
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
| 15-M Movement Anti-austerity movement in Spain | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the 2008–2014 Spanish financial crisis, the European debt crisis and the impact of the Arab Spring | |||
 The Puerta del Sol square in Madrid, shown here on 20 May 2011, became a focal point and a symbol during the protests. | |||
| Date | 15 May 2011 – 2015 | ||
| Location | |||
| Caused by | Unemployment, economic conditions, welfare cuts, political corruption, particracy, unrepresentative bipartidism, democratic deficit | ||
| Goals | Direct democracy, reduce influence of economic powers in politics, | ||
| Methods | Demonstrations, civil disobedience, civil resistance, rioting, sit-ins, online activism, protest camps occupations | ||
| Number | |||
| |||
| Injuries and arrests | |||
| Injuries | 1,527+ injuries | ||
| Anti-austerity protests in the European Union |
|---|
| By member state |
| Principal protest parties |
The anti-austerity movement in Spain, also referred to as the 15-M Movement (Spanish: Movimiento 15-M),[2] and the Indignados Movement,[3] was a series of protests, demonstrations, and occupations against austerity policies in Spain that began around the local and regional elections of 2011 and 2012.[4][3] Beginning on 15 May 2011, many of the subsequent demonstrations spread through various social networks such as Real Democracy NOW (Spanish: Democracia Real YA) and Youth Without a Future (Spanish: Juventud Sin Futuro).[5]
Spanish media related the movement to the 2008–14 Spanish financial crisis, the Arab Spring, as well as demonstrations in North Africa,[6] Iran,[7] Greece,[8] Portugal,[9] and Iceland.[10] The movement was also compared to Stéphane Hessel's political manifesto Time for Outrage!,[11] which was seen to empower Spanish youth who were not in education, employment, or training (NEET). Protestors rallied against high unemployment rates, welfare cuts, politicians, and the two-party system in Spain, as well as the political system, capitalism, banks, and public corruption.[12] Many called for basic rights, of home, work, culture, health, and education.[13] The movement transferred to Europe the model of the protest camp which had been formed in the Arab Spring, adapting it to a more countercultural framework.[14] This would later expand until influencing the creation of Occupy Wall Street.[15]
According to RTVE, the Spanish public broadcasting company, between 6.5 and 8 million Spaniards participated in these events.[16]
Background
Since the 2008–2014 Spanish financial crisis began, Spain has had one of the highest unemployment rates in Europe, reaching a eurozone record of 21.3%.[17][18] The number of unemployed people in Spain stood at 4,910,200 at the end of March 2011, up about 214,000 from the previous quarter,[19] while the youth unemployment rate stands at 43.5%, the highest in the European Union.[20] In September 2010 the government approved a sweeping overhaul of the labour market designed to reduce unemployment and revive the economy.[21][22] Large trade unions such as CCOO and Unión General de Trabajadores (UGT), among other minor ones, rejected the plan because it made it easier and cheaper for employers to hire and fire workers. Trade unions called for the first general strike in a decade, on 29 September 2010.[23]

For the rest of the year, the government proceeded with economic reforms. In January 2011, the government reached an agreement with the main trade unions to increase the retirement age from 65 to 67. Anarcho-syndicalist and other related unions rejected the plan and called for a strike on 27 January in Galicia, Catalonia and the Basque Country. Other demonstrations in Madrid ended up in altercations with the police.[24][25] The majority of Spaniards also rejected the higher retirement age.[26] In February a wide-sweeping internet copyright infringement policy known as the Sinde law passed, adding another motivation for the protests.[27] The law allowed an administrative commission to shut down any website that showed links or allowed irregular downloading of copyrighted content without judicial supervision.[27] Users on Spanish forums and social networks criticized the law; the PSOE, PP and Convergence and Union affirmed these criticisms. An anonymous campaign with the #nolesvotes appeared online, calling on citizens to vote against any of the parties that passed the law.[28]
Prior to 15 May, other demonstrations served as precursors to the main protests in Madrid.[4] These demonstrations include the 7 April protest in Madrid by the student group Youth without Future (Juventud Sin Futuro), which gathered 5,000 people.[4] Spanish media drew comparisons between the demonstrations and the 2008-09 protests against the Bologna Process.[29] The anti-austerity movement in Portugal also inspired the demonstrations undertaken in Spain.[9] According to Peter Gelderloos, the movement led to the creation of hundreds of police-free zones across the country, hospitals were occupied and saved from privatisation, neighbourhood assemblies sprang up, unused land and homes were occupied and squatted, worker cooperatives were founded and urban community gardens were established.[30]
Organization
In January 2011, users on Spanish social media networks and forums created the digital platform ¡Democracia Real YA![31] Using Twitter and Facebook, it called "the unemployed, poorly paid, the subcontractors, the precarious, young people..." to take to the streets on 15 May in the following places: A Coruña, Albacete, Algeciras, Alicante, Almería, Arcos de la Frontera, Badajoz, Barcelona, Bilbao, Burgos, Cáceres, Cadiz, Cartagena, Castellón, Ciudad Real, Córdoba, Cuenca, Ferrol, Figueres, Fuengirola, Gijón, Granada, Guadalajara, Huelva, Jaén, Lanzarote, La Palma, León, Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Lleida, Logroño, Lugo, Madrid, Málaga, Menorca, Mérida, Monforte de Lemos, Murcia, Ourense, Oviedo, Palma, Pamplona, Plasencia, Ponferrada, Puertollano, Salamanca, San Sebastián, Santa Cruz de Tenerife, Santander, Santiago de Compostela, Seville, Soria, Tarragona, Toledo, Torrevieja, Ubrique, Valencia, Valladolid, Vigo, Vitoria and Zaragoza.[32] That same day, small demonstrations in support of the Spanish ones were organised in Dublin, Lisbon, Amsterdam, Istanbul, Bologna, London and Paris.[4]
Before the demonstrations, ¡Democracia Real YA! staged several symbolic events, such as the occupation of a bank in Murcia on 13 May.[33]
2011 events
May 2011
15 May
The first event was called under the motto "we are not goods in the hands of politicians and bankers" and was focused on opposition to what the demonstrators called "antisocial means in the hands of bankers."[34][35] The motto referred partly to the changes made in 2010 to contain the ongoing European sovereign debt crisis through bailout of the banks, which the Spanish society saw as responsible for the crisis. At the same time, the government continued to announce social program cutbacks. Protesters demanded spiritual philanthropy.

According to ¡Democracia Real YA!, 50,000 people gathered in Madrid alone.[4] The National Police placed the number at 20,000.[36] The march started in Plaza de Cibeles and ended in Puerta del Sol, where several manifestos were read. Also according to the organizers, 15,000 gathered in the demonstration in Barcelona, which ended in front of the Parliament of Catalonia.[37] In other cities such as Granada, up to 5,000 protesters attended. These protests took place mostly without incident, except for an exchange of insults between some protesters and members of the Fraternity of the Virgin of Rosario, whose procession overlapped with the end of the protest after the latter continued longer than expected. In Santiago de Compostela, a group of eight hooded people smashed several banks and local businesses.[38][39][40] It was estimated by Deconomia that about 130,000 people throughout Spain followed the protesters that day.[41][42]
At the end of the demonstrations in Madrid, protesters blocked the Gran Vía avenue and staged a peaceful sit-in in Callao street, to which police responded by beating protesters with truncheons. As a result of the clashes and the following riots, several shop windows were destroyed and trash containers burned. Police officers arrested 24 people, and five police officers were injured.[43] On 17 May, ¡Democracia Real YA! condemned the "brutal police repression" and rejected any association with the incidents.[44] After the incidents, a group of 100 people headed to Puerta del Sol and started camping in the middle of the square, which would result in the following day's protests.[45][46]
16 May
During the day, several people gathered in Puerta del Sol and decided to stay in the square until the elections on 22 May. Meanwhile, 200 people started a similar action in Barcelona's Plaça Catalunya, although police initially attempted to disperse the crowds. That day the tag #spanishrevolution, as well as other ones related to the protests, became trending topics on Twitter.[45]
17 May

In the early hours of 17 May, police cleared the Puerta del Sol square and removed the 150 people who had camped out. Two protesters were arrested and one injured.[47][48] In response to the eviction and police violence, protesters (independent of the ¡Democracia Real YA! organization[49]) used SMS, Facebook and Twitter to call for a mass response at 8 p.m. in several Spanish squares.[47] Large groups of demonstrators returned to protest in various cities, standing apart from the group in Madrid. The police allowed protesters to camp out in a few cities, like A Coruña, where more than 1,000 people gathered.[50] In Madrid more than 12,000 people gathered and about 200 protesters organized into an assembly, during which they decided to organize themselves for spending the night in the square, creating cleaning, communication, extension, materials and legal committees. Previously, small businesses had provided a great deal of assistance with supplies, including food.[49][51][52] Dozens of people also gathered in front of the courthouse in Madrid, where the people arrested during the 15 May demonstration were being held. All detainees were released.[47]
Protests and nighttime camp-outs took place in 30 cities around Spain, including Barcelona and Valencia.[53] The protests gained the support of some people in the United Kingdom, who announced that they would sit outside of the Spanish embassy from 18 to 22 May.[53] The protest in Plaza del Sol on the night of 17 May consisted of about 4,000 people, according to the authorities. As evening fell, the protesters put up a large tarp canopy beneath which they passed out signs with the intention of spending the night.[54] Three hundred of them stayed until the dawn of 18 May.[52] The camp can be considered a form of prefigurative politics and can be understood as a small symbolic city within the city.[14]
18 May

According to El País, many protesters wore carnations, imitating protesters during the Portuguese Carnation Revolution. In addition, protesters organized a food stand, which provided food donated by local businesses, and set up a webcam to provide news from Puerta del Sol through the website Ustream.tv. The protesters were advised not to drink alcohol or to organize into groups of more than 20 people, as these acts could provoke a legal police crackdown.[54]
The police ordered protesters to disperse in Valencia, Tenerife and Las Palmas. During the evacuation of the Plaza del Carmen in Granada, three people were arrested.[52][55][56] Speeches continued throughout the afternoon. The protests grew to include León, Seville (where a campout started as of 19 May),[52] and other provincial capitals and cities in Spain. Protesters created support groups for each campout on Twitter and other national and international networks. Google Docs and other servers began to receive download requests for documents needed to legally request permission for new protests.[57] In the morning, the Federación de Asociaciones de Vecinos de Barcelona (FAVB) announced its support of the protests in Barcelona.[58] Protesters agreed to hold meetings between their organizing committees each day at 1 p.m. and assemblies at 8 p.m.[59]
The Washington Post covered the protests on 15 May; on 18 May, more media outlets began to publish news reports. Among them was Le Monde, the most widely circulated newspaper written in French, with an article that noted the rarity of such large-scale protests in Spain.[60] The German newspaper Der Spiegel noted the importance of the effects of what has been called "The Facebook Generation" on the protests.[61] The Portuguese paper Jornal de Notícias reported on the protests in Madrid as soon as it was known that they had been prohibited.[62] The New York Times cited El País and noted the strong organization of the protesters, particularly the 200 people who had been placed in charge of security, and the use of Twitter to ensure dissemination of their message.[63] The Washington Post again reported on the protests in Puerta del Sol, giving them the name of a "revolution," estimating that 10,000 people attended Wednesday afternoon's protest, and comparing the protests with those in Cairo's Tahrir Square, which had recently ousted Egyptian president Hosni Mubarak.[64] The BBC made reference to the peaceful nature of the protests in Puerta del Sol.[6]
In the evening, the President of the Regional Electoral Committee of Madrid issued a statement declaring the protests illegal because "calls for a responsible vote can change the results of the elections."[65] Police units stationed at Plaza del Sol, however, received orders from the Government Delegation not to take out any further action.[66]


20 May
According to Britain's The Guardian, "tens of thousands" had camped out in Madrid and throughout the country on the night of 19–20 May.[67]
At 10:00 AM United Left appealed the Electoral Board's decision to ban the protests before Spain's Supreme Court.[68] Hours later, the State Prosecution presented its arguments to the court.[69]
Appeal before the Supreme Court
Spain's public broadcaster, RTVE, reported that the State Prosecutor upheld the decision taken by the Central Electoral Board[70] to ban the rallies.[71] Meanwhile, the police announced that they had been given instructions not to dissolve the crowd at Puerta del Sol provided that there was no disturbance of the peace.[72]
Appeal before the Tribunal Constitucional
RTVE later reported that the country's Constitutional Court had been deliberating since 7:30 p.m. whether to review an appeal against the decision of the Central Electoral Board.[73] At 10:08 p.m., RTVE reported that the Constitutional Court had rejected the appeal on the formality that the appellant had not appealed first to the Supreme Court.[74]
At 10:47 p.m. United Left announced it would appeal the Supreme Court's decision before the Tribunal Constitucional. They had until midnight.[75]
At around 11:00 p.m., some 16,000 (according to the police) to 19,000 (according to RTVE) people were gathered at and around Puerta del Sol.[76]
21 May
In Madrid, Barcelona, Malaga and other cities, 21 May started with a "mute scream" followed by cheers and applause.[77] Smaller cities, such as Granada, decided to start before midnight to avoid disturbing the neighbors.[78] These protests occurred even though protests on the day before elections are banned.[78]
Around 28,000 people (according to the police) crowded Puerta del Sol and the neighboring streets despite the prohibition. Other cities also gathered large numbers of people: 15,000 in Malaga, 10,000 in Valencia, 8,000 in Barcelona, 6,000 in Zaragoza, 4,000 in Seville, 3,000 in Bilbao, 3,000 in Palma, 2,000 in Gijón, 2,000 in Oviedo, 1,500 in Granada, 1,000 in Vigo, 800 in Almeria, around 800 in Avilés, 600 in Cadiz, 200 in Huelva, and around 100 in Jaen.[77] Demonstrations also occurred in other European cities, with 300 protesters participating in London, 500 in Amsterdam,[79] 600 in Brussels and 200 in Lisbon. Minor demonstrations occurred in Athens, Milan, Budapest, Tangiers, Paris, Berlin, Vienna and Rome.[77]
22 May
Just after 2:00 p.m. on election day, the indignados (outraged) that had gathered at Puerta del Sol announced that they had voted to stay at least another week, until noon on 29 May.[80] Early analysis of the local and regional elections, won by the People's Party, suggested the protest movement could have contributed to losses for the ruling PSOE,[81] and to increased numbers of spoilt or blank votes, which reached record levels.[82]
24 May
In Murcia about 80 people gained access to the headquarters of the television channel 7 Región de Murcia, avoiding security staff, in order to read a manifesto denouncing media manipulation.[83] Approximately 30 people gained unobstructed entry to the Tarragona office of the Ministry of Economy and Finance and shouted slogans against the political and economic systems, before moving to several financial sites in the city centre to do the same.[84]
25 May
In Málaga, the Ministry of Defence decided to relocate various activities for Armed Forces Day, including the King's visit, planned for Friday 27. Protesters had already been occupying the Plaza de la Constitución, where the events were scheduled to take place, for eight days.[85]
27 May
| External media | |
|---|---|
| Images | |
| Video | |
At approximately 7 a.m. on 27 May, another incident occurred when the city council of Barcelona decided to send 350 police officers from the Mossos d'Esquadra and roughly 100 more from the Guàrdia Urbana to temporarily vacate Plaça de Catalunya so that it could be cleaned ahead of the Champions League final on 28 May, in which FC Barcelona were playing against Manchester United.[86][87] The resulting violent clash ended in 121 light injuries and provoked new calls to protest in all squares still occupied across Spain.[86][88] The majority of those injured suffered bruises and open wounds caused by police officers' truncheons; one protester left with a broken arm.[88] The protesters who had been vacated returned to the square by early afternoon.[89]
Similar incidents also occurred in Lleida and Sabadell, where Mossos d'Esquadra officers dismantled the protesters' encampments.[86] According to police figures, more than 12,000 people gathered in Barcelona through the course of the day, angry about the earlier actions of the police and painting their hands white and carrying flowers as symbols of protest. They demanded, among other things, the resignation of the head of the Mossos d'Esquadra, Felip Puig. They also claimed that, following the incident, the encampment likely would not be taken down on Sunday, 29 May, as had previously been stated.[90]
The clearing of the Barcelona camp was broadcast live by two Spanish television channels, including Antena 3, and was also widely dispersed through social networks such as Twitter.[91][92]
The Catalan ombudsman opened an investigation into the incident to check if police action was disproportionate and violated citizens' rights.[93]

June 2011
2 June
At least 40 people gathered in Montcada i Reixac, Barcelona. They prevented court officials from serving a family with the order to leave their home immediately and protested against banks repossessing people's homes.[94]
4 June
Representatives from 53 assemblies around Spain gathered in a mass assembly in Puerta del Sol.[94]
8 June
In Madrid, hundreds of people gathered in front of the Congreso de los Diputados, with a police barrier preventing them from entering the building. Demonstrations in front of the Parliament are banned in Madrid, but the protest finished without incident.[95] In Valencia, dozens of people decided to stay in front of the regional Parliament.[96] In Barcelona, around 50 people protested outside the Catalan Parliament against Felip Puig.[97]
9 June
In the morning, police clashed with protesters in Valencia, injuring 18.[98] As a response to the police violence, demonstrators called for a protest in the city later that day, which gathered around 2,000 people. Support demonstrations were held in Barcelona and Madrid, the latter ending up in front of the Parliament for a second night. Barcelona's protest finished in front of the Popular Party's office.[99][100]
11 June
Thousands of indignados from the whole country concentrated at the gates of major city halls during the mayors' swearing-ins after the elections. Protesters broke in on the act in Granada, while two activists were arrested in Burgos and three in Palma. In Castellón, the police dissolved the demonstration violently.[101]
12 June
On Sunday, 12 June, four weeks after the protests had begun, protesters in the Puerta del Sol in Madrid began to leave, dismantling the camp site; packing up tents, libraries, and shops; and removing protest signs from surrounding sites.[102]
14 Juneedit
Thousands of people assembled in front of Barcelona's Parc de la Ciutadella and organized themselves to spend the night, in order to start a blockade of the Catalan Parliament (which is inside the park) on the following day and prevent deputies from entering the building, where the debate on the 2011 budget, which would result in cuts in education and health, was to take place.[103]
15 Juneedit

Clashes between protesters and Mossos d'Esquadra occurred in the early hours of the morning when hundreds of protesters gathered in front of the police cordon, while officers fired plastic bullets in order to disperse a group of protesters who had set up barricades using rubbish containers. Hours later, scuffles broke out as Mossos de Esquadra pushed protesters back so the deputies who arrived on foot could pass through. Some deputies, such as former Minister of Labour Celestino Corbacho, were jostled, heckled and sprayed on their way in, while others used police helicopters to get to the parliament, including the president of Catalonia, Artur Mas.[104] Although lawmakers managed to enter the Catalan Parliament, the scheduled session started with a 15-minute delay.[105]
The protest was criticized by politicians across the country. During a press conference, Mas warned of a possible "legitimate use of force" in case demonstrators stayed outside the Parliament, and he called on the public to be understanding. Some politicians went so far as to denounce an attempted "coup d'etat."[106] Acampadabcn, the organiser of the event, and ¡Democracia Real YA! rejected the use of violence but denounced the criminalization of the movement by the media.[107] On Twitter and other social networks, many users suggested the possibility that secret police, infiltrated to cause the violence, started most of the clashes.[108] [109]
19 Juneedit

A massive demonstration was carried out in almost 80 Spanish cities and towns. It is believed that more than three million people rallied that day.
20–25 Juneedit
The first columns of the Indignant People's March began walking towards Madrid from throughout the country, planning to arrive in the capital on 23 July. The March's goal was to expand the proposals of the Movement while visiting rural areas, collecting their demands, and starting people's assemblies.[110]
The March was organized in eight columns, consisting of dozens of activists from 16 cities:[111]
- Eastern route: from Valencia, 20 June
- Murcia route: from Murcia, 20 June
- Northern route: from Santander, Bilbao and Pamplona, 23 and 29 June
- Northwest route: from Santiago de Compostela, Vigo, Ferrol, Avilés and Gijón, between 24 and 30 June
- Southern route: from Cádiz, 24 June
- Southeastern route: from Málaga and Motril, 25 June
- Northeastern route: from Barcelona, 25 June
- N-II route: from Zaragoza, 7 July


July 2011edit
1 Julyedit
Dozens of people protested outside Barcelona's town hall during the swearing-in ceremony of Spanish Convergence and Union's candidate Xavier Trias.[112]
23 Julyedit
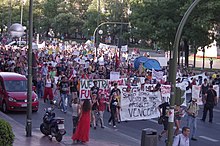
After a month-long walk, the columns of the Indignant People's March joined in Puerta del Sol, where the movement first emerged. Thousands collapsed the main entrances of Madrid in an improvised demonstration, as sympathizers from Madrid and all over Spain joined the walkers.
The eight columns reunited at 9 p.m. in Puerta del Sol under a banner saying "WELCOME DIGNITY," received with cheers and applause. The march culminated in a wrap up and after-action review assembly, at which participants shared the social, political and economic problems of the towns visited along the way, as well as the proposals made by the townspeople. The protesters created The Book of the People to collect these experiences and redacted it into an official document to be deposited in the Congress of Deputies' register.[113] A provisional camp was established in Paseo del Prado to host the thousands of newly arrived walkers.[114]
24 Julyedit
During the day's rally, protesters sprayed red hand graffiti on buildings and posted bills saying "GUILTY" on bank offices and ministries, referencing the widely held belief that the crisis was caused by banks, the Government, and cuts in social services. Due to the large crowds, the demonstration split into two columns to avoid congestion. The demonstration ended with a protest camp in front of the Congress of Deputies.
| External videos | |
|---|---|
25 Julyedit
The "I Foro Social del 15M" was held in order to coordinate the mobilizations of the following winter. During the economics assembly, 2001 Nobel Prize winner Joseph Stiglitz appeared to show his support to the movement.[115] The camp in front of the Congress continued.
26 Julyedit
Fifty indignados left Puerta del Sol walking in an International March to Brussels planning to arrive on 8 October, a week before the demonstrations of 15 October, in order to give the people's proposals to the European Parliapoment.
27 Julyedit
Police violently removed the camp in Paseo del Prado, injuring a dozen people.[116] As a response, 500 demonstrators rallied towards the Congress. Meanwhile, several activists crossed the police line in the Congress wearing formal dresses and succeeded entering the Congress of Deputies, where the Book of the People, containing the rural problematics found during the Indignant People's March, was delivered. Deputy Gaspar Llamazares compromised on presenting it to the Congress and forwarded it to the Prime Minister. However, he made clear that he had no connection to the Movement.[117][118]
August 2011edit
2 Augustedit
When the assembly decided on 12 June to dismantle the tent city in Puerta del Sol, it also decided by consensus to leave behind an information booth, called PuntoSol, where people interested in the movement could find information about how it had been decentralized to the neighborhood assemblies.[119] An organic garden surrounding one of the fountains in Sol was also left behind in the square. At 6:30 a.m. on 2 August, the national and municipal police evicted the remaining protesters at the information booth, and cleaning crews dismantled PuntoSol[120] and the organic garden.[121] At the same time, they evicted the tent city that had sprung up on the Paseo del Prado. The police then blocked off all access to Sol, including Metro and Cercanías, and filled the square with over 300 police, including riot police, and 50 police vans.[122]
In response, protesters called an immediate convergence to try to access the square. The heavy police presence impeded their entry. The protestors, then numbering over 5,000,[122] decided to turn to the streets, demonstrating from Callao, Gran Vía, Cibeles, and Paseo del Prado, all the way to the Congress of Deputies building, where they were met by more riot police, police barricades and police vans.[123] Protesters then turned to Atocha and once more to Sol, where they again encountered an overwhelming police presence. The decision was then made by the protesters to occupy Plaza Mayor, where an emergency participatory assembly was held in order to decide what to do.[124] Ultimately, protesters set up a temporary information booth in Plaza Mayor, and some stayed to camp through the night.[125] At the end of the night, two people were arrested, and released the day after.[126]
Zdroj:https://en.wikipedia.org?pojem=Anti-austerity_movement_in_SpainText je dostupný za podmienok Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších podmienok. Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky použitia.
Antropológia
Aplikované vedy
Bibliometria
Dejiny vedy
Encyklopédie
Filozofia vedy
Forenzné vedy
Humanitné vedy
Knižničná veda
Kryogenika
Kryptológia
Kulturológia
Literárna veda
Medzidisciplinárne oblasti
Metódy kvantitatívnej analýzy
Metavedy
Metodika
Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative
Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších
podmienok.
Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky
použitia.
www.astronomia.sk | www.biologia.sk | www.botanika.sk | www.dejiny.sk | www.economy.sk | www.elektrotechnika.sk | www.estetika.sk | www.farmakologia.sk | www.filozofia.sk | Fyzika | www.futurologia.sk | www.genetika.sk | www.chemia.sk | www.lingvistika.sk | www.politologia.sk | www.psychologia.sk | www.sexuologia.sk | www.sociologia.sk | www.veda.sk I www.zoologia.sk
