
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9


| Part of a series on |
| World trade |
|---|
 |
| Part of a series on |
| Economic systems |
|---|
|
Major types
|
Protectionism, sometimes referred to as trade protectionism, is the economic policy of restricting imports from other countries through methods such as tariffs on imported goods, import quotas, and a variety of other government regulations. Proponents argue that protectionist policies shield the producers, businesses, and workers of the import-competing sector in the country from foreign competitors and raise government revenue. Opponents argue that protectionist policies reduce trade, and adversely affect consumers in general (by raising the cost of imported goods) as well as the producers and workers in export sectors, both in the country implementing protectionist policies and in the countries against which the protections are implemented.[1]
Protectionism has been advocated mainly by parties that hold economic nationalist[a] positions, while economically liberal[b] political parties generally support free trade.[2][3][4][5][6]
There is a consensus among economists that protectionism has a negative effect on economic growth and economic welfare,[7][8][9][10] while free trade and the reduction of trade barriers have a significantly positive effect on economic growth.[8][11][12][13][14][15] Some scholars, such as Douglas Irwin, have implicated protectionism as the cause of some economic crises, most notably the Great Depression.[16] Although trade liberalization can sometimes result in large and unequally distributed losses and gains, and can, in the short run, cause significant economic dislocation of workers in import-competing sectors,[17][18] free trade often lowers the costs of goods and services for both producers and consumers.[19]
Protectionist policies

A variety of policies have been used to achieve protectionist goals. These include:
- Tariffs and import quotas are the most common types of protectionist policies.[20] A tariff is an excise tax levied on imported goods. Originally imposed to raise government revenue, modern tariffs are now used primarily to protect domestic producers and wage rates from lower-priced importers. An import quota is a limit on the volume of a good that may be legally imported, usually established through an import licensing regime.[20]
- Protection of technologies, patents, technical and scientific knowledge [21][22][23]
- Restrictions on foreign direct investment,[24] such as restrictions on the acquisition of domestic firms by foreign investors.[25]
- Administrative barriers: Countries are sometimes accused of using their various administrative rules (e.g., regarding food safety, environmental standards, electrical safety, etc.) as a way to introduce barriers to imports.
- Anti-dumping legislation: "Dumping" is the practice of firms selling to export markets at lower prices than are charged in domestic markets. Supporters of anti-dumping laws argue that they prevent the import of cheaper foreign goods that would cause local firms to close down. However, in practice, anti-dumping laws are usually used to impose trade tariffs on foreign exporters.
- Direct subsidies: Government subsidies (in the form of lump-sum payments or cheap loans) are sometimes given to local firms that cannot compete well against imports. These subsidies are purported to "protect" local jobs and to help local firms adjust to the world markets.
- Export subsidies: Export subsidies are often used by governments to increase exports. Export subsidies have the opposite effect of export tariffs because exporters get payment, which is a percentage or proportion of the value of exported. Export subsidies increase the amount of trade, and in a country with floating exchange rates, have effects similar to import subsidies.
- Exchange rate control: A government may intervene in the foreign exchange market to lower the value of its currency by selling its currency in the foreign exchange market. Doing so will raise the cost of imports and lower the cost of exports, leading to an improvement in its trade balance. However, such a policy is only effective in the short run, as it will lead to higher inflation in the country in the long run, which will, in turn, raise the real cost of exports, and reduce the relative price of imports.
- International patent systems: There is an argument for viewing national patent systems as a cloak for protectionist trade policies at a national level. Two strands of this argument exist: one when patents held by one country form part of a system of exploitable relative advantage in trade negotiations against another, and a second where adhering to a worldwide system of patents confers "good citizenship" status despite 'de facto protectionism'. Peter Drahos explains that "States realized that patent systems could be used to cloak protectionist strategies. There were also reputational advantages for states to be seen to be sticking to intellectual property systems. One could attend the various revisions of the Paris and Berne conventions, participate in the cosmopolitan moral dialogue about the need to protect the fruits of authorial labor and inventive genius...knowing all the while that one's domestic intellectual property system was a handy protectionist weapon."[26]
- Political campaigns advocating domestic consumption (e.g. the "Buy American" campaign in the United States, which could be seen as an extra-legal promotion of protectionism.)
- Preferential governmental spending, such as the Buy American Act, federal legislation which called upon the United States government to prefer US-made products in its purchases.
In the modern trade arena, many other initiatives besides tariffs have been called protectionist. For example, some commentators, such as Jagdish Bhagwati, see developed countries' efforts in imposing their own labor or environmental standards as protectionism. Also, the imposition of restrictive certification procedures on imports is seen in this light.
Further, others point out that free trade agreements often have protectionist provisions such as intellectual property, copyright, and patent restrictions that benefit large corporations. These provisions restrict trade in music, movies, pharmaceuticals, software, and other manufactured items to high-cost producers with quotas from low-cost producers set to zero.[27]
History


In the 18th century, Adam Smith famously warned against the "interested sophistry" of industry, seeking to gain an advantage at the cost of the consumers.[28] Friedrich List saw Adam Smith's views on free trade as disingenuous, believing that Smith advocated for free trade so that British industry could lock out underdeveloped foreign competition.[29]
Some have argued that no major country has ever successfully industrialized without some form of economic protection.[30][31] Economic historian Paul Bairoch wrote that "historically, free trade is the exception and protectionism the rule".[32]
According to economic historians Douglas Irwin and Kevin O'Rourke, "shocks that emanate from brief financial crises tend to be transitory and have a little long-run effect on trade policy, whereas those that play out over longer periods (the early 1890s, early 1930s) may give rise to protectionism that is difficult to reverse. Regional wars also produce transitory shocks that have little impact on long-run trade policy, while global wars give rise to extensive government trade restrictions that can be difficult to reverse."[33]
One study shows that sudden shifts in comparative advantage for specific countries have led some countries to become protectionist: "The shift in comparative advantage associated with the opening up of New World frontiers, and the subsequent "grain invasion" of Europe, led to higher agricultural tariffs from the late 1870s onwards, which as we have seen reversed the move toward freer trade that had characterized mid-nineteenth-century Europe. In the decades after World War II, Japan's rapid rise led to trade friction with other countries. Japan's recovery was accompanied by a sharp increase in its exports of certain product categories: cotton textiles in the 1950s, steel in the 1960s, automobiles in the 1970s, and electronics in the 1980s. In each case, the rapid expansion in Japan's exports created difficulties for its trading partners and the use of protectionism as a shock absorber."[33]
In the United States



According to economic historian Douglas Irwin, a common myth about US trade policy is that low tariffs harmed American manufacturers in the early 19th century and then that high tariffs made the United States into a great industrial power in the late 19th century.[34] A review by The Economist of Irwin's 2017 book Clashing over Commerce: A History of US Trade Policy states:[34]
Political dynamics would lead people to see a link between tariffs and the economic cycle that was not there. A boom would generate enough revenue for tariffs to fall, and when the bust came pressure would build to raise them again. By the time that happened, the economy would be recovering, giving the impression that tariff cuts caused the crash and the reverse generated the recovery. 'Mr. Irwin' also attempts to debunk the idea that protectionism made America a great industrial power, a notion believed by some to offer lessons for developing countries today. As its share of global manufacturing powered from 23% in 1870 to 36% in 1913, the admittedly high tariffs of the time came with a cost, estimated at around 0.5% of GDP in the mid-1870s. In some industries, they might have sped up development by a few years. But American growth during its protectionist period was more to do with its abundant resources and openness to people and ideas.
According to Irwin, tariffs have served three primary purposes in the United States: "to raise revenue for the government, to restrict imports and protect domestic producers from foreign competition, and to reach reciprocity agreements that reduce trade barriers."[35] From 1790 to 1860, average tariffs increased from 20 percent to 60 percent before declining again to 20 percent.[35] From 1861 to 1933, which Irwin characterizes as the "restriction period", the average tariffs increased to 50 percent and remained at that level for several decades. From 1934 onwards, which Irwin characterizes as the "reciprocity period", the average tariff declined substantially until it leveled off at 5 percent.[35]
Economist Paul Bairoch documented that the United States imposed among the highest rates in the world from around the founding of the country until the World War II period, describing the United States as "the mother country and bastion of modern protectionism" since the end of the 18th century and until the post-World War II period.[36] Alexander Hamilton, the first United States Secretary of the Treasury, was of the view, as articulated most famously in his "Report on Manufactures", that developing an industrialized economy was impossible without protectionism because import duties are necessary to shelter domestic "infant industries" until they could achieve economies of scale.[37] The industrial takeoff of the United States occurred under protectionist policies 1816–1848 and under moderate protectionism 1846–1861, and continued under strict protectionist policies 1861–1945.[38] In the late 19th century, higher tariffs were introduced on the grounds that they were needed to protect American wages and to protect American farmers.[39] Between 1824 and the 1940s, the U.S. imposed much higher average tariff rates on manufactured products than did Britain or any other European country, with the exception for a period of time of Spain and Russia.[40] Up until the end of World War II, the United States had the most protectionist economy on Earth.[41]
The Bush administration implemented tariffs on Chinese steel in 2002; according to a 2005 review of existing research on the tariff, all studies found that the tariffs caused more harm than gains to the US economy and employment.[42] The Obama administration implemented tariffs on Chinese tires between 2009 and 2012 as an anti-dumping measure; a 2016 study found that these tariffs had no impact on employment and wages in the US tire industry.[43]
In 2018, EU Trade Commissioner Cecilia Malmström stated that the US was "playing a dangerous game" in applying tariffs on steel and aluminum imports from most countries and stated that she saw the Trump administration's decision to do so as both "pure protectionist" and "illegal".[44]
The tariffs imposed by the Trump administration during the China–United States trade war led to a reduction in the United States trade deficit with China.[45]
Europe
In the United Kingdom
Great Britain, and England in particular, became one of the most prosperous economic regions in the world between the late 1600s and early 1800s as a result of being the birthplace of the industrial revolution that began in the mid-eighteenth century.[46] The government protected its merchants—and kept others out—by trade barriers, regulations, and subsidies to domestic industries in order to maximize exports from and minimize imports to the realm. The Navigation Acts of the late 17th century required all trade to be carried in English ships, manned by English crews (this later encompassed all Britons after the Acts of Union 1707 united Scotland with England).[47] Colonists were required to send their produce and raw materials first of all to Britain, where the surplus was then sold-on by British merchants to other colonies in the British empire or bullion-earning external markets. The colonies were forbidden to trade directly with other nations or rival empires. The goal was to maintain the North American and Caribbean colonies as dependent agricultural economies geared towards producing raw materials for export to Britain. The growth of native industry was discouraged, in order to keep the colonies dependent on the United Kingdom for their finished goods.[48][49] From 1815 to 1870, the United Kingdom reaped the benefits of being the world's first modern, industrialised nation. It described itself as "the workshop of the world", meaning that its finished goods were produced so efficiently and cheaply that they could often undersell comparable, locally manufactured goods in almost any other market.[50]
By the 1840s, the United Kingdom had adopted a free-trade policy, meaning open markets and no tariffs throughout the empire.[51] The Corn Laws were tariffs and other trade restrictions on imported food and corn enforced in the United Kingdom between 1815 and 1846, and enhanced the profits and political power associated with land ownership. The laws raised food prices and the costs of living for the British public, and hampered the growth of other British economic sectors, such as manufacturing, by reducing the disposable income of the British public.[52] The Prime Minister, Sir Robert Peel, a Conservative, achieved repeal in 1846 with the support of the Whigs in Parliament, overcoming the opposition of most of his own party.
The possessions of the East India Company in India, known as British India, was the centrepiece of the British Empire, and because of an efficient taxation system it paid its own administrative expenses as well as the cost of the large British Indian Army. In terms of trade, India turned only a small profit for British business.[53] However, transfers to the British government was massive: in 1801 unrequited (unpaid, or paid from Indian-collected revenue) was about 30% of British domestic savings available for capital formation in the United Kingdon.[54][55]
By the late nineteenth century, the United Kingdom was the quintessential free-trade country. However, that did not mean that it was unaffected by foreign tariffs, especially those of the United States under the McKinley Tariff and Dingley Tariff.[56] Economic historian Brian Varian estimated that, but for the protectionism in british overseas markets, the United Kingdom exports would have been 57% higher in 1902.[57]
By the interwar era, the United Kingdom began to drift away from free trade. There was a piecemeal erosion of free trade in the 1920s, including under the system of so-called safeguarding duties.[58][59][60] Then, with the Import Duties Act of 1932, the United Kingdom moved in a decisively protectionist direction.[61][62]
In continental Europe
Europe became increasingly protectionist during the eighteenth century.[63] Economic historians Findlay and O'Rourke write that in "the immediate aftermath of the Napoleonic Wars, European trade policies were almost universally protectionist", with the exceptions being smaller countries such as the Netherlands and Denmark.[63]
Europe increasingly liberalized its trade during the 19th century.[64] Countries such as the Netherlands, Denmark, Portugal and Switzerland, and arguably Sweden and Belgium, had fully moved towards free trade prior to 1860.[64] Economic historians see the repeal of the Corn Laws in 1846 as the decisive shift toward free trade in Britain.[64][65] A 1990 study by the Harvard economic historian Jeffrey Williamson showed that the Corn Laws (which imposed restrictions and tariffs on imported grain) substantially increased the cost of living for British workers, and hampered the British manufacturing sector by reducing the disposable incomes that British workers could have spent on manufactured goods.[66] The shift towards liberalization in Britain occurred in part due to "the influence of economists like David Ricardo", but also due to "the growing power of urban interests".[64]
Findlay and O'Rourke characterize 1860 Cobden Chevalier treaty between France and the United Kingdom as "a decisive shift toward European free trade."[64] This treaty was followed by numerous free trade agreements: "France and Belgium signed a treaty in 1861; a Franco-Prussian treaty was signed in 1862; Italy entered the "network of Cobden-Chevalier treaties" in 1863 (Bairoch 1989, 40); Switzerland in 1864; Sweden, Norway, Spain, the Netherlands, and the Hanseatic towns in 1865; and Austria in 1866. By 1877, less than two decades after the Cobden Chevalier treaty and three decades after British Repeal, Germany "had virtually become a free trade country" (Bairoch, 41). Average duties on manufactured products had declined to 9–12% on the Continent, a far cry from the 50% British tariffs, and numerous prohibitions elsewhere, of the immediate post-Waterloo era (Bairoch, table 3, p. 6, and table 5, p. 42)."[64]
Some European powers did not liberalize during the 19th century, such as the Russian Empire and Austro-Hungarian Empire which remained highly protectionist. The Ottoman Empire also became increasingly protectionist.[67] In the Ottoman Empire's case, however, it previously had liberal free trade policies during the 18th to early 19th centuries, which British prime minister Benjamin Disraeli cited as "an instance of the injury done by unrestrained competition" in the 1846 Corn Laws debate, arguing that it destroyed what had been "some of the finest manufacturers of the world" in 1812.[36]
The countries of Western Europe began to steadily liberalize their economies after World War II and the protectionism of the interwar period,[63] but John Tsang, then Hong Kong's Secretary for Commerce, Industry and Technology and chair of the Sixth Ministerial Conference of the World Trade Organization, MC6, commented in 2005 that the EU spent around €70 billion per year on "trade-distorting support".[68]
In Canada
Since 1971 Canada has protected producers of eggs, milk, cheese, chicken, and turkey with a system of supply management. Though prices for these foods in Canada exceed global prices, the farmers and processors have had the security of a stable market to finance their operations.[citation needed] Doubts about the safety of bovine growth hormone, sometimes used to boost dairy production, led to hearings before the Senate of Canada, resulting in a ban in Canada. Thus, supply management of milk products is consumer protection of Canadians.[69]
In Latin America
Most Latin American countries gained independence in the early 19th century, with notable exceptions including Spanish Cuba and Spanish Puerto Rico. Following the achievement of their independence, most of the Latin American countries adopted protectionism. They both feared that any foreign competition would stomp out their newly created state and believed that lack of outside resources would drive domestic production.[70] The protectionist behavior continued up until and during the World Wars. During World War 2, Latin America had, on average, the highest tariffs in the world.[71][72]
Argentina
Juan Perón erected a system of almost complete protectionism against imports, largely cutting off Argentina from the international market in the 1940s. Protectionism created a domestically oriented industry with high production costs, incapable of competing in international markets. At the same time, output of beef and grain, the country's main export goods, stagnated.[73] The IAPI began shortchanging growers and, when world grain prices dropped in the late 1940s, it stifled agricultural production, exports and business sentiment, in general.[74] Despite these shortcomings, protectionism and government credits did allow an exponential growth of the internal market: radio sales increased 600% and fridge sales grew 218%, among others.[75] During this period Argentina's economy continued to grow, on average, but more slowly than the world as a whole or than its neighbors, Brazil and Chile. By 1950, Argentina's GDP per capita accounted fell to less than half of that of the United States.[76]
Impact
There is a broad consensus among economists that protectionism has a negative effect on economic growth and economic welfare, while free trade and the reduction of trade barriers has a positive effect on economic growth.[11][12][13][8][77][78][79] However, protectionism can be used to raise government revenue and enable access to intellectual property, including essential medicines.[80]
Protectionism is frequently criticized by economists as harming the people it is intended to help. Mainstream economists instead support free trade.[28][81] The principle of comparative advantage shows that the gains from free trade outweigh any losses as free trade creates more jobs than it destroys because it allows countries to specialize in the production of goods and services in which they have a comparative advantage.[82] Protectionism results in deadweight loss; this loss to overall welfare gives no-one any benefit, unlike in a free market, where there is no such total loss. Economist Stephen P. Magee claims the benefits of free trade outweigh the losses by as much as 100 to 1.[83]
Armed conflicts
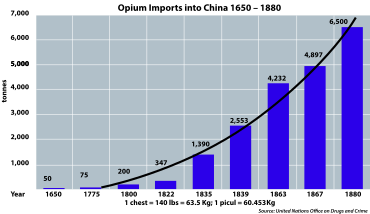
Protectionism has been accused of being one of the major causes of war. Proponents of this theory point to the constant warfare in the 17th and 18th centuries among European countries whose governments were predominantly mercantilist and protectionist, the American Revolution, which came about ostensibly due to British tariffs and taxes. According to a slogan of Frédéric Bastiat (1801–1850), "When goods cannot cross borders, armies will."[84]
On the other hand, archaeologist Lawrence H. Keeley argues in his book War Before Civilization that disputes between trading partners escalate to war more frequently than disputes between nations that don't trade much with each other.[85] The Opium Wars were fought between the UK[c] and China over the right of British merchants to engage in the free trade of opium. For many opium users, what started as recreation soon became a punishing addiction: many people who stopped ingesting opium suffered chills, nausea, and cramps, and sometimes died from withdrawal. Once addicted, people would often do almost anything to continue to get access to the drug.[86]
Barbara Tuchman says both European intellectuals and leaders overestimated the power of free trade on the eve of World War I. They believed that the interconnectedness of European nations through trade would stop a continent-wide war from breaking out, as the economic consequences would be too great. However, the assumption proved incorrect. For example, Tuchman noted that Helmuth von Moltke the Younger, when warned of such consequences, refused to even consider them in his plans, arguing he was a "soldier," not an "economist."[87]
The ongoing Russo-Ukraine War began in the aftermath of the Revolution of Dignity and the signing of the European Union–Ukraine Association Agreement in 2014, which included a Deep and Comprehensive Free Trade Area for Ukraine and the European Union (EU).[88]
Positive impacts
Intellectual property
The Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) is an international legal agreement between all the member nations of the World Trade Organization (WTO). It establishes minimum standards for the regulation by national governments of different forms of intellectual property (IP) as applied to nationals of other WTO member nations.[89] TRIPS was negotiated at the end of the Uruguay Round of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT)[d] between 1989 and 1990[90] and is administered by the WTO. Statements by the World Bank indicate that TRIPS has not led to a demonstrable acceleration of investment to low-income countries, though it may have done so for middle-income countries.[91]
Critics argue that TRIPS limits the ability of governments to introduce competition for generic producers.[92] The TRIPS agreement allows the grant of compulsory licenses at a nation's discretion. TRIPS-plus conditions in the United States' FTAs with Australia, Jordan, Singapore and Vietnam have restricted the application of compulsory licenses to emergency situations, antitrust remedies, and cases of public non-commercial use.[92]
Access to essential medicines
One of the most visible conflicts over TRIPS has been AIDS drugs in Africa. Despite the role that patents have played in maintaining higher drug costs for public health programs across Africa, this controversy has not led to a revision of TRIPS. Instead, an interpretive statement, the Doha Declaration, was issued in November 2001, which indicated that TRIPS should not prevent states from dealing with public health crises and allowed for compulsory licenses. After Doha, PhRMA, the United States and to a lesser extent other developed nations began working to minimize the effect of the declaration.[93]
In 2020, conflicts re-emerged over patents, copyrights and trade secrets related to COVID-19 vaccines, diagnostics and treatments. South Africa and India proposed that WTO grant a temporary waiver to enable more widespread production of the vaccines, since suppressing the virus as quickly as possible benefits the entire world.[94][95] The waivers would be in addition to the existing, but cumbersome, flexibilities in TRIPS allowing countries to impose compulsory licenses.[96][97] Over 100 developing nations supported the waiver but it was blocked by the G7 members.[98] This blocking was condemned by 400 organizations including Doctors Without Borders and 115 members of the European Parliament.[99] In June 2022, after extensive involvement of the European Union, the WTO instead adopted a watered-down agreement that focuses only on vaccine patents, excludes high-income countries and China, and contains few provisions that are not covered by existing flexibilities.[100][101]
Government Revenue
Proponents of protectionism argue that tariffs raise government revenue via customs. Developing countries, including least developed countries (LDCs), often do not collect income taxes because personal incomes are often too low to tax and they lack the capability to collect such taxes from individuals.[102]
United States
| U.S. Historical Tariffs (Customs) and Tax Collections by the Federal Government | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(All dollar amounts are in millions of U.S. dollars)
| ||||||
| Year | Tariff Income |
Budget % Tariff |
Federal Receipts |
Income Tax |
Payroll Tax |
Average Tariff |
| 1792 | $4.4 | 95.0% | $4.6 | $- | $- | 15.1% |
| 1795 | $5.6 | 91.6% | $6.1 | $- | $- | 8.0% |
| 1800 | $9.1 | 83.7% | $10.8 | $- | $- | 10.0% |
| 1805 | $12.9 | 95.4% | $13.6 | $- | $- | 10.7% |
| 1810 | $8.6 | 91.5% | $9.4 | $- | $- | 10.1% |
| 1815 | $7.3 | 46.4% | $15.7 | $- | $- | 6.5% |
| 1820 | $15.0 | 83.9% | $17.9 | $- | $- | 20.2% |
| 1825 | $20.1 | 97.9% | $20.5 | $- | $- | 22.3% |
| 1830 | $21.9 | 88.2% | $24.8 | $- | $- | 35.0% |
| 1835 | $19.4 | 54.1% | $35.8 | $- | $- | 14.2% |
| 1840 | $12.5 | 64.2% | $19.5 | $- | $- | 12.7% |
| 1845 | $27.5 | 91.9% | $30.0 | $- | $- | 24.3% |
| 1850 | $39.7 | 91.0% | $43.6 | $- | $- | 22.9% |
| 1855 | $53.0 | 81.2% | $65.4 | $- | $- | 20.6% |
| 1860 | $53.2 | 94.9% | $56.1 | $- | $- | 15.0% |
| 1863 | $63.0 | 55.9% | $112.7 | $- | $- | 25.9% |
| 1864 | $102.3 | 38.7% | $264.6 | $- | $- | 32.3% |
| 1865 | $84.9 | 25.4% | $333.7 | $61.0 | $- | 35.6% |
| 1870 | $194.5 | 47.3% | $411.3 | $37.8 | $- | 44.6% |
