
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
| Finnish Civil War | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of World War I, Russian Civil War and Revolutions of 1917–1923 | |||||||
 Tampere's civilian buildings destroyed during the Battle of Tampere | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| |||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Strength | |||||||
|
| ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
| ||||||
The Finnish Civil War[a][b] was a civil war in Finland in 1918 fought for the leadership and control of the country between White Finland and the Finnish Socialist Workers' Republic (Red Finland) during the country's transition from a grand duchy ruled by the Russian Empire to a fully independent state. The clashes took place in the context of the national, political, and social turmoil caused by World War I (Eastern Front) in Europe. The war was fought between the Red Guards, led by a section of the Social Democratic Party, and the White Guards, conducted by the senate and those who opposed socialism with assistance late in the war by the German Imperial Army at the request of the Finnish civil government. The paramilitary Red Guards, which were composed of industrial and agrarian workers, controlled the cities and industrial centres of southern Finland. The paramilitary White Guards, which consisted of land owners and those in the middle and upper classes, controlled rural central and northern Finland, and were led by General C. G. E. Mannerheim.
In the years before the conflict, Finland had experienced rapid population growth, industrialisation, urbanisation and the rise of a comprehensive labour movement. The country's political and governmental systems were in an unstable phase of democratisation and modernisation. The socio-economic condition and education of the population had gradually improved, and national awareness and culture had progressed. World War I led to the collapse of the Russian Empire, causing a power vacuum in Finland, and the subsequent struggle for dominance led to militarisation and an escalating crisis between the left-leaning labour movement and the conservatives. The Reds carried out an unsuccessful general offensive in February 1918, supplied with weapons by Soviet Russia. A counteroffensive by the Whites began in March, reinforced by the German Empire's military detachments in April. The decisive engagements were the Battles of Tampere and Viipuri, won by the Whites, and the Battles of Helsinki and Lahti, won by German troops, leading to overall victory for the Whites and the German forces. Political violence became a part of this warfare. Around 12,500 Red prisoners died of malnutrition and disease in camps. About 39,000 people, of whom 36,000 were Finns, died in the conflict.
In the immediate aftermath, the Finns passed from Russian governance to the German sphere of influence with a plan to establish a German-led Finnish monarchy. The scheme ended with Germany's defeat in World War I, and Finland instead emerged as an independent, democratic republic. The civil war divided the nation for decades. Finnish society was reunited through social compromises based on a long-term culture of moderate politics and religion and a post-war economic recovery.
Names
The war has been assigned several designations according to different political and ideological viewpoints. War of Independence (Finnish: vapaussota) was used during the war by both sides to express the fight for liberation from capitalism for the Reds and freedom from Soviet Russian influence by the Whites; Civil War is the term increasingly employed by the reconstituted social democrats after their defeat in the war.[6] The general terms for the conflict, Civil War (Finnish: sisällissota) and Citizen War (Finnish: kansalaissota), are synonymous and appeared mostly after the war. More ideologic names were also used including Class War (Finnish: luokkasota) and Revolution (Finnish: vallankumous) by the Reds and their supporters while Red Rebellion (Finnish: punakapina) was used by the Whites and their supporters.[7] Another designation, Brethren War (Finnish: veljessota), is applied in some poetic settings.[8] According to a 2008 interview of 1,005 people done by the newspaper Aamulehti, the most popular names were as follows: Civil War: 29%, Citizen War: 25%, Class War: 13%, War of Independence: 11%, Red Rebellion: 5%, Revolution: 1%, other name: 2% and no answer: 14%.[9]
Background

Finland as grand duchy: 1809–1917
From 1809 to 1898, a period called Pax Russica,[10] the peripheral authority of the Finns gradually increased, and relations between Russian Empire and Grand Duchy of Finland were exceptionally peaceful for a many years. Russia's defeat in the Crimean War in the 1850s led to attempts to speed up the modernisation of the country. This caused more than 50 years of economic, industrial, cultural and educational progress in the Grand Duchy of Finland, including an improvement in the status of the Finnish language. All this encouraged Finnish nationalism and cultural unity through the birth of the Fennoman movement, which bound the Finns to the domestic administration and led to the idea that the Grand Duchy was an increasingly autonomous state ruled by the Russian Empire.[11]
However in 1899, the Russian Empire begun to initiate a policy of integration through the Russification of Finland. The strengthened, pan-slavist central power tried to unite the "Russian Multinational Dynastic Union" as the military and strategic situation of Russia became more perilous due to the rise of Germany and Japan. Finns called the increased military and administrative control, "the First Period of Oppression", and for the first time Finnish politicians drew up plans for disengagement from Russia or full sovereignty for Finland. In the struggle against integration, activists drawn from sections of the working class and the Swedish-speaking intelligentsia carried out terrorist acts. During World War I and the rise of Germanism, the pro-Swedish Svecomans began their covert collaboration with Imperial Germany and, from 1915 to 1917, a Jäger (Finnish: jääkäri; Swedish: jägare) battalion consisting of 1,900 Finnish volunteers was trained in Germany.[12]
Domestic politics
The major reasons for rising political tensions among Finns were the autocratic rule of the Russian tsar and the undemocratic class system of the estates of the realm. The latter system originated in the regime of the Swedish Empire that preceded Russian governance and divided the Finnish people economically, socially and politically. Finland's population grew rapidly in the nineteenth century (from 860,000 in 1810 to 3,130,000 in 1917), and a class of agrarian and industrial workers, as well as crofters, emerged over the period. The Industrial Revolution was rapid in Finland, though it started later than in the rest of Western Europe. Industrialisation was financed by the state and some of the social problems associated with the industrial process were diminished by the administration's actions. Among urban workers, socio-economic problems steepened during periods of industrial depression. The position of rural workers worsened after the end of the nineteenth century, as farming became more efficient and market-oriented, and the development of industry was insufficiently vigorous to fully utilise the rapid population growth of the countryside.[13]
The difference between Scandinavian-Finnish and Russian-Slavic culture affected the nature of Finnish national integration. The upper social strata took the lead and gained domestic authority from the Russian tsar in 1809. The estates planned to build an increasingly autonomous Finnish state, led by the elite and the intelligentsia. The Fennoman movement aimed to include the common people in a non-political role; the labour movement, youth associations and the temperance movement were initially led "from above".[14]
Between 1870 and 1916 industrialisation gradually improved social conditions and the self-confidence of workers, but while the standard of living of the common people rose in absolute terms, the rift between rich and poor deepened markedly. The commoners' rising awareness of socio-economic and political questions interacted with the ideas of socialism, social liberalism and nationalism. The workers' initiatives and the corresponding responses of the dominant authorities intensified social conflict in Finland.[15]
The Finnish labour movement, which emerged at the end of the nineteenth century from temperance, religious movements and Fennomania, had a Finnish nationalist, working-class character. From 1899 to 1906, the movement became conclusively independent, shedding the paternalistic thinking of the Fennoman estates, and it was represented by the Finnish Social Democratic Party, established in 1899. Workers' activism was directed both toward opposing Russification and in developing a domestic policy that tackled social problems and responded to the demand for democracy. This was a reaction to the domestic dispute, ongoing since the 1880s, between the Finnish nobility-bourgeoisie and the labour movement concerning voting rights for the common people.[16] Despite their obligations as obedient, peaceful and non-political inhabitants of the Grand Duchy (who had, only a few decades earlier, accepted the class system as the natural order of their life), the commoners began to demand their civil rights and citizenship in Finnish society. The power struggle between the Finnish estates and the Russian administration gave a concrete role model and free space for the labour movement. On the other side, due to an at-least century-long tradition and experience of administrative authority, the Finnish elite saw itself as the inherent natural leader of the nation.[17] The political struggle for democracy was solved outside Finland, in international politics: the Russian Empire's failed 1904–1905 war against Japan led to the 1905 Revolution in Russia and to a general strike in Finland. In an attempt to quell the general unrest, the system of estates was abolished in the Parliamentary Reform of 1906. The general strike increased support for the social democrats substantially. The party encompassed a higher proportion of the population than any other socialist movement in the world.[18]
The Reform of 1906 was a giant leap towards the political and social liberalisation of the common Finnish people because the Russian House of Romanov had been the most autocratic and conservative ruler in Europe. The Finns adopted a unicameral parliamentary system, the Parliament of Finland (Finnish: eduskunta; Swedish: riksdag) with universal suffrage. The number of voters increased from 126,000 to 1,273,000, including female citizens. The reform led to the social democrats obtaining about fifty per cent of the popular vote, but the Tsar regained his authority after the crisis of 1905. Subsequently, during the more severe programme of Russification, called "the Second Period of Oppression" by the Finns, the Tsar neutralised the power of the Finnish Parliament between 1908 and 1917. He dissolved the assembly, ordered parliamentary elections almost annually, and determined the composition of the Finnish Senate, which did not correlate with the Parliament.[19]
The capacity of the Finnish Parliament to solve socio-economic problems was stymied by confrontations between the largely uneducated commoners and the former estates. Another conflict festered as employers denied collective bargaining and the right of the labour unions to represent workers. The parliamentary process disappointed the labour movement, but as dominance in the Parliament and legislation was the workers' most likely way to obtain a more balanced society, they identified themselves with the state. Overall domestic politics led to a contest for leadership of the Finnish state during the ten years before the collapse of the Russian Empire.[20]
International politics
The main factor behind the Finnish Civil War was a political crisis arising out of World War I. Under the pressures of the Great War, the Russian Empire collapsed, leading to the February and October Revolutions in 1917. This breakdown caused a power vacuum and a subsequent struggle for power in Eastern Europe. The Grand Duchy of Finland became embroiled in the turmoil. Geopolitically less important than the continental Moscow–Warsaw gateway, Finland, isolated by the Baltic Sea, was relatively peaceful until early 1918. The war between the German Empire and Russia had only indirect effects on the Finns. Since the end of the 19th century, the Grand Duchy had become a vital source of raw materials, industrial products, food and labour for the growing Imperial Russian capital Petrograd (modern Saint Petersburg), and World War I emphasised that role. Strategically, the Finnish territory was the less important northern section of the Estonian–Finnish gateway and a buffer zone to and from Petrograd through the Narva area, the Gulf of Finland and the Karelian Isthmus.[21]
The German Empire saw Eastern Europe - particularly Russia - as a major source of vital products and raw materials, both during World War I and for the future. Her resources overstretched by the two-front war, Germany attempted to divide Russia by providing financial support to revolutionary groups, such as the Bolsheviks and the Socialist Revolutionary Party, and to radical, separatist factions, such as the Finnish national activist movement leaning toward Germanism. Between 30 and 40 million marks were spent on this endeavour. Controlling the Finnish area would allow the Imperial German Army to penetrate Petrograd and the Kola Peninsula, an area rich in raw materials for the mining industry. Finland possessed large ore reserves and a well-developed forest industry.[22]
February Revolution
Build-up

The February Revolution removed Tsar Nicholas II. The collapse of the Russian Empire was caused by military defeats, war-weariness against the duration and hardships of the Great War, and the collision between the most conservative regime in Europe and a Russian people desiring modernisation. The Tsar's power was transferred to the State Duma (Russian Parliament) and the left-leaning Provisional Government, but this new authority was challenged by the Petrograd Soviet (city council), leading to dual power in the country.[23]
In Finland, mass meetings and local strikes of early 1917 escalated to a general strike in support of the Finnish state's power struggle and for increased availability of foodstuffs. The Second Period of Russification was stopped and the autonomous status of 1809–1899 was returned to the Finns by the 15th March 1917 manifesto of the Russian Provisional Government. For the first time in history, de facto political power existed in the Parliament of Finland. The political left, consisting mainly of social democrats, covered a wide spectrum from moderate to revolutionary socialists. The political right was even more diverse, ranging from social liberals and moderate conservatives to rightist conservative elements. The four main parties were:
- The conservative Finnish Party;
- the Young Finnish Party, which included both liberals and conservatives, with the liberals divided between social liberals and economic liberals;
- the social reformist, centrist Agrarian League, which drew its support mainly from peasants with small or mid-sized farms; and
- the conservative Swedish People's Party, which sought to retain the rights of the former nobility and the Swedish-speaking minority of Finland.[24]
During 1917, a power struggle and social disintegration interacted. The collapse of Russia induced a chain reaction of disintegration, starting from the government, military and economy, and spreading to all fields of society, such as local administration, workplaces and to individual citizens. The social democrats wanted to retain the civil rights already achieved and to increase the socialists' power over society. The conservatives feared the loss of their long-held socio-economic dominance. Both factions collaborated with their equivalents in Russia, deepening the split in the nation.[25]
The Social Democratic Party gained an absolute majority in the parliamentary elections of 1916. A new Senate was formed in March 1917 by Oskari Tokoi, but it did not reflect the socialists' large parliamentary majority: it comprised six social democrats and six non-socialists. In theory, the Senate consisted of a broad national coalition, but in practice (with the main political groups unwilling to compromise and top politicians remaining outside of it), it proved unable to solve any major Finnish problem. After the February Revolution, political authority descended to the street level: mass meetings, strike organisations and worker-soldier councils on the left and to active organisations of employers on the right, all serving to undermine the authority of the state.[26]
The February Revolution halted the Finnish economic boom caused by the Russian war-economy. The collapse in business led to unemployment and high inflation, but the employed workers gained an opportunity to resolve workplace problems. The commoners' call for the eight-hour working day, better working conditions and higher wages led to demonstrations and large-scale strikes in industry and agriculture.[27]
While the Finns had specialised in milk and butter production, the bulk of the food supply for the country depended on cereals produced in southern Russia. The cessation of cereal imports from disintegrating Russia led to food shortages in Finland. The Senate responded by introducing rationing and price controls. The farmers resisted the state control and thus a black market, accompanied by sharply rising food prices, formed. As a consequence, export to the free market of the Petrograd area increased. Food supply, prices and, in the end, the fear of starvation became emotional political issues between farmers and urban workers, especially those who were unemployed. Common people, their fears exploited by politicians and an incendiary, polarised political media, took to the streets. Despite the food shortages, no actual large-scale starvation hit southern Finland before the civil war and the food market remained a secondary stimulator in the power struggle of the Finnish state.[28]
Contest for leadership

The passing of the Tokoi Senate bill called the "Law of Supreme Power" (Finnish: laki Suomen korkeimman valtiovallan käyttämisestä, more commonly known as valtalaki; Swedish: maktlagen) in July 1917, triggered one of the key crises in the power struggle between the social democrats and the conservatives. The fall of the Russian Empire opened the question of who would hold sovereign political authority in the former Grand Duchy. After decades of political disappointment, the February Revolution offered the Finnish social democrats an opportunity to govern; they held the absolute majority in Parliament. The conservatives were alarmed by the continuous increase of the socialists' influence since 1899, which reached a climax in 1917.[29]
The "Law of Supreme Power" incorporated a plan by the socialists to substantially increase the authority of Parliament, as a reaction to the non-parliamentary and conservative leadership of the Finnish Senate between 1906 and 1916. The bill furthered Finnish autonomy in domestic affairs: the Russian Provisional Government was only allowed the right to control Finnish foreign and military policies. The Act was adopted with the support of the Social Democratic Party, the Agrarian League, part of the Young Finnish Party and some activists eager for Finnish sovereignty. The conservatives opposed the bill and some of the most right-wing representatives resigned from Parliament.[30]
In Petrograd, the social democrats' plan had the backing of the Bolsheviks. They had been plotting a revolt against the Provisional Government since April 1917, and pro-Soviet demonstrations during the July Days brought matters to a head. The Helsinki Soviet and the Regional Committee of the Finnish Soviets, led by the Bolshevik Ivar Smilga, both pledged to defend the Finnish Parliament, were it threatened with attack.[31] However, the Provisional Government still had sufficient support in the Russian army to survive and as the street movement waned, Vladimir Lenin fled to Karelia. In the aftermath of these events, the "Law of Supreme Power" was overruled and the social democrats eventually backed down; more Russian troops were sent to Finland and, with the co-operation and insistence of the Finnish conservatives, Parliament was dissolved and new elections announced.[32]
In the October 1917 elections, the social democrats lost their absolute majority, which radicalised the labour movement and decreased support for moderate politics. The crisis of July 1917 did not bring about the Red Revolution of January 1918 on its own, but together with political developments based on the commoners' interpretation of the ideas of Fennomania and socialism, the events favoured a Finnish revolution. In order to win power, the socialists had to overcome Parliament.[33]
The February Revolution resulted in a loss of institutional authority in Finland and the dissolution of the police force, creating fear and uncertainty. In response, both the right and left assembled their own security groups, which were initially local and largely unarmed. By late 1917, following the dissolution of Parliament, in the absence of a strong government and national armed forces, the security groups began assuming a broader and more paramilitary character. The Civil Guards (Finnish: suojeluskunnat; Swedish: skyddskåren; lit. 'protection corps') and the later White Guards (Finnish: valkokaartit; Swedish: vita gardet) were organised by local men of influence: conservative academics, industrialists, major landowners, and activists. The Workers' Order Guards (Finnish: työväen järjestyskaartit; Swedish: arbetarnas ordningsgardet) and the Red Guards (Finnish: punakaartit; Swedish: röda gardet) were recruited through the local social democratic party sections and from the labour unions.[34]
October Revolution
The Bolsheviks' and Vladimir Lenin's October Revolution of 7 November 1917 transferred political power in Petrograd to the radical, left-wing socialists. The German government's decision to arrange safe-conduct for Lenin and his comrades from exile in Switzerland to Petrograd in April 1917, was a success. An armistice between Germany and the Bolshevik regime came into force on 6 December and peace negotiations began on 22 December 1917 at Brest-Litovsk.[35]
November 1917 became another watershed in the 1917–1918 rivalry for the leadership of Finland. After the dissolution of the Finnish Parliament, polarisation between the social democrats and the conservatives increased markedly and the period witnessed the appearance of political violence. An agricultural worker was shot during a local strike on 9 August 1917 at Ypäjä and a Civil Guard member was killed in a local political crisis at Malmi on 24 September.[36] The October Revolution disrupted the informal truce between the Finnish non-socialists and the Russian Provisional Government. After political wrangling over how to react to the revolt, the majority of the politicians accepted a compromise proposal by Santeri Alkio, the leader of the Agrarian League. Parliament seized the sovereign power in Finland on 15 November 1917 based on the socialists' "Law of Supreme Power" and ratified their proposals of an eight-hour working day and universal suffrage in local elections, from July 1917.[37]

The purely non-socialist, conservative-led government of Pehr Evind Svinhufvud was appointed on 27 November. This nomination was both a long-term aim of the conservatives and a response to the challenges of the labour movement during November 1917. Svinhufvud's main aspirations were to separate Finland from Russian rule, to strengthen the Civil Guards, and to return a part of Parliament's new authority to the Senate.[38] There were 149 Civil Guards on 31 August 1917 in Finland, counting local units and subsidiary White Guards in towns and rural communes; 251 on 30 September; 315 on 31 October; 380 on 30 November and 408 on 26 January 1918. The first attempt at serious military training among the Guards was the establishment of a 200-strong cavalry school at the Saksanniemi estate in the vicinity of the town of Porvoo, in September 1917. The vanguard of the Finnish Jägers and German weaponry arrived in Finland during October–November 1917 on the Equity freighter and the German U-boat UC-57; around 50 Jägers had returned by the end of 1917.[39]
After political defeats in July and October 1917, the social democrats put forward an uncompromising program called "We Demand" (Finnish: Me vaadimme; Swedish: Vi kräver) on 1 November, in order to push for political concessions. They insisted upon a return to the political status before the dissolution of Parliament in July 1917, disbandment of the Civil Guards and elections to establish a Finnish Constituent Assembly. The program failed and the socialists initiated a general strike during 14–19 November to increase political pressure on the conservatives, who had opposed the "Law of Supreme Power" and the parliamentary proclamation of sovereign power on 15 November.[40]
Revolution became the goal of the radicalised socialists after the loss of political control, and events in November 1917 offered momentum for a socialist uprising. In this phase, Lenin and Joseph Stalin, under threat in Petrograd, urged the social democrats to take power in Finland. The majority of Finnish socialists were moderate and preferred parliamentary methods, prompting the Bolsheviks to label them "reluctant revolutionaries". The reluctance diminished as the general strike appeared to offer a major channel of influence for the workers in southern Finland. The strike leadership voted by a narrow majority to start a revolution on 16 November, but the uprising had to be called off the same day due to the lack of active revolutionaries to execute it.[41]

At the end of November 1917, the moderate socialists among the social democrats won a second vote over the radicals in a debate over revolutionary versus parliamentary means, but when they tried to pass a resolution to completely abandon the idea of a socialist revolution, the party representatives and several influential leaders voted it down. The Finnish labour movement wanted to sustain a military force of its own and to keep the revolutionary road open, too. The wavering Finnish socialists disappointed V. I. Lenin and in turn, he began to encourage the Finnish Bolsheviks in Petrograd.[42]
Among the labour movement, a more marked consequence of the events of 1917 was the rise of the Workers' Order Guards. There were 20–60 separate guards between 31 August and 30 September 1917, but on 20 October, after defeat in parliamentary elections, the Finnish labour movement proclaimed the need to establish more worker units. The announcement led to a rush of recruits: on 31 October the number of guards was 100–150; 342 on 30 November 1917 and 375 on 26 January 1918. Since May 1917, the paramilitary organisations of the left had grown in two phases, the majority of them as Workers' Order Guards. The minority were Red Guards, these were partly underground groups formed in industrialised towns and industrial centres, such as Helsinki, Kotka and Tampere, based on the original Red Guards that had been formed during 1905–1906 in Finland.[43]
The presence of the two opposing armed forces created a state of dual power and divided sovereignty on Finnish society. The decisive rift between the guards broke out during the general strike: the Reds executed several political opponents in southern Finland and the first armed clashes between the Whites and Reds took place. In total, 34 casualties were reported. Eventually, the political rivalries of 1917 led to an arms race and an escalation towards civil war.[44]
Full independence of Finland
The disintegration of Russia offered Finns a historic opportunity to gain national independence. After the October Revolution, the conservatives were eager for secession from Russia in order to control the left and minimise the influence of the Bolsheviks. The socialists were skeptical about sovereignty under conservative rule, but they feared a loss of support among nationalistic workers, particularly after having promised increased national liberty through the "Law of Supreme Power". Eventually, both political factions supported an independent Finland, despite strong disagreement over the composition of the nation's leadership.[45]
Nationalism had become a "civic religion" in Finland by the end of nineteenth century, but the goal during the general strike of 1905 had been a return to the autonomy of 1809–1898, not full independence. In contrast to their status under the unitary Swedish regime, the domestic power of Finns had increased under the less uniform Russian rule. Economically, the Grand Duchy of Finland benefited from having an independent domestic state budget, a central bank with national currency, the markka (deployed 1860), and customs organisation and the industrial progress of 1860–1916. The economy was dependent on the huge Russian market and separation would disrupt the profitable Finnish financial zone. The economic collapse of Russia and the power struggle of the Finnish state in 1917 were among the key factors that brought sovereignty to the fore in Finland.[46]
Svinhufvud's Senate introduced Finland's Declaration of Independence on 4 December 1917 and Parliament adopted it on 6 December. The social democrats voted against the Senate's proposal, while presenting an alternative declaration of sovereignty. The establishment of an independent state was not a guaranteed conclusion for the small Finnish nation. Recognition by Russia and other great powers was essential; Svinhufvud accepted that he had to negotiate with Lenin for the acknowledgement. The socialists, having been reluctant to enter talks with the Russian leadership in July 1917, sent two delegations to Petrograd to request that Lenin approve Finnish sovereignty.[47]
In December 1917, Lenin was under intense pressure from the Germans to conclude peace negotiations at Brest-Litovsk, and the Bolsheviks' rule was in crisis, with an inexperienced administration and the demoralised army facing powerful political and military opponents. Lenin calculated that the Bolsheviks could fight for central parts of Russia but had to give up some peripheral territories, including Finland in the geopolitically less important north-western corner. As a result, Svinhufvud's delegation won Lenin's concession of sovereignty on 31 December 1917.[48]
By the beginning of the Civil War, Austria-Hungary, Denmark, France, Germany, Greece, Norway, Sweden and Switzerland had recognised Finnish independence. The United Kingdom and United States did not approve it; they waited and monitored the relations between Finland and Germany (the main enemy of the Allies), hoping to override Lenin's regime and to get Russia back into the war against the German Empire. In turn, the Germans hastened Finland's separation from Russian rule so as to move the country to within their sphere of influence.[49]
Warfare

Escalation
The final escalation towards war began in early January 1918, as each military or political action of the Reds or the Whites resulted in a corresponding counteraction by the other. Both sides justified their activities as defensive measures, particularly to their own supporters. On the left, the vanguard of the movement was the urban Red Guards from Helsinki, Kotka and Turku; they led the rural Reds and convinced the socialist leaders who wavered between peace and war to support the revolution. On the right, the vanguard was the Jägers, who had transferred to Finland, and the volunteer Civil Guards of southwestern Finland, southern Ostrobothnia and Viipuri province in the southeastern corner of Finland. The first local battles were fought during 9–21 January 1918 in southern and southeastern Finland, mainly to win the arms race and to control Viipuri.[50]

On 12 January 1918, Parliament authorised the Svinhufvud Senate to establish internal order and discipline on behalf of the state. On 15 January, Carl Gustaf Emil Mannerheim, a former Finnish general of the Imperial Russian Army, was appointed the commander-in-chief of the Civil Guards. The Senate appointed the Guards, henceforth called the White Guards, as the White Army of Finland. Mannerheim placed his Headquarters of the White Army in the Vaasa–Seinäjoki area. The White Order to engage was issued on 25 January. The Whites gained weaponry by disarming Russian garrisons during 21–28 January, in particular in southern Ostrobothnia.[51]
The Red Guards, led by Ali Aaltonen, refused to recognise the Whites' hegemony and established a military authority of their own. Aaltonen installed his headquarters in Helsinki and nicknamed it Smolna echoing the Smolny Institute, the Bolsheviks' headquarters in Petrograd. The Red Order of Revolution was issued on 26 January, and a red lantern, a symbolic indicator of the uprising, was lit in the tower of the Helsinki Workers' House. A large-scale mobilisation of the Reds began late in the evening of 27 January, with the Helsinki Red Guard and some of the Guards located along the Viipuri-Tampere railway having been activated between 23 and 26 January, in order to safeguard vital positions and escort a heavy railroad shipment of Bolshevik weapons from Petrograd to Finland. White troops tried to capture the shipment: 20–30 Finns, Red and White, died in the Battle of Kämärä at the Karelian Isthmus on 27 January 1918.[52] The Finnish rivalry for power had culminated.[53]
Opposing parties
Red Finland and White Finland
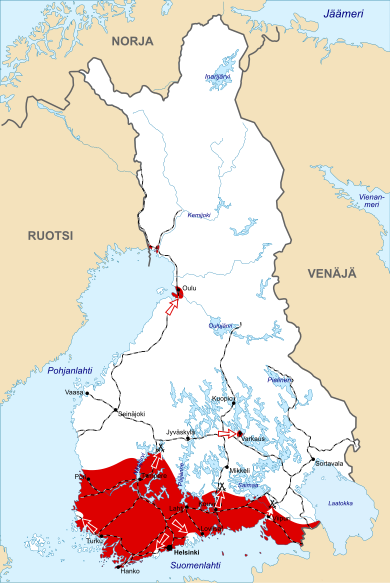
At the beginning of the war, a discontinuous front line ran through southern Finland from west to east, dividing the country into White Finland and Red Finland. The Red Guards controlled the area to the south, including nearly all the major towns and industrial centres, along with the largest estates and farms with the highest numbers of crofters and tenant farmers. The White Army controlled the area to the north, which was predominantly agrarian and contained small or medium-sized farms and tenant farmers. The number of crofters was lower and they held a better social status than those in the south. Enclaves of the opposing forces existed on both sides of the front line: within the White area lay the industrial towns of Varkaus, Kuopio, Oulu, Raahe, Kemi and Tornio; within the Red area lay Porvoo, Kirkkonummi and Uusikaupunki. The elimination of these strongholds was a priority for both armies in February 1918.[54]
Red Finland was led by the Finnish People's Delegation (Finnish: kansanvaltuuskunta; Swedish: folkdelegationen), established on 28 January 1918 in Helsinki, which was supervised by the Central Workers' Council. The delegation sought democratic socialism based on the Finnish Social Democratic Party's ethos; their visions differed from Lenin's dictatorship of the proletariat. Otto Ville Kuusinen formulated a proposal for a new constitution, influenced by those of Switzerland and the United States. With it, political power was to be concentrated to Parliament, with a lesser role for a government. The proposal included a multi-party system; freedom of assembly, speech and press; and the use of referendums in political decision-making. In order to ensure the authority of the labour movement, the common people would have a right to permanent revolution. The socialists planned to transfer a substantial part of property rights to the state and local administrations.[55]
In foreign policy, Red Finland leaned on Bolshevist Russia. A Red-initiated Finno–Russian treaty and peace agreement was signed on 1 March 1918, where Red Finland was called the Finnish Socialist Workers' Republic (Finnish: Suomen sosialistinen työväentasavalta; Swedish: Finlands socialistiska arbetarrepublik). The negotiations for the treaty implied that – as in World War I in general – nationalism was more important for both sides than the principles of international socialism. The Red Finns did not simply accept an alliance with the Bolsheviks and major disputes appeared, for example, over the demarcation of the border between Red Finland and Soviet Russia. The significance of the Russo–Finnish Treaty evaporated quickly due to the signing of the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk between the Bolsheviks and the German Empire on 3 March 1918.[56]
Lenin's policy on the right of nations to self-determination aimed at preventing the disintegration of Russia during the period of military weakness. He assumed that in war-torn, splintering Europe, the proletariat of free nations would carry out socialist revolutions and unite with Soviet Russia later. The majority of the Finnish labour movement supported Finland's independence. The Finnish Bolsheviks, influential, though few in number, favoured annexation of Finland by Russia.[57]
The government of White Finland, Pehr Evind Svinhufvud's first senate, was called the Vaasa Senate after its relocation to the safer west-coast city of Vaasa, which acted as the capital of the Whites from 29 January to 3 May 1918. In domestic policy, the White Senate's main goal was to return the political right to power in Finland. The conservatives planned a monarchist political system, with a lesser role for Parliament. A section of the conservatives had always supported monarchy and opposed democracy; others had approved of parliamentarianism since the revolutionary reform of 1906, but after the crisis of 1917–1918, concluded that empowering the common people would not work. Social liberals and reformist non-socialists opposed any restriction of parliamentarianism. They initially resisted German military help, but the prolonged warfare changed their stance.[58]
In foreign policy, the Vaasa Senate relied on the German Empire for military and political aid. Their objective was to defeat the Finnish Reds; end the influence of Bolshevist Russia in Finland and expand Finnish territory to East Karelia, a geopolitically significant home to people speaking Finnic languages. The weakness of Russia inspired an idea of Greater Finland among the expansionist factions of both the right and left: the Reds had claims concerning the same areas. General Mannerheim agreed on the need to take over East Karelia and to request German weapons, but opposed actual German intervention in Finland. Mannerheim recognised the Red Guards' lack of combat skill and trusted in the abilities of the German-trained Finnish Jägers. As a former Russian army officer, Mannerheim was well aware of the demoralisation of the Russian army. He co-operated with White-aligned Russian officers in Finland and Russia.[59]

Aviation
During the war, the Red Guard utilized aircraft, however, little information regarding their activities and the organisation of detachments was preserved.[60] Its various operations included bombings, reconnaissance, spreading of propaganda literature, and connection flights.[61] Since the Reds had no Finnish pilots, they solely relied on foreign pilots, most of whom were Russian.[60] The Reds had four main operational flight detachments located in Helsinki, Tampere, Kouvola and Viipuri. They divided their detachments into three fronts. The northern front, which was overseen by the detachment in Tampere, consisted of the red troops between the Gulf of Bothnia and Lake Päijänne. The central front was between the Lake Päijänne and Lake Saimaa that was operated by the Kouvola detachment. The base in Viipuri acted as the base for the eastern front, which was located between Lake Saimaa and the national border.[62] Due to poor central command, inadequate fuel quality, low training experience, and poor maintenance, the aerial activity of the Reds was scattered and ineffective.[61]

The White Guard's also had aircraft during the course of the war, which would later evolve into the Finnish Air Force. In February 1918, the Whites would have received an aircraft donation of a reconnaissance and training plane from Sweden, the NAB Type 9 Albatros, however its transport to Vaasa was stopped when the ferry's engine failed at Jakobstad. Therefore, the first plane to officially arrive to the Whites was the license manufactured Morane-Saulnier MS Parasol/Thulin D donated on 6 March 1918 by Swedish Count Eric von Rosen.[63] The aircraft carried Rosen's personal symbol of luck, a right-facing, blue swastika. The symbol was further adopted as the official insignia of the Finnish Air Force till the end of World War II. During the war, the Whites obtained seven additional aircraft which included four Friedrichshafens, two DFWs, and one Rumpler, all of which were bought from Germany. Like the Reds, the Whites also had no domestic pilots and relied on Swedish, Danish, and Russian pilots.[64] The White Guard had two flight detachments during the war; one based at Kolho in northern Pirkanmaa and the other at Antrea in the Viipuri Province. They carried out rather small operations of reconnaissance, leaflet drops, and bombings.[63]
Soldiers and weapons
The number of Finnish troops on each side varied from 70,000 to 90,000 and both had around 100,000 rifles, 300–400 machine guns and a few hundred cannons. While the Red Guards consisted mostly of volunteers, with wages paid at the beginning of the war, the White Army consisted predominantly of conscripts with 11,000–15,000 volunteers. The main motives for volunteering were socio-economic factors, such as salary and food, as well as idealism and peer pressure. The Red Guards included 2,600 women, mostly recruited from the industrial centres and cities of southern Finland. Urban and agricultural workers constituted the majority of the Red Guards, whereas land-owning farmers and well-educated people formed the backbone of the White Army.[65] Both armies used child soldiers, mainly between 14 and 17 years of age. The use of juvenile soldiers was not rare in World War I; children of the time were under the absolute authority of adults and were not shielded against exploitation.[66]
Rifles and machine guns from Imperial Russia were the main armaments of the Reds and the Whites. The most commonly used rifle was the Russian 7.62mm (.30 cal) Mosin–Nagant Model 1891. In total, around ten different rifle models were in service, causing problems for ammunition supply. The Maxim gun was the most-used machine gun, along with the less-used M1895 Colt–Browning, Lewis and Madsen guns. The machine guns caused a substantial part of the casualties in combat. Russian field guns were mostly used with direct fire.[67]
The Civil War was fought primarily along railways; vital means for transporting troops and supplies, as well for using armoured trains, equipped with light cannons and heavy machine guns. The strategically most important railway junction was Haapamäki, approximately 100 kilometres (62 mi) northeast of Tampere, connecting eastern and western Finland and as well as southern and northern Finland. Other critical junctions included Kouvola, Riihimäki, Tampere, Toijala and Viipuri. The Whites captured Haapamäki at the end of January 1918, leading to the Battle of Vilppula.[68]

Red Guards and Soviet troops
The Finnish Red Guards seized the early initiative in the war by taking control of Helsinki on 28 January 1918 and by undertaking a general offensive lasting from February till early March 1918. The Reds were relatively well-armed, but a chronic shortage of skilled leaders, both at the command level and in the field, left them unable to capitalise on this momentum, and most of the offensives came to nothing. The military chain of command functioned relatively well at company and platoon level, but leadership and authority remained weak as most of the field commanders were chosen by the vote of the troops. The common troops were more or less armed civilians, whose military training, discipline and combat morale were both inadequate and low.[69]
Ali Aaltonen was replaced on 28 January 1918 by Eero Haapalainen as commander-in-chief. He, in turn, was displaced by the Bolshevik triumvirate of Eino Rahja, Adolf Taimi and Evert Eloranta on 20 March. The last commander-in-chief of the Red Guard was Kullervo Manner, from 10 April until the last period of the war when the Reds no longer had a named leader. Some talented local commanders, such as Hugo Salmela in the Battle of Tampere, provided successful leadership, but could not change the course of the war. The Reds achieved some local victories as they retreated from southern Finland toward Russia, such as against German troops in the Battle of Syrjäntaka on 28–29 April in Tuulos.[70]
Around 50,000 of the former tsar's army troops were stationed in Finland in January 1918. The soldiers were demoralised and war-weary, and the former serfs were thirsty for farmland set free by the revolutions. The majority of the troops returned to Russia by the end of March 1918. In total, 7,000 to 10,000 Red Russian soldiers supported the Finnish Reds, but only around 3,000, in separate, smaller units of 100–1,000 soldiers, could be persuaded to fight in the front line.[71]
The revolutions in Russia divided the Soviet army officers politically and their attitude towards the Finnish Civil War varied. Mikhail Svechnikov led Finnish Red troops in western Finland in February and Konstantin Yeremejev Soviet forces on the Karelian Isthmus, while other officers were mistrustful of their revolutionary peers and instead co-operated with General Mannerheim, in disarming Soviet garrisons in Finland. On 30 January 1918, Mannerheim proclaimed to Russian soldiers in Finland that the White Army did not fight against Russia, but that the objective of the White campaign was to beat the Finnish Reds and the Soviet troops supporting them.[72]
The number of Soviet soldiers active in the civil war declined markedly once Germany attacked Russia on 18 February 1918. The German-Soviet Treaty of Brest-Litovsk of 3 March restricted the Bolsheviks' support for the Finnish Reds to weapons and supplies. The Soviets remained active on the south-eastern front, mainly in the Battle of Rautu on the Karelian Isthmus between February and April 1918, where they defended the approaches to Petrograd.[73]
White Guards and Sweden's role

While the conflict has been called by some, "The War of Amateurs", the White Army had two major advantages over the Red Guards: the professional military leadership of Gustaf Mannerheim and his staff, which included 84 Swedish volunteer officers and former Finnish officers of the tsar's army; and 1,450 soldiers of the 1,900-strong, Jäger battalion. The majority of the unit arrived in Vaasa on 25 February 1918.[74] On the battlefield, the Jägers, battle-hardened on the Eastern Front, provided strong leadership that made disciplined combat of the common White troopers possible. The soldiers were similar to those of the Reds, having brief and inadequate training. At the beginning of the war, the White Guards' top leadership had little authority over volunteer White units, which obeyed only their local leaders. At the end of February, the Jägers started a rapid training of six conscript regiments.[74]
The Jäger battalion was politically divided, too. Four-hundred-and-fifty –mostly socialist– Jägers remained stationed in Germany, as it was feared they were likely to side with the Reds. White Guard leaders faced a similar problem when drafting young men to the army in February 1918: 30,000 obvious supporters of the Finnish labour movement never showed up. It was also uncertain whether common troops drafted from the small-sized and poor farms of central and northern Finland had strong enough motivation to fight the Finnish Reds. The Whites' propaganda promoted the idea that they were fighting a defensive war against Bolshevist Russians, and belittled the role of the Red Finns among their enemies.[75] Social divisions appeared both between southern and northern Finland and within rural Finland. The economy and society of the north had modernised more slowly than that of the south. There was a more pronounced conflict between Christianity and socialism in the north, and the ownership of farmland conferred major social status, motivating the farmers to fight against the Reds.[76]
Sweden declared neutrality both during World War I and the Finnish Civil War. General opinion, in particular among the Swedish elite, was divided between supporters of the Allies and the Central powers, Germanism being somewhat more popular. Three war-time priorities determined the pragmatic policy of the Swedish liberal-social democratic government: sound economics, with export of iron-ore and foodstuff to Germany; sustaining the tranquility of Swedish society; and geopolitics. The government accepted the participation of Swedish volunteer officers and soldiers in the Finnish White Army in order to block expansion of revolutionary unrest to Scandinavia.[77]
A 1,000-strong paramilitary Swedish Brigade, led by Hjalmar Frisell, took part in the Battle of Tampere and in the fighting south of the town.[78] In February 1918, the Swedish Navy escorted the German naval squadron transporting Finnish Jägers and German weapons and allowed it to pass through Swedish territorial waters. The Swedish socialists tried to open peace negotiations between the Whites and the Reds. The weakness of Finland offered Sweden a chance to take over the geopolitically vital Finnish Åland Islands, east of Stockholm, but the German army's Finland operation stalled this plan.[79]
German intervention

Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších podmienok. Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky použitia.
Antropológia
Aplikované vedy
Bibliometria
Dejiny vedy
Encyklopédie
Filozofia vedy
Forenzné vedy
Humanitné vedy
Knižničná veda
Kryogenika
Kryptológia
Kulturológia
Literárna veda
Medzidisciplinárne oblasti
Metódy kvantitatívnej analýzy
Metavedy
Metodika
Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative
Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších
podmienok.
Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky
použitia.
www.astronomia.sk | www.biologia.sk | www.botanika.sk | www.dejiny.sk | www.economy.sk | www.elektrotechnika.sk | www.estetika.sk | www.farmakologia.sk | www.filozofia.sk | Fyzika | www.futurologia.sk | www.genetika.sk | www.chemia.sk | www.lingvistika.sk | www.politologia.sk | www.psychologia.sk | www.sexuologia.sk | www.sociologia.sk | www.veda.sk I www.zoologia.sk
