
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
This article may contain an excessive amount of intricate detail that may interest only a particular audience. (May 2022) |
Marketing communications (MC, marcom(s), marcomm(s) or just simply communications) refers to the use of different marketing channels and tools in combination.[1] Marketing communication channels focus on how businesses communicate a message to its desired market, or the market in general. It is also in charge of the internal communications of the organization. Marketing communication tools include advertising, personal selling, direct marketing, sponsorship, communication, public relations, social media, customer journey and promotion.[1]
MC are made up of the marketing mix which is made up of the 4 Ps: Price, Promotion, Place and Product, for a business selling goods, and made up of 7 Ps: Price, Promotion, Place, Product, People, Physical evidence and Process, for a service-based business.[2]
Overview
This overview section duplicates the intended purpose of the article's lead section, which should provide an overview of the subject. (May 2023) |
Marketing communications include advertising, promotions, sales, branding, campaigns, events, and online promotions.[3] The process allows the public to know or understand a brand and get a clear idea of what the brand has to offer. Brand awareness is the first stage, then brand preference over its competitors is the desired outcome. With growing technology and techniques, the direct participation of customers is made. This is done by including their ideas and creations, in product development and brand promotion. Successful branding involves targeting audiences who appreciate the organization's mission and vision, business values and marketing program.
Advertising is a small but important part of marketing communications; the marketing communications mix is a set of tools that can be used to deliver a clear and consistent message to target audiences. It is also commonly called the promotional mix. Crosier (1990) states that all terms have the same meaning in the context of the 4ps: product, price, place and promotion.[1] Price can send a message to the target audience. For example, comparing a $50 bag to a $10 bag, the former may be viewed as a luxury or more durable item. The higher goal of advertising is to establish a relationship between the brand and its target market.
The marketing plan identifies key opportunities, threats, weaknesses, and strengths, sets objectives, and develops an action plan to achieve marketing goals. Each section of the 4P's sets its own objective; for instance, the pricing objective might be to increase sales in a certain geographical market by pricing their own product or service lower than their competitors. This creates a significant change in the market because more people in the target market would aim to do business with your organization than with your competitors because pricing is one of the most significant aspects of marketing that can change the whole market positively or negatively.
Definitions
- Communication barriers: Communication barriers are factors that hinder the objectives of marketing communication. Major communication barriers are Noise and clutter, consumer apathy, brand parity, and weak information design, creative ideas, or strategies. Noise is an unrelated sensory stimulus that distracts a consumer from the marketing message (for example, people talking nearby making it hard to hear a radio advertisement). Clutter is the high number and concentration of advertisements presented to a consumer at any time. As attention cannot be divided, there is a limit to how much can be taken in and processed, which means that strong marketing communication needs to stand out from the clutter and be heard above the noise.[4]
- "Consumer apathy" is the tendency of a consumer to avoid marketing communications. The consumer may not be interested, or consider themselves "in the market," and as such attempt to shut out the irrelevant marketing stimuli; this is known as selective attention. Alternatively, a consumer may be "in the market," yet not be aware of the brand or product's existence or prevalence. Consumers tend to purchase familiar brands, and will not be inspired to investigate alternatives. One approach marketers use to overcome apathy is to create incentives, such as competitive pricing or loyalty rewards.[4]
- Brand parity means a brand is not significantly different from its competition. Without a distinct value proposition, consumers do not develop brand preference or associations and instead purchase purely based on price.[5] This is not ideal, as effective marketing communication increases brand equity. One important objective of marketing communications is to develop a strong, unique brand identity that allows the brand to be positioned separately from its competition.
- Marketing mix is the most important part of marketing strategy, which is "the framework to manage marketing and incorporate it within a business context[6]".
- Marketing strategy: how a business achieves its marketing objectives. The initial step to achieve a marketing strategy is to identify the market target and build up a business plan.[6]
- Marketing Research does not involve a proven order of steps resulting in an ultimate inference. It is a repeated process that requires a broader outlook. At times, projects may require going in-depth and changing the entire process. Let us take the example of Nokia when they were preparing themselves to compete against the smartphone market. In November 2011, they decided on coming up with something new, especially targeting the youth, who were switching over to the Finnish Smartphones. This switchover required bringing several changes, starting from brand fundamentals to training in-house teams, from targeting to product advancement, and from hiring talented marketing people to new innovations.[7]
Communications
Communications is one important aspect of the marketing mix.[8] Marketing communication is often the largest component of communication within a company, which may be to present company values, objectives or specific products and services to investors, customers or the general public. In the 21st century, communications objectives focus on more customized messages, targeting customer groups or individuals to create high responses and greater brand interaction.[8]
As business becomes increasingly global with greater access to the Internet, mobile phones and social media, new challenges exist to inform people in targeted foreign markets. Shifts in the global economy and access to new markets lead also to greater demands for product shipping and associated services. To be effective, marketing communications must be tailored to its channels. For example: public relations messaging set is customized to its target audience which is media and the industry, there the messaging will be about data proofed achievements, whereas in social media messaging content is more friendly and about the brand soft qualities. communication strategies must converge with marketing objectives while also accounting for local languages, dialects and cultural norms.
External communications might involve market research questionnaires, office website, guarantees, company annual report and presentations for investors. Internal communication can be the marketing materials, price list, product catalogs, sales presentations and management communications. On the other hand, each market demands different types of communications. For example, the industrial market demands a more personal communication but the consumer market demands non-personal communication.[8]
Types of communication
There are also 4 different fundamental types of communication.
- One-to-many: this kind of communication is the most original communication. It is "generated from a single broadcast point and then available over airwaves or in mass print runs[8]". This type of communication is usually adapted to news distribution that is not specific, not even interactive. Such as in an urgent notice play over airwave from broadcast in an industry, it is helpful for the general announcement.
- Many-to-one: many-to-one is usually connected to the one-to-many communication.[8] For example, a reply button in your email box, a prepaid number bought from Spark. All the communication techniques proceeded to the public with bi-directional communication from mass communications.[8]
- One-to-one: this is the most intensive and interactive communication at a one-to-one level.[8] There are so many examples like a sales presentation; a negotiation in the market or direct delivery is based on one-to-one communication. Most of this communication is face-to-face. But with the development of the Internet, email and online shopping are taking the chance to be face to face with people. Which provided the chance for sellers and buyers to talk more directly. Another important is instant message 'chat' channels like Wechat and Facebook, which are becoming extremely popular in business.[8]
- Many-to-many: on the background of the highly developed Internet, the many-to-many communication has been growing up such as online chat rooms, 'blogging' websites.[8] The many-to-many communication stands for the participants being able to exchange their ideas and experiences.
One-to-one is more immediate, while the many-to-many channels tend to be less urgent but with greater longevity.[8]
Psychology of communication
One of the primary goals of marketing communication is to persuade consumers or businesses, by either changing their perception of a brand, product, or service or persuading them to purchase (or feel motivated / tempted to purchase) a product or service. The "Elaboration Likelihood Model" is used to demonstrate how persuasion occurs. When a marketing communication message is sent out, first it must be acknowledged and attended by the receiver. By giving their attention to marketing communication, consumers will begin to process and comprehend the message. There are two routes to persuasion: Central and peripheral. Central route processing is used in high-involvement purchase decisions. These are infrequent, high-risk purchases, usually involving large amounts of money and a significant amount of time (for example, purchasing a house or car). Because these purchase decisions are high risk, a large cognitive effort is expended in order to rationally select the most logical and valuable option available. In these marketing messages, information about the product or service itself is most valuable. Peripheral route processing is employed in low involvement purchase decisions. These are frequent, low-risk purchases, generally of a low or medium cost in which choices are made more on affective (or emotion-based) values rather than cognitive (or rational) values. Because of this, marketing messages will employ more storytelling and imagery, focusing on how the product or service makes one feel, and the associations it has, rather than the attributes and specifications it possesses.
Linguistic devices and modes of persuasion
A big part of marketing is how companies communicate, whether that be with clients and potential customers or internally with other departments within the business. When companies advertise, they can utilize linguistic devices to persuade the targeted audience; Different devices can produce differing effects.[9] One of the linguistic device categories is a simple language. The different devices under simple language include phonetic symbolism, numbers, sound repetition, and pronunciation. All four devices use the cognitive effort of automatic processing. Phonetic symbolism is "a non-arbitrary relation between sound and meaning, and suggests that the sound of a word can convey meaning apart from its definition".[9] Back vowels and consonants are lower in pitch due to the positioning of the tip of the tongue being further back in the throat. These sounds are associated with heaviness, masculinity, and psychological distance. Conversely, front vowels and consonants are higher in pitch and associated with closeness, femininity, and light. The sound of a brand name can influence the perception of the brand from the consumers' perspective along with product attitude and product recommendations.[9] This being said, when a brand name sound preference is in alignment with the consumers' preference, the perception of the preferred attributes is enhanced.
Communication process
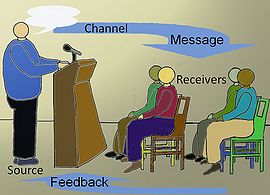
Communication can be defined as the process of using, word, sound, or visual cues to supply information to one or more people.[10] A communication process is defined as information that is shared with the intent that the receiver understands the message that the business intended to send.[11] The communication process was once thought of as having the source of the message, which is then encoded, put through the chosen communication channel, which is then decoded by the recipient and then received.[12] Throughout the middle of the channel there is the potential for noise to distort the message being sent.[12] Once the receiver has the message they then give feedback to the original source, where they then find out whether the campaign has been successful or not.[12]
With the prevalent use of technology, customers are seeking out information about brands, products, and businesses prior to purchase.[13] This means that there is a need for an additional channel within the communication process, so it is a more accurate representation of the current business environment. Businesses are now having to take into consideration both opinion leaders and opinion formers who have a great influence over today's society and their perceptions. So they have to be included in the communication process before the recipient of the message receives it.[14]
This model is more effective when there is common ground between the senders and receivers so they can communicate effectively. Choosing the appropriate source helps develop the message and appeal to the targeted audience. The source will be more effective if they are relatable to the target audience. This realm of understanding is represented by overlapping circles. The more knowledge the source has about who they are targeting, the better they can understand how the receiver may interpret or react to the message.[15]
The components of the transactional model are:
- Source: The source is an individual or organization that has information to share. The source (or sender) creates and sends the information to another person or group of people. The source may be an individual (e.g. a salesperson or spokesperson) or a non-personal identity (e.g. a corporation or organization). The communication process begins with the source, marketers must carefully choose a source as it affects how the message will be perceived by the target audience.[15]
- Encoding: This is transposing the intended meaning of the message with words, symbols, or pictures to show a message. Encoding is the development of the message that contains the information the source hopes to convey. It is putting together the thoughts, ideas, and information into a symbolic form that can be transmitted and understood by the receiver.[15] Encoding the message is the second step in the communication process. The encoding process leads to the development of a message that contains the information or meaning the source hopes to convey. Encoding is extremely important, it is a brain activity that takes effect when the receiver makes sense of a brand message or idea used to convey meaning: words, color, pictures, signs, symbols, or even music. The message may be verbal or nonverbal, oral or written, or symbolic (e.g. the sound of a brass band being redolent of simpler times or heritage). or it can often include 'cues' such as the Nike 'swoosh' which indicates success. Often things can get in the way of the "correct" encoding and the interpretation of the intended message (decoding). There are methods the sender can use to make sure the receiver interprets the message correctly, these methods include; channels, consumer insights, having similarities with the receiver, and frame of reference (e.g. age, values, culture).[12] Finally, it is extremely important for the sender to get to know its receiver and this is accomplished through research for targeting strategy. These concepts help craft the intended message in the minds of the consumer.
- Message: The message comes from the encoding process, it is the content, meaning, or information the sources hope to convey. The message can be in many forms such as verbal, non-verbal, oral, written, or symbolic.[15]
- Channel: The channel is the method by which the communication travels from the source or sender to the receiver.[12] There are two types of channels, personal and non-personal. Personal channels of communication are direct and target individual groups. Personal communication channels are connected with two or more persons who communicate directly with each other face-to-face, person-to-person through telephone, email, or fax. Social channels also fall under the category of personal communications. Friends, neighbors, associates, co-workers, or family members are all means of social channels.[3] Carrying a message without interpersonal contact between sender and receiver is known as non-personal channels of communication. Mass media or mass communications are examples of non-personal channels since the message is sent to many individuals at one time. Non-personal channels of communication are made up out of two main types, the first being print. Print media includes newspapers, magazines, direct mail, and billboards. The second type is broadcast; broadcast media includes radio and television.[16]
- Decoding: The receiver unravels the symbols to interpret what is being communicated. Transforming the sender's message back into thought. This is influenced greatly by the receiver's frame of reference (or realm of understanding) which involves their values, attitudes and state of mind when receiving the message. For the model to be effective the decoding by the receiver would match the encoding by the source, meaning they correctly understand the message that was sent.[15] Decoding is the process of interpreting messages and relies on correct encoding and the ability of the receiver to deconstruct transmitted meaning. Decoding occurs when the message reaches one or more of the receiver's senses. Consumers both hear and see television ads, others consumers handle (touch) and read (see) an advertising offer (e.g. coupon). According to Belch & Belch this process is deeply influenced by the receiver's frame of reference or field of experience, which refers to the experiences, perceptions, attitudes, and values he or she brings to the communication situation.[12] For effective communication to occur, the message decoding process of the receiver must match the encoding of the sender. Over this entire means the receiver comprehends and correctly translates what the source is trying to communicate. Effective communication is more likely to emerge when there is some common ground between the two parties. The more familiarity the sender has about the receivers, the better the sender can understand their needs, communicate with them, and overall communicate more effectively.
- Receiver: The individual (s) that the source shares thoughts or information with. The receiver hears, sees or reads the message and decodes it.
- Noise: Noise is any external interference during this communication process. Any external factors that create unplanned distortion. This distortion can make it difficult for the receiver to interpret or assign meaning to a message as it was intended by the source. Examples of noise in the encoding of the message could be lack of radio or television signal. Noise can also occur when the sender and receivers fields of experience do not overlap, if there is no common ground between them, which may result in a misunderstanding in the meaning of the message.[15] Throughout the communication process, the message is subject to irrelevant factors that can distort or interfere with its reception. Noise is the physical or Psychological fundamentals either from inside or outside of the process of communication. Noise acts as a barrier as it makes the message less accurate, less productive and unclear. It may even prevent the message from ever reaching the receiver. Physical noise is often triggered by badly made images or messages (e.g. poor print quality) or elements of distraction (e.g. consumer scrolling through TV advertisements). Psychological noise could be mixed meanings, poor credibility of source or the insignificance of the message to the consumer requirements. Not having a connection with the receiver and lacking in common ground usually cause this. This may result in unsuitable encoding of the message such as; using a sign, symbol, or word that is unfamiliar or has a different meaning to the receiver (e.g. sending a message in a foreign language that is not understood by the receiver). The more common ground there is between the sender and the receiver, the less likely it is for noise and barriers to interrupt a message.[12]
- Response/Feedback: The receiver's reaction to the message provides feedback to the sender. This is the set of reactions after seeing, hearing or reading the message. The receiver's response is the feedback and lets the sender know how the message was decoded and received. A form of feedback in an interpersonal selling situation could be questions, comments or any reactions (such as expressions) about the message. In mass media, an indication of how the marketing communications were perceived is the amount of sales after the message has been sent. There are many different ways such as attitude change, store visits and inquiries that provide feedback in mass media. Feedback can help to improve the communication process and the success of future messages.[15] The receiver's particular type of reaction after seeing, hearing, or reading a message is known as a response. Receivers' responses can range from either non-noticeable actions or noticeable actions. Non-noticeable responses can be storing their information in memory and noticeable responses are immediate action such as dialing the commercials number to order a product advertised on television. One of the main goals of communication is receiving appropriate receiver responses, feedback closes the loop in the communications flow and lets the sender monitor how the intended message is being decoded and received. To achieve this goal one can ask indirectly or directly for the response, or assist the receiver in giving the response.[3] Receiving feedback can be more difficult for parties that advertise through the channels of mass media, because advertisers are not in direct contact with their customers so other methods must be obtained to determine how their messages have been received. While the critical form of feedback happens through sales, it is often hard to show a direct relationship between advertising and purchase behavior. So marketers; visit stores, check coupon redemption, use reply cards and listen to customer inquiries to achieve feedback. Once a significant amount of feedback/response study has been gathered advertisers would then have enough information to determine reasons for success or failure in the communication process and from there they can make appropriate adjustments.
Opinion leaders and opinion formers
Opinion leaders are consumers who have large influence over the purchasing behavior of other consumers.[17] These can be peers or celebrities, and often represent a "desired state" in the eye of the influenced consumer. By following the consumption patterns of opinion leaders, consumers aspire to achieve a similar status or lifestyle, and project a similar image. Because of this, opinion leaders are powerful factors in marketing communications. Having opinion leaders endorse a brand can increase brand awareness and sales. Due to this, large companies pay highly influential celebrities to endorse their products.
You can receive the opinion leaders' thoughts or feelings towards the product/service through paid advertising, social media, blogs, or any other form of written media.[18] These can be direct, or indirect influences.
Opinion formers are consumers who are regarded by their peers as being highly knowledgeable and trustworthy.[19] They are considered experts in selecting the highest quality products due to their extensive knowledge, and as such are able to influence the purchasing behavior of other consumers despite lacking the celebrity status of an opinion leader. They have specialized knowledge about the area which corresponds with the product, service or business. For example, this could be a doctor sponsoring a form of medication, or a personal trainer recommending a sports brand to the customer. This means that both opinion leaders and opinion formers have a large influence on the consumer and their perceived view of the business, product, or service provided.[20] If a brand is specializing in the sale and manufacturing of makeup products, the business would want to look at someone who is both known for their knowledge about makeup and also someone who they know is popular within that community, so that the message is as widespread throughout their target market as possible.[20] Opinion leaders add another link in the communication process, acting as a "meaning filter" for the receivers of the message.[21] The message is sent from the sender and the opinion leaders share their opinions with the targeted audience.
Mass media
Television
Television has since its inception dominated the advertising media scene, due to its combination of visual and aural stimulation, allowing for greater attention grabbing and more effective transmission of messages than other forms of media. It has a few disadvantages: television commercials suffer from being "zipped" and zapped". "Zipping" is the term given to fast forwarding commercial break sessions during the pre-recording of programs. Often viewers will record programs purely so they can be viewed without the commercial breaks. "Zapping" is the term given to the habit of many consumers to change channels during commercial breaks. This is also done to avoid watching advertisements. Using television advertisements is beneficial due to its wide reach and the degree to which content can be segmented according to the intended target market. Advertisements are carefully paired with time segments and / or linked with appropriate programming, known as "media vehicles". This helps to ensure the intended audience is being reached with the marketing message.[22]
While initial production costs of a television advertisement are high, it is likely to reach a mass audience and, therefore, maintains a low cost per viewer, making it an efficient communication platform.[23]
Radio
Radio by definition is the broadcasting of sound programs to the public and today can be live streamed through a broadband connection or digitally transmitted into people's cars or homes.[24] Despite being the oldest form of media transmission still being used, marketing via radio remains a popular and effective choice due to its relatively lower cost and convenience (radio exposure can occur during transit, at work, and during recreational activities). Due to the lack of a visual aspect, radio advertising attempts to create imagery in the consumer's mind. Radio advertising is also extremely effective at reinforcing messages encountered in other channels (such as television).[25] A familiar jingle or voice associated with a brand enhances brand and ad awareness, ultimately increasing brand equity. This is an example of "Integrated Marketing Communications", in which multiple marketing channels are simultaneously utilized to increase the strength and reach of the marketing message. Like television, radio marketing benefits from the ability to select specific time slots and programs (in this case in the form of radio stations and segments within).
Fill et al.[23] argue that radio communication promotes "emotional consumer–centric associations" as each listener is forced to construct a visual representation of the words and sounds such as music in their minds. A common technique used by companies is known as imagery transfer, where a complementary visual television advertisement is used alongside a one-dimensional radio advertisement featuring a similar audio track to stimulate a visual association between the two.[26] Research suggests this sub-conscience relational thought process greatly benefits future brand recognition and awareness.[23]
Radio infomercials are often a simple script that is read out by the presenter. This is quick and does not require extensive lead times due to minimal production efforts.[24]
Printed media is the most basic form of media advertising. It is the most challenging to create strong imagery with, due to its lack of sensory stimulation, but can be effective in efficient, clear information communication and message delivery. Where a consumer may miss a message in video promoted by ads or audio (A loud noise interrupts, or someone blocks their view) in print the message remains visible indefinitely. Aspects such as size, color and style can be used to increase effectiveness relative to other print advertisements, which is important as despite being a basic media communication channel, print is the second largest medium after television.[27]
Traditionally, marketing communications practitioners focused on the creation and execution of printed marketing collateral. Traditional media, or as some refer to as old media, has been used within the marketing and advertising world for many years.[28] Traditional media encompasses conventional forms of advertising media, such as television, magazines, newspapers, radio, and direct mail and outdoor. For many decades, these forms of communication have been the main source for marketers to reach both consumers and other companies. In a world with no internet and the vast world of social media, roots of advertising and promotion lie within traditional media, where there is a more direct, physical way of advertising.
Advertising in the form of print is used by businesses in the form of billboards and posters, as well as magazines and newspapers, to get their message across to the target audience. Businesses will usually place a billboard in areas where it can be easily seen and where the target audience will spend their daily activities. Newspapers, magazines and posters are smaller in size and can be found in numerous places allowing the general public to read them. Depending on the product or service that is being advertised, marketers may specify where the majority of their prints may go to, such as advertisements of a new shampoo promoting more common within salons.
Print media are highly customizable, varying in print size, font, positioning and color combination. Newspapers commonly use coarse paper and tend to have poor reproduction quality, while magazines can enhance the appearance of a certain product due to the heavy weight gloss paper used which translates color well and offers a long lasting quality and likeability.[23] Magazines function as a frame, a psychological device which manipulates perspective and judgement.[29] For example, Vogue, a leading paid circulation fashion magazine,[30] publishes advertising efforts alongside beautiful imagery and elegant photography, the association of the two communicates respectability and sophistication and promotes the credibility of the brands which appear in the same publication. Due to the high-quality reproduction, magazines tend to last longer and are often found in hair salons and waiting rooms. Consumers often cut out individual images which further prolongs the message and increases potential exposure. Although the relevance of the message may be lost during this extended time, brand awareness may still be raised.[23]
Magazines are often segmented by subjects such as women's health, automotive or fashion and therefore effectively reach a particular target market. Newspapers focus on geographical regions which tend to appeal to a broad representative population sample, offering low impact in selectivity. Newspapers are often run on a weekly schedule offering up-to-date information and coverage of local events and businesses as a lower cost alternative to other forms of media. Such advertisements are in smaller typeface and are black and white.[23]
Decline
Past forms of media are said by many to be gradually losing effectiveness as more contemporary forms become more popular.[31] This change is driven by two key factors: audience fragmentation and ability to choose commercial content. Television, radio, magazines, and newspapers are becoming more fragmented and reaching smaller and more selective audiences. The rapid growth of communication due to interactive messaging, particularly the internet, had caused the changes in the use of communication throughout promotion mediums, with businesses preferring to use modern media over more traditional media methods. Consumers cannot avoid new and innovative ways of communication.[28] Many marketers believe that traditional techniques of advertising have become too expensive and not cost-effective compared to modern ones. Older forms of marketing communications such as TV and newspaper advertising are one way in nature, whereas new media allows marketers to perform a variety of functions.
Modes of communication and advertisement
Communication platforms like Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, TikTok, Snapchat, Skype, or other types of media have become an extremely important means of communication. Although there are other methods of communications that aren't related to social media, people can be hugely influenced by their peers. This process is known as social mediation. Marketing communication platforms personalizes and expends marketing contents in an automated fashion based on the profile of the recipients.[16]
A platform functions as a similar principle in marketing communications, providing awareness and information about a specific brand or product.[21] Strategic selection of various communication platforms is known as a media strategy which aims to engage an audience in a conversation and, as a result, attempt to create a lasting relationship.[32] Modern technology has expanded the use of platforms and ways in which consumers and the brand can interact. As a result, the context of platforms and how they are defined has changed.[33] There are various platforms by which communication is transmitted,[23] and these can be categorized as paid, owned, earned, or shared, formally named as the integrated communication triangle by Grönroos and Lindberg-Repo.[34] The model acknowledges that communication must be credible and trustworthy to be effective. Studies reveal that many consumers look at review forums and ask friends or peers whom they trust for ratings on products before making a purchase decision.[33] Therefore, effective communication relies on an integrated approach of one dimensional[vague] and interactive platforms.[21]
Explicitly planned market content is shared through non-personal communication platforms.[35] The brand controls the platform, message content, frequency and repetition of the communication message.[36] These factors are typically accomplished through traditional paid platforms, such as print, electronic, outdoor and alternative media, that aims to target a mass segment of the market.[35]
Other aspects of noise decrease the effectiveness of message penetration. For example, most paid communication platforms, print, and electronic media are filled with marketing and advertising messages and are subject to clutter, often forcing brands to compete for attention.[21] To eliminate noise, brands often choose to include inserts such as samples and scent strips within magazines while newspapers utilize "call to action" inserts such as coupons which encourage consumers to visit or try a local service or good.[23]
Social media
Social media's market penetration is rising thanks to services like YouTube, Facebook, Instagram, Pinterest, Snapchat and TikTok. Companies are using these external platforms to engage existing and future customers, reinforce brand messaging, influence customer opinions, provide target offers, and serve customers more efficiently.[37] Social media are flexible communication tools that go beyond the traditional means of advertising and allow brands to interact with their audience personally or professionally.[38][39]
Influencer Marketing used to be focused on applying celebrity endorsement to help to influence audiences. Nowadays, with the growing outreach of social media, "common people" like bloggers are becoming popular and are connected with brands and products as influencers. Companies are beginning to invest time and money creating influence through resonance and reach. Return on Influence is not metrically trackable like Return on Investment is, but mechanisms such as links with UTM parameters can be created to track conversion behavior of influence.[40]
The internet
The Internet features both non-personal and personal forms of communication. It has become one of the most dominant sources of information for most consumers. Belch & Belch as of 2012[update] explained that the internet is mostly a non-personal form of communication as consumers absorb information online with no personal contact between the consumer and the organizations that are providing the information on their websites. However, as the internet develops, it is including personal communication as consumers interact with marketers online as well as communicate and share information with one another through the use of social media.[12]
The Internet allows multimedia documents to be shared among its users. As of 2003[update] approximately 30 million websites have been registered worldwide and 650 million were connected to the Internet.[41] The Internet as a marketing tool can be used to reach and inform customers directly, create brand loyalty, and build relationships. Online advertising includes elements such as: graphic images as website banners, pop-up advertisements, homepage restyling and anchor deals (co-operation between two organizations ).[42]
Interactivity
Interactivity is a characteristic feature of the Internet that was described in 1996 by John Deighton.[43] He argued that in the then-new Internet business environment, clients rather than the marketers usually start the interaction, by actively looking for the information that they need. Moreover, personal responses of customers will be collected by corporations and their individual demands will be met according to their desires.
On the one hand, traditional media are "push" formats where marketers broadcast their messages to customers, but do not allow direct feedback. The interaction between the two parties is few and far between. On the other hand, Internet media have the attribute of "pull" where customers have the freedom to search for whatever they wish. For instance, whenever a consumer types "flower" Google's search engine, an advertisement of a specific flower shop might be placed on the top or bottom of the search result page by the Google AdWords program.[44] Google makes use of the client's search history and location to place an appropriate ad. The traditional one-way "push" communication is supplanted by the more productive two-way "push and pull" interaction.
Individualization
Compared with the traditional media where the same information is received by all consumers, As another advantage of two-way interaction, internet media can carry information "tailored" to the needs of a specific consumer. One of the first and most prominent examples is the personalized service provided by Amazon in which consumers are called by their names and "tailored" recommendations are provided according to their previous purchase records.[45] Furthermore, besides "tailored" individual service, with the accumulation of consumers' information on the Internet, mass customization becomes possible in which companies provide "tailored" content to particular segments of consumers with similar interests. Douban is a Chinese social networking service website that allows its users to rate movies, TV dramas, music and concerts. It rapidly grew to 200 million registered users in 2013 (founded in 2005). In addition, people who like the same TV drama, like Game of Thrones, or fans of the same movie star, such as Tom Cruise, will group together to discuss and share their feelings. This allows companies to take advantage of mass customization to sell products or reinforce their brand equity in suitable target groups. By doing so, the interaction and co-operation of companies and consumers are deepening, widening and multiplying in a variety of ways.
Industry restructuring
Restructuring followed by disintermediation and reintermediation is one of the essential features of the transition from traditional to Internet marketing communications. The Internet may force traditional distributors or retailers out of business simply because Internet transactions are less costly. JD.com significantly impacted the distribution channels for personal computers in China as of 2009 by allowing consumers to order different parts of the computers that were then assembled by the online business, leaving tens of thousands of retailers in that field out of their jobs. In 2015, JD.com accounted for 22.9% of the Chinese online shopping's market share.[46] Again, according to Financial Times, with the shifting trend of using mobile phones for online purchase in China, the people using cellphones to log on to the Internet outnumbered those using PC,[47] the next wave of restructuring faced by JD.com and its major competitors like Alibaba. In 2014, JD.com's orders deriving from mobile phones increased by 543%, compared with the last year's quarter of the same period. Haoyu Shen, the chief executive of the JD.com, ascribed this result to its own company's app rather than the co-operation with Tecent, the Chinese second largest online corporation, although it invested in JD.com in March 2014. As an ecommerce business, JD.com has been constantly facing challenges and opportunities of reintermediation with the rapid shifts of the technology development of the Internet.
Email marketing is directly marketing a commercial message to a group of people using email. In its broadest sense, every email sent to a potential or current customer could be considered email marketing. It usually involves using email to send ads, request business, or solicit sales or donations, and is meant to build loyalty, trust, or brand awareness. Email marketing can be done to either sold lists or a current customer database. Broadly, the term is usually used to refer to sending email messages with the purpose of enhancing the relationship of a merchant with its current or previous customers, to encourage customer loyalty and repeat business, acquiring new customers or convincing current customers to purchase something immediately, and adding advertisements to email messages sent by other companies to their customers.
In-product communication
Another channel for direct digital marketing is in-product communication (or in-product marketing), which delivers marketing content directly to a user's internet-connected device or software application. In-product marketing content is often very similar to that of email marketing campaigns, but the segmentation and delivery is more targeted. Because email has become a standard tool in the digital marketing toolkit, the email channel often is overloaded and overused, leading to much lower open rates, lower engagement rates, lower click-through rates (CTR), and lower conversion rates. The rise of internet-connected (IOT) devices is enabling a growing number of consumer products manufacturers to take advantage of this channel of marketing communications, to supplement other digital marketing channels.
Guerrilla marketing
Due to the rise in advertising clutter, there has been a push for non-traditional media such as guerrilla marketing.[48] Guerrilla marketing is usually a low-cost way of generating buzz through creative or unexpected communication platforms.[49] Outdoor settings provide potential ground to gain attention from a large audience. An example is customizing street infrastructure or creating an event such as a flash mob. Research rates guerrilla advertising as having a higher perceived value compared to other communication platforms, which tends to result in a positive consumer response.[48] An example of successful guerrilla marketing was created by Volkswagen (VW) in their promotional "driven by fun" campaign, where consumers could use VW "fast lane" slide instead of the escalator to get to the bottom of the stairs faster.[50]
Touch points
Every point of contact is a form of communication and it is, therefore, necessary to consider touch points as a communication platform. Touch points can be either physical or a human interaction between a brand and the consumer which influence customer decision-making process during pre-purchase, purchase and post-purchase.[51]
There are many ways in which a customer may interact with a business.[21] Interactions occur through direct customer service exchanges, a company website, the point of purchase environment and product packaging or performance.[51] These all contribute to consumer perceptions of a particular brand. For instance, the service-scape of a purchase touch point such as a retail store can influence the perception of quality and service through lighting and layout or other sensory touch points, for example, smell.[21] Fast fashion retailers such as Topshop maintain a white store interior and exterior which is perceived as luxurious.[52] Likewise, the higher price point and packaging of Ferrero Rocher may communicate sophistication and better quality. Visual appearance can have a significant effect on purchase decision,[51] companies such as Coke a Cola and Pepsi provide a free fridge to distributors to control how products are displayed at the point of purchase.[21]
Multiplier effect
While boarding a United Airlines flight, Dave Carroll saw baggage handlers on the tarmac damage his Taylor guitar.[53] After failed attempts to solve the issue through customer service, Carroll uploaded a humorous YouTube video titled "United breaks guitars",[32] which experienced over 15 million views.[54] Carroll's YouTube video is an example of the multiplier effect, and how consumer experiences are shared through user-generated content (UGC) networks and word of mouth communication.[32] Research shows customers are more likely to pass on negative experiences, and therefore, such interactive platforms have a significant impact on purchase decisions and brand outlook.[36]
This highlights a trend in integration of consumer behavior with marketing communications, where technology has facilitated social group communication. Communication has changed from one direction with companies in control of their message to a dialogue where businesses interact with consumer feedback.[36] As Andy Lark, Commonwealth Bank CMO states "the power has shifted, we are now entering a transparent age where there are no secrets".[55]
Traditional models viewed paid media platforms as the primary source of information. However, technology has enabled dialogue within a consumer-centric communication platform.[33] This flow of information allows a many-to-many exchange through UGC, which includes all types of creative content online through blogs, chats, forums, online platforms for product reviews and social media websites such as Facebook, YouTube and Instagram,[36] which are known as earned and shared media.[32]
Co-creationedit
Co-creation takes place when customers not only buy the company's products but also help in designing and developing them. Nike built an example of co-creation and customer empowerment through earned and shared media. Nike ID is an online application that allows customers to design their shoe and therefore "Just do it online".[21][36] Market-generated media remain an important communication platform and information source.[36] Consumers tend to consider both market-generated and UGC when making a purchase decision,[33] particularly, for higher involvement product like vinyl record albums.[56] The transition from traditional media to various forms of online and UGC marketing is increasing. Academics recognize that marketing communication is an open system and customers are influenced by multiple communication platforms.[21] Ultimately positive brand encounters manifest brand supporters who contribute to positive earned and shared media, through product recommendations online and offline.[33]
Direct marketingedit
In direct marketing the producer communicates directly with potential customers, instead of through third-party media. Individual customer's responses and transactions are recorded.[57] Direct marketing is a growing form of marketing communication. It is designed to build the relationship between the customer and the brand,[58] known as customer relationship management (CRM). Organizations use customer accounts in order to monitor and understand their needs. They manage detailed information about the customer's touch points with the objective to maximize satisfaction and loyalty. The communication can be in person, by telephone, mail, email or website.[42] The interaction between the organization and the customer is usually a two-way communication. Direct marketing relies on CRM databases that contain valuable customer information. Good quality databases can provide a competitive advantage and increase profitability. Treating the customer database as an expense rather than an investment, or not continuously maintaining or updating them can be detrimental.[42]
Direct mailedit
Direct mail is a letter, card, catalog, or sample sent through post, email, fax, or courier. This communication is most effective when the recipient has shown interest in or has previously purchased from the organization. Advantages of direct mail are personalization, careful targeting, creativity and flexibility. Email is low-cost, but can be lost through spam and junk email filters. Direct mail is dependent on accurate databases.[42]
Telemarketingedit
Telemarketing is marketing communication via telephone. There are two types of telemarketing: outbound and inbound.[42] Outbound telemarketing is used by organizations to reach out to potential customers, generate sales, make appointments with salespeople and introduce new products. Inbound telemarketing is where people call the organization to complain or inquire about products. Both outbound and inbound can be used as a customer service strategy to boost sales and receive suggestions for improvement. Advantages of telemarketing include targeted communications, flexible and direct interaction between the organization and the customer, it can be an effective personal selling partner and it is cost-effective compared to face-to-face contact. A disadvantage is that call centers are usually used to handle outbound and inbound telemarketing, which need to be implemented, managed and financed.[42]
Mail orderedit
Mail order marketing is a catalog of products that customers can order to receive in the mail. This form of direct marketing dates back over 100 years. Home shopping, online shopping and teleshopping now accompany it. With current technology mail order has improved. Now there can be a larger range in catalog, delivery is faster, and complaints are dealt with professionally. Mail order exerts less pressure on the customer than telemarketing and sales are easy to manage, however costly infrastructure is required in maintaining the back-end.[42]
Direct-response advertisingedit
Zdroj:https://en.wikipedia.org?pojem=Integrated_marketingText je dostupný za podmienok Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších podmienok. Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky použitia.
Antropológia
Aplikované vedy
Bibliometria
Dejiny vedy
Encyklopédie
Filozofia vedy
Forenzné vedy
Humanitné vedy
Knižničná veda
Kryogenika
Kryptológia
Kulturológia
Literárna veda
Medzidisciplinárne oblasti
Metódy kvantitatívnej analýzy
Metavedy
Metodika
Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative
Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších
podmienok.
Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky
použitia.
www.astronomia.sk | www.biologia.sk | www.botanika.sk | www.dejiny.sk | www.economy.sk | www.elektrotechnika.sk | www.estetika.sk | www.farmakologia.sk | www.filozofia.sk | Fyzika | www.futurologia.sk | www.genetika.sk | www.chemia.sk | www.lingvistika.sk | www.politologia.sk | www.psychologia.sk | www.sexuologia.sk | www.sociologia.sk | www.veda.sk I www.zoologia.sk
