brooklyn.[50] Bloomberg said that the numbers for Queens and Brooklyn, the two most populous boroughs, are implausible.[51] According to the census, they grew by only 0.1% and 1.6%, respectively, while the other boroughs grew by between 3% and 5%. He also stated that the census showed improbably high numbers of vacant housing in vital neighborhoods such as Jackson Heights, Queens.
The District of Columbia announced in August 2011 that it would also challenge its census results. The Mayor's Office claimed that the detailed information provided for 549 census blocks is "nonsensical", listing examples of census data that show housing units located in the middle of a street that does not actually exist. However, officials do not believe the city's total population will drastically change as a result of the challenge.[52]
State rankings
The state with the highest percentage rate of growth was Nevada, while the state with the largest population increase was Texas.[53] Michigan, the 8th largest by population, was the only state to lose population (although Puerto Rico, a U.S. territory, lost population as well), and the District of Columbia saw its first gain since the 1950s.[54] The resident populations listed below do not include people living overseas. For Congressional apportionment, the sum of a state's resident population and its population of military personnel and federal contractors living overseas (but not other citizens overseas, such as missionaries or expatriate workers) is used.[55]

| Rank | State | Population as of 2010 census |
Population as of 2000 census[56] |
Change | Percent change |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 37,253,956 | 33,871,648 | 3,382,308 |
10.0% | |
| 2 | 25,145,561 | 20,851,820 | 4,293,741 |
20.6% | |
| 3 | 19,378,102 | 18,976,457 | 401,645 |
2.1% | |
| 4 | 18,801,310 | 15,982,378 | 2,818,932 |
17.6% | |
| 5 | 12,830,632 | 12,419,293 | 411,339 |
3.3% | |
| 6 | 12,702,379 | 12,281,054 | 421,325 |
3.4% | |
| 7 | 11,536,504 | 11,353,140 | 183,364 |
1.6% | |
| 8 | 9,883,640 | 9,938,444 | −54,804 |
−0.6% | |
| 9 | 9,687,653 | 8,186,453 | 1,501,200 |
18.3% | |
| 10 | 9,535,483 | 8,049,313 | 1,486,170 |
18.5% | |
| 11 | 8,791,894 | 8,414,350 | 377,544 |
4.5% | |
| 12 | 8,001,024 | 7,078,515 | 922,509 |
13.0% | |
| 13 | 6,724,540 | 5,894,121 | 830,419 |
14.1% | |
| 14 | 6,547,629 | 6,349,097 | 198,532 |
3.1% | |
| 15 | 6,483,802 | 6,080,485 | 403,317 |
6.6% | |
| 16 | 6,392,017 | 5,130,632 | 1,261,385 |
24.6% | |
| 17 | 6,346,105 | 5,689,283 | 656,822 |
11.5% | |
| 18 | 5,988,927 | 5,595,211 | 393,716 |
7.0% | |
| 19 | 5,773,552 | 5,296,486 | 477,066 |
9.0% | |
| 20 | 5,686,986 | 5,363,675 | 323,311 |
6.0% | |
| 21 | 5,303,925 | 4,919,479 | 384,446 |
7.8% | |
| 22 | 5,029,196 | 4,301,261 | 727,935 |
16.9% | |
| 23 | 4,779,736 | 4,447,100 | 332,636 |
7.5% | |
| 24 | 4,625,364 | 4,012,012 | 613,352 |
15.3% | |
| 25 | 4,533,372 | 4,468,976 | 64,396 |
1.4% | |
| 26 | 4,339,367 | 4,041,769 | 297,598 |
7.4% | |
| 27 | 3,831,074 | 3,421,399 | 409,675 |
12.0% | |
| 28 | 3,751,351 | 3,450,654 | 300,697 |
8.7% | |
| 29 | 3,574,097 | 3,405,565 | 168,532 |
4.9% | |
| 30 | 3,046,355 | 2,926,324 | 120,031 |
4.1% | |
| 31 | 2,967,297 | 2,844,658 | 122,639 |
4.3% | |
| 32 | 2,915,918 | 2,673,400 | 242,518 |
9.1% | |
| 33 | 2,853,118 | 2,688,418 | 164,700 |
6.1% | |
| 34 | 2,763,885 | 2,233,169 | 530,716 |
23.8% | |
| 35 | 2,700,551 | 1,998,257 | 702,294 |
35.1% | |
| 36 | 2,059,179 | 1,819,046 | 240,133 |
13.2% | |
| 37 | 1,852,994 | 1,808,344 | 44,650 |
2.5% | |
| 38 | 1,826,341 | 1,711,263 | 115,078 |
6.7% | |
| 39 | 1,567,582 | 1,293,953 | 273,629 |
21.1% | |
| 40 | 1,360,301 | 1,211,537 | 148,764 |
12.3% | |
| 41 | 1,328,361 | 1,274,923 | 53,438 |
4.2% | |
| 42 | 1,316,470 | 1,235,786 | 80,684 |
6.5% | |
| 43 | 1,052,567 | 1,048,319 | 4,248 |
0.4% | |
| 44 | Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších podmienok. Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky použitia.
Analytika
Antropológia Aplikované vedy Bibliometria Dejiny vedy Encyklopédie Filozofia vedy Forenzné vedy Humanitné vedy Knižničná veda Kryogenika Kryptológia Kulturológia Literárna veda Medzidisciplinárne oblasti Metódy kvantitatívnej analýzy Metavedy Metodika Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative
Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších
podmienok. www.astronomia.sk | www.biologia.sk | www.botanika.sk | www.dejiny.sk | www.economy.sk | www.elektrotechnika.sk | www.estetika.sk | www.farmakologia.sk | www.filozofia.sk | Fyzika | www.futurologia.sk | www.genetika.sk | www.chemia.sk | www.lingvistika.sk | www.politologia.sk | www.psychologia.sk | www.sexuologia.sk | www.sociologia.sk | www.veda.sk I www.zoologia.sk |
