A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
This article needs additional citations for verification. (August 2014) |
| Part of a series on |
| Taxation |
|---|
 |
| An aspect of fiscal policy |
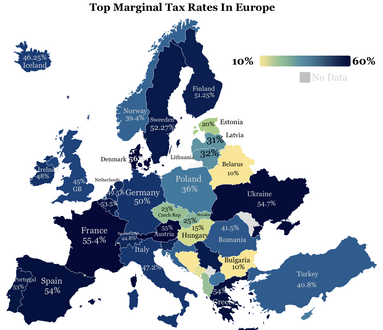
This is a list of the maximum potential tax rates around Europe for certain income brackets. It is focused on three types of taxes: corporate, individual, and value added taxes (VAT). It is not intended to represent the true tax burden to either the corporation or the individual in the listed country.
Graphs
-
Top Marginal Tax Rates In Europe 2022
-
Payroll and income tax by OECD Country (2021)
-
Federal Sales Taxes
Summary list
The quoted income tax rate is, except where noted, the top rate of tax: most jurisdictions have lower rate of taxes for low levels of income. Some countries also have lower rates of corporation tax for smaller companies. In 1980, the top rates of most European countries were above 60%. Today most European countries have rates below 50%.[1]
| Country | Corporate tax | Maximum income tax rate | Standard VAT rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Albania[2] | 15% | 23%[3] | 20% |
| Andorra | 10% | 10% | 4.5% |
| Armenia[4] | 18% | 22% | 20% |
| Austria | 25% | 55%[5] | 20%[6] (Reduced rates 10% + 13%)[7] |
| Belarus | 18% | 15% | 20%[2] |
| Belgium[8] | 25% (For SME's 20% from 2018 on the first €100,000 profit)[9] | 50% (excluding 13.07% social security paid by the employee and also excluding 32% social security paid by the employer) | 21% (Reduced rates of 6% and 12%)[6] |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina[10][11][12] | 10% | 10% | 17% |
| Bulgaria[13] | 10% | 40.8% (10% income tax + additional 12.9% by the employee for social security contributions, i.e. health insurance, pension and unemployment fund); and additional 17.9% by the employer for various social security contributions)[14] | 20%[6] (Reduced rates 9%)[7] |
| Croatia | 18% (Reduced rate 10% for small business) | 15% to 35,4% (depending on the income and municipality) | 25% (Reduced rates 13% + 5%)(Reduced rates 9%)[7] |
| Cyprus | 12.5% | 35% | 19% (Reduced rates 5% + 9%)(Reduced rates 9%)[7] |
| Czech Republic | 21% | 34% (15% or 23% tax, 4,5% health insurance, 6,5% social security) + additional payments by employer (11,5% healthcare, 24,8% social security) | 21% (reduced rate 12%)[6] |
| Denmark | 22% | 56% (avg commune) (including 8% social security paid by the employee but excluding 0.42–1.48% church tax imposed on members of the national Church of Denmark) | 25% (reduced rate 0% on transportation of passengers and newspapers normally published at a rate of more than one issue per month)[6] |
| Estonia | 0% on undistributed profits. 20% CIT on distributed profit. 14% on regular distribution.[15] | 57.8% (20% income tax + 2.4% of unemployment insurance tax, 0.8% paid by employer, 1.6% paid by employee and 33% social security which is paid before gross wage by employer), around 57,8% in total | 22% (reduced rate 9%)[6] |
| Finland | 20% | 67% to 25% depending on the net income and municipality, including 7.8%[16][17][18] social insurance fees, employee unemployment payment and employer unemployment payment, which is on average 18% (2018).[16] | 24%[6][19] (reduced rate of 14% for groceries and restaurants, 10% for books, medicine, transport of passengers and some others) |
| France | 30% (including social contributions) after 2018 ('PFU'), before: 33.3% (36.6% above €3.5M, 15% below €38k)[20] | 49% (45% +4% for annual incomes above €250,000 for single taxpayers or above €500,000 for married couples) [21] + social security and social contribution taxes at various rates, for example 17,2 % for capital gains, interests and dividends. | 20% (reduced rate of 10%, 5.5%, 2.1% and 0% for specific cases like some food, transportation, cultural goods, etc.)[6][22] |
| Germany | 22.825% (few small villages) to 32.925% (in Munich) depending on the municipality. This includes the 15% CIT, 5.5% solidarity surcharge plus the trade tax payable to the municipality. | 47.475% which includes 45% income tax and 5.5% solidarity surcharge based on the total tax bill for incomes above €256,304. The entry tax rate is 14% for incomes exceeding the basic annual threshold of €9,000. | 19% (reduced rate of 7% applies e.g. on sales of certain foods, books and magazines, flowers and transports)[6] |
| Georgia | 15% | 18% | |
| Greece | 24% | 65.67% (45% for >€40,000+ 7.5% Solidarity Tax for >€40000)+(26.95% Social Security for employees or up to 47.95% for private professionals) | 24%[6] (Reduced rates 13% and 5%)[7] |
| Hungary | 9% | Total: 43.16%
Employee: 33.5% of gross salary (Employee expenses altogether of gross salary without children: 15% Income Tax (flat), Social Security: 10% Pension, 3% in cash + 4% in kind healthcare, 1.5% Labor Market contributions)[23] Employer: 17% in addition to gross salary (15.5% Social Tax, 1.5% Training Fund Contribution)[24] |
27%[6][25][26] (Reduced rates 18% and 5%)[7] |
| Iceland | 20%[27] | 36.94% from 0 - 834.707 and 46.24% over 834.707 kr (2017)[28] | 24% (12% reduced rate)[27] |
| Ireland | 12.5% for trading income
25% for non-trading income |
40% over €40,000 for single, €49,000 for married taxpayers.Plus USC(Universal Social Charge)4.5% on income up to €70,044 and 8% on balance. Social insurance 4% | 23% [29] |
| Isle of Man | 0%[30] | 20% plus national insurance of under 12.8%[30] | Same as United Kingdom (see below)[31] |
| Italy | 27.9% (24% plus 3.9% municipal) | 45.83% (43% income tax + 2.03% regional income tax + 0.8% municipal income tax) | 22%[6] (Reduced rates 10%, 5%, 4%)[7] |
| Latvia | 20% CIT on distributed profit. 0% on undistributed profits. 15% on small businesses[32] | 20%(income tax) 35.09%(social insurance)[33] Total up to 55.09% | 21% (reduced rates 12% and 0%)[34] |
| Liechtenstein | 12.5% [35] | 28% (max. 8% national and 20% municipal income tax) plus 4% of the taxpayer's net worth is subject to the same rate as wealth tax. 0% on capital gains. | 8% / 2.5% (till 31.12.2017) 7.7% / 2.5% (from 01.01.2018)[36] |
| Lithuania | 15% (5% for small businesses)[37] | 44.27% (effective tax rates: 34.27% social insurance (nominally it is 1.77% payable by employer + 19.5% payable by employee + from 1.8% to 3% optional accumulation of pence), 20% income | 21% (Reduced rates 5%, 9%)[7] |
| Luxembourg | 24.94% (commercial activity); 5.718% on intellectual property income, royalties. | 45.78% (42% income tax + 9% solidarity surcharge calculated on the income tax)[38] | 17%[6] (Reduced rates 3%, 8%, 14%)[7] |
| Republic of North Macedonia[39] | 10% | 37% [40] (includes income tax 10%, mandatory state pension 18%, mandatory public health insurance 7.3%, mandatory unemployment insurance 1.2%, mandatory personal injury insurance 0.5%) | 18% |
| Malta | 35% (6/7 or 5/7 tax refunds gives an effective rate of 5% or 10% for most companies[41]) | 35% (additional 10% by the employee for social security contributions, i.e. health insurance, pension and education); and additional 10% by the employer for various social security contributions) | 18%[6] (Reduced rates 5%, 7% and 0% for life necessities – groceries, water, prescription medications, medical equipment and supplies, public transport, children's education fees) [7] |
| Monaco | 0% (>75% revenue within Monaco) or 33.33%[42] | ||
| Moldova | 12% or 7% for IT businesses [43] | ||
| Montenegro | 9%[44] | 12.65% (11% income tax + 15% of the income tax bill to the municipality)[44] | 21%[44] |
| Netherlands | 19% for the first €200.000 of profit, 25,8% for the rest.[45] | 49.5%[46] (excluding income dependent bracket discount for incomes up to €98.604[47]) | 21%[48] (reduced rate of 9% and 0% for some goods and services) |
| Norway[49][50] | 22%[51] | 46.4% (53.0% including 14.1% social security contribution by employer. All taxes include 8.2% pension fund payments). | 25% (reduced rate of 15% for groceries, and 10% for transport and culture.) |
| Poland | 19% (Reduced rate 9% for small business since 01.01.2019) | 17% up to 120 000 zł (from 1.01.2022)
32% above 120 000 zł (~25 000 euro) |
23% (reduced rates of 5% and 8%)[6] |
| Portugal | 21% + 3 to 9% depending on profit | 48% + 5% solidarity surcharge + 11% social security (paid by the employee) + 23,75% (social security paid by the company) | 23% (reduced rates 13% and 6%) |
| Romania | Revenue <€1m & at least one employee: 1% of all sales + 8% on dividends Revenue >€1m or no employee: 16% on profit + 8% on dividends |
Employee: 41.5% - Gross incomes below RON 3,600 benefit from personal deductions of up to RON 1,310 from taxable income. Employer: 2.25% (compulsory work insurance)[52] |
19% (reduced rates of 9% and 5%)[53] |
| Russia | 20% | Zdroj:https://en.wikipedia.org?pojem=Tax_rates_in_Europe