
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9

Heritability is a statistic used in the fields of breeding and genetics that estimates the degree of variation in a phenotypic trait in a population that is due to genetic variation between individuals in that population.[1] The concept of heritability can be expressed in the form of the following question: "What is the proportion of the variation in a given trait within a population that is not explained by the environment or random chance?"[2]
Other causes of measured variation in a trait are characterized as environmental factors, including observational error. In human studies of heritability these are often apportioned into factors from "shared environment" and "non-shared environment" based on whether they tend to result in persons brought up in the same household being more or less similar to persons who were not.
Heritability is estimated by comparing individual phenotypic variation among related individuals in a population, by examining the association between individual phenotype and genotype data,[3][4] or even by modeling summary-level data from genome-wide association studies (GWAS).[5] Heritability is an important concept in quantitative genetics, particularly in selective breeding and behavior genetics (for instance, twin studies). It is the source of much confusion due to the fact that its technical definition is different from its commonly-understood folk definition. Therefore, its use conveys the incorrect impression that behavioral traits are "inherited" or specifically passed down through the genes.[6] Behavioral geneticists also conduct heritability analyses based on the assumption that genes and environments contribute in a separate, additive manner to behavioral traits.[7]
Overview
Heritability measures the fraction of phenotype variability that can be attributed to genetic variation. This is not the same as saying that this fraction of an individual phenotype is caused by genetics. For example, it is incorrect to say that since the heritability of personality traits is about 0.6, that means that 60% of your personality is inherited from your parents and 40% comes from the environment. In addition, heritability can change without any genetic change occurring, such as when the environment starts contributing to more variation. As a case in point, consider that both genes and environment have the potential to influence intelligence. Heritability could increase if genetic variation increases, causing individuals to show more phenotypic variation, like showing different levels of intelligence. On the other hand, heritability might also increase if the environmental variation decreases, causing individuals to show less phenotypic variation, like showing more similar levels of intelligence. Heritability increases when genetics are contributing more variation or because non-genetic factors are contributing less variation; what matters is the relative contribution. Heritability is specific to a particular population in a particular environment. High heritability of a trait, consequently, does not necessarily mean that the trait is not very susceptible to environmental influences.[8] Heritability can also change as a result of changes in the environment, migration, inbreeding, or the way in which heritability itself is measured in the population under study.[9] The heritability of a trait should not be interpreted as a measure of the extent to which said trait is genetically determined in an individual.[10][11]
The extent of dependence of phenotype on environment can also be a function of the genes involved. Matters of heritability are complicated because genes may canalize a phenotype, making its expression almost inevitable in all occurring environments. Individuals with the same genotype can also exhibit different phenotypes through a mechanism called phenotypic plasticity, which makes heritability difficult to measure in some cases. Recent insights in molecular biology have identified changes in transcriptional activity of individual genes associated with environmental changes. However, there are a large number of genes whose transcription is not affected by the environment.[12]
Estimates of heritability use statistical analyses to help to identify the causes of differences between individuals. Since heritability is concerned with variance, it is necessarily an account of the differences between individuals in a population. Heritability can be univariate – examining a single trait – or multivariate – examining the genetic and environmental associations between multiple traits at once. This allows a test of the genetic overlap between different phenotypes: for instance hair color and eye color. Environment and genetics may also interact, and heritability analyses can test for and examine these interactions (GxE models).
A prerequisite for heritability analyses is that there is some population variation to account for. This last point highlights the fact that heritability cannot take into account the effect of factors which are invariant in the population. Factors may be invariant if they are absent and do not exist in the population, such as no one having access to a particular antibiotic, or because they are omni-present, like if everyone is drinking coffee. In practice, all human behavioral traits vary and almost all traits show some heritability.[13]
Definition
Any particular phenotype can be modeled as the sum of genetic and environmental effects:[14]
- Phenotype (P) = Genotype (G) + Environment (E).
Likewise the phenotypic variance in the trait – Var (P) – is the sum of effects as follows:
- Var(P) = Var(G) + Var(E) + 2 Cov(G,E).
In a planned experiment Cov(G,E) can be controlled and held at 0. In this case, heritability, is defined as[15]
H2 is the broad-sense heritability. This reflects all the genetic contributions to a population's phenotypic variance including additive, dominant, and epistatic (multi-genic interactions), as well as maternal and paternal effects, where individuals are directly affected by their parents' phenotype, such as with milk production in mammals.
A particularly important component of the genetic variance is the additive variance, Var(A), which is the variance due to the average effects (additive effects) of the alleles. Since each parent passes a single allele per locus to each offspring, parent-offspring resemblance depends upon the average effect of single alleles. Additive variance represents, therefore, the genetic component of variance responsible for parent-offspring resemblance. The additive genetic portion of the phenotypic variance is known as Narrow-sense heritability and is defined as
An upper case H2 is used to denote broad sense, and lower case h2 for narrow sense.
For traits which are not continuous but dichotomous such as an additional toe or certain diseases, the contribution of the various alleles can be considered to be a sum, which past a threshold, manifests itself as the trait, giving the liability threshold model in which heritability can be estimated and selection modeled.
Additive variance is important for selection. If a selective pressure such as improving livestock is exerted, the response of the trait is directly related to narrow-sense heritability. The mean of the trait will increase in the next generation as a function of how much the mean of the selected parents differs from the mean of the population from which the selected parents were chosen. The observed response to selection leads to an estimate of the narrow-sense heritability (called realized heritability). This is the principle underlying artificial selection or breeding.
Example
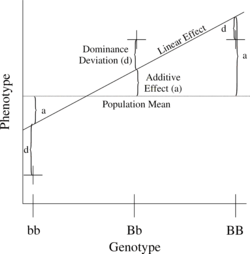
The simplest genetic model involves a single locus with two alleles (b and B) affecting one quantitative phenotype.
The number of B alleles can be 0, 1, or 2. For any genotype, (Bi,Bj), where Bi and Bj are either 0 or 1, the expected phenotype can then be written as the sum of the overall mean, a linear effect, and a dominance deviation (one can think of the dominance term as an interaction between Bi and Bj):
The additive genetic variance at this locus is the weighted average of the squares of the additive effects:
where
There is a similar relationship for the variance of dominance deviations:
where
The linear regression of phenotype on genotype is shown in Figure 1.
Assumptions
Estimates of the total heritability of human traits assume the absence of epistasis, which has been called the "assumption of additivity". Although some researchers have cited such estimates in support of the existence of "missing heritability" unaccounted for by known genetic loci, the assumption of additivity may render these estimates invalid.[16] There is also some empirical evidence that the additivity assumption is frequently violated in behavior genetic studies of adolescent intelligence and academic achievement.[17]
Estimating heritability
Since only P can be observed or measured directly, heritability must be estimated from the similarities observed in subjects varying in their level of genetic or environmental similarity. The statistical analyses required to estimate the genetic and environmental components of variance depend on the sample characteristics. Briefly, better estimates are obtained using data from individuals with widely varying levels of genetic relationship - such as twins, siblings, parents and offspring, rather than from more distantly related (and therefore less similar) subjects. The standard error for heritability estimates is improved with large sample sizes.
In non-human populations it is often possible to collect information in a controlled way. For example, among farm animals it is easy to arrange for a bull to produce offspring from a large number of cows and to control environments. Such experimental control is generally not possible when gathering human data, relying on naturally occurring relationships and environments.
In classical quantitative genetics, there were two schools of thought regarding estimation of heritability.
One school of thought was developed by Sewall Wright at The University of Chicago, and further popularized by C. C. Li (University of Chicago) and J. L. Lush (Iowa State University). It is based on the analysis of correlations and, by extension, regression. Path Analysis was developed by Sewall Wright as a way of estimating heritability.
The second was originally developed by R. A. Fisher and expanded at The University of Edinburgh, Iowa State University, and North Carolina State University, as well as other schools. It is based on the analysis of variance of breeding studies, using the intraclass correlation of relatives. Various methods of estimating components of variance (and, hence, heritability) from ANOVA are used in these analyses.
Today, heritability can be estimated from general pedigrees using linear mixed models and from genomic relatedness estimated from genetic markers.
Studies of human heritability often utilize adoption study designs, often with identical twins who have been separated early in life and raised in different environments. Such individuals have identical genotypes and can be used to separate the effects of genotype and environment. A limit of this design is the common prenatal environment and the relatively low numbers of twins reared apart. A second and more common design is the twin study in which the similarity of identical and fraternal twins is used to estimate heritability. These studies can be limited by the fact that identical twins are not completely genetically identical, potentially resulting in an underestimation of heritability.
In observational studies, or because of evocative effects (where a genome evokes environments by its effect on them), G and E may covary: gene environment correlation. Depending on the methods used to estimate heritability, correlations between genetic factors and shared or non-shared environments may or may not be confounded with heritability.[18]
Regression/correlation methods of estimation
The first school of estimation uses regression and correlation to estimate heritability.
Comparison of close relatives
In the comparison of relatives, we find that in general,
where r can be thought of as the coefficient of relatedness, b is the coefficient of regression and t is the coefficient of correlation.
Parent-offspring regression

Heritability may be estimated by comparing parent and offspring traits (as in Fig. 2). The slope of the line (0.57) approximates the heritability of the trait when offspring values are regressed against the average trait in the parents. If only one parent's value is used then heritability is twice the slope. (This is the source of the term "regression," since the offspring values always tend to regress to the mean value for the population, i.e., the slope is always less than one). This regression effect also underlies the DeFries–Fulker method for analyzing twins selected for one member being affected.[19]
Sibling comparison
A basic approach to heritability can be taken using full-Sib designs: comparing similarity between siblings who share both a biological mother and a father.[20] When there is only additive gene action, this sibling phenotypic correlation is an index of familiarity – the sum of half the additive genetic variance plus full effect of the common environment. It thus places an upper limit on additive heritability of twice the full-Sib phenotypic correlation. Half-Sib designs compare phenotypic traits of siblings that share one parent with other sibling groups.
Twin studies

Heritability for traits in humans is most frequently estimated by comparing resemblances between twins. "The advantage of twin studies, is that the total variance can be split up into genetic, shared or common environmental, and unique environmental components, enabling an accurate estimation of heritability".[21] Fraternal or dizygotic (DZ) twins on average share half their genes (assuming there is no assortative mating for the trait), and so identical or monozygotic (MZ) twins on average are twice as genetically similar as DZ twins. A crude estimate of heritability, then, is approximately twice the difference in correlation between MZ and DZ twins, i.e. Falconer's formula H2=2(r(MZ)-r(DZ)).
The effect of shared environment, c2, contributes to similarity between siblings due to the commonality of the environment they are raised in. Shared environment is approximated by the DZ correlation minus half heritability, which is the degree to which DZ twins share the same genes, c2=DZ-1/2h2. Unique environmental variance, e2, reflects the degree to which identical twins raised together are dissimilar, e2=1-r(MZ).
Analysis of variance methods of estimation
The second set of methods of estimation of heritability involves ANOVA and estimation of variance components.
Basic model
We use the basic discussion of Kempthorne.[14] Considering only the most basic of genetic models, we can look at the quantitative contribution of a single locus with genotype Gi as
where is the effect of genotype Gi and is the environmental effect.
Consider an experiment with a group of sires and their progeny from random dams. Since the progeny get half of their genes from the father and half from their (random) mother, the progeny equation is
Antropológia
Aplikované vedy
Bibliometria
Dejiny vedy
Encyklopédie
Filozofia vedy
Forenzné vedy
Humanitné vedy
Knižničná veda
Kryogenika
Kryptológia
Kulturológia
Literárna veda
Medzidisciplinárne oblasti
Metódy kvantitatívnej analýzy
Metavedy
Metodika
Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative
Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších
podmienok.
Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky
použitia.
www.astronomia.sk | www.biologia.sk | www.botanika.sk | www.dejiny.sk | www.economy.sk | www.elektrotechnika.sk | www.estetika.sk | www.farmakologia.sk | www.filozofia.sk | Fyzika | www.futurologia.sk | www.genetika.sk | www.chemia.sk | www.lingvistika.sk | www.politologia.sk | www.psychologia.sk | www.sexuologia.sk | www.sociologia.sk | www.veda.sk I www.zoologia.sk












