
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
 French singles player Guillaume Rufin serves to Czech player Tomáš Berdych in a tennis match at the 2013 Australian Open | |
| Highest governing body | International Tennis Federation |
|---|---|
| First played | 19th century, Birmingham, England, United Kingdom |
| Characteristics | |
| Contact | No |
| Team members | Singles or doubles |
| Mixed-sex | Yes, separate tours and mixed doubles |
| Type | Outdoor or indoor |
| Equipment | Ball, racket, net |
| Venue | Tennis court |
| Glossary | Glossary of tennis terms |
| Presence | |
| Country or region | Worldwide |
| Olympic | Part of Summer Olympic programme from 1896 to 1924 Demonstration sport in the 1968 and 1984 Summer Olympics Part of Summer Olympic programme since 1988 |
| Paralympic | Part of Summer Paralympic programme since 1992 |
Tennis is a racket sport that is played either individually against a single opponent (singles) or between two teams of two players each (doubles). Each player uses a tennis racket that is strung with cord to strike a hollow rubber ball covered with felt over or around a net and into the opponent's court. The object of the game is to manoeuvre the ball in such a way that the opponent is not able to play a valid return. The player who is unable to return the ball validly will not gain a point, while the opposite player will.[1][2]
Tennis is an Olympic sport and is played at all levels of society and at all ages. The sport can be played by anyone who can hold a racket, including wheelchair users. The original forms of tennis developed in France during the late Middle Ages.[3] The modern form of tennis originated in Birmingham, England, in the late 19th century as lawn tennis.[4] It had close connections both to various field (lawn) games such as croquet and bowls as well as to the older racket sport today called real tennis.[5]
The rules of modern tennis have changed little since the 1890s. Two exceptions are that until 1961 the server had to keep one foot on the ground at all times,[6][7] and the adoption of the tiebreak in the 1970s.[8] A recent addition to professional tennis has been the adoption of electronic review technology coupled with a point-challenge system, which allows a player to contest the line call of a point, a system known as Hawk-Eye.[9][10]
Tennis is played by millions of recreational players and is a popular worldwide spectator sport.[11] The four Grand Slam tournaments (also referred to as the majors) are especially popular: the Australian Open, played on hardcourts; the French Open, played on red clay courts; Wimbledon, played on grass courts; and the US Open, also played on hardcourts.[12]
History
Predecessors


Historians believe that the game's ancient origin lay in 12th-century northern France, where a ball was struck with the palm of the hand.[13] Louis X of France was a keen player of jeu de paume ("game of the palm"), which evolved into real tennis, and became notable as the first person to construct indoor tennis courts in the modern style. Louis was unhappy with playing tennis outdoors and accordingly had indoor, enclosed courts made in Paris "around the end of the 13th century".[14] In due course this design spread across royal palaces all over Europe.[14] In June 1316 at Vincennes, Val-de-Marne, and following a particularly exhausting game, Louis drank a large quantity of cooled wine and subsequently died of either pneumonia or pleurisy, although there was also suspicion of poisoning.[15] Because of the contemporary accounts of his death, Louis X is history's first tennis player known by name.[15] Another of the early enthusiasts of the game was King Charles V of France, who had a court set up at the Louvre Palace.[16]
It was not until the 16th century that rackets came into use and the game began to be called "tennis", from the French term tenez, which can be translated as "hold!", "receive!" or "take!", an interjection used as a call from the server to his opponent.[17] It was popular in England and France, although the game was only played indoors, where the ball could be hit off the wall. Henry VIII of England was a big fan of this game, which is now known as real tennis.[18]
An epitaph in St Michael's Church, Coventry, written c. 1705, read, in part:[19]
Here lyes an old toss'd Tennis Ball:
Was racketted, from spring to fall,
With so much heat and so much hast,
Time's arm for shame grew tyred at last.
During the 18th and early 19th centuries, as real tennis declined, new racket sports emerged in England.[20]
The invention of the first lawn mower in Britain in 1830 is believed to have been a catalyst for the preparation of modern-style grass courts, sporting ovals, playing fields, pitches, greens, etc. This in turn led to the codification of modern rules for many sports, including lawn tennis, most football codes, lawn bowls and others.[21]
Origins of the modern game

Between 1859 and 1865, Harry Gem, a solicitor, and his friend Augurio Perera developed a game that combined elements of racquets and the Basque ball game pelota, which they played on Perera's croquet lawn in Birmingham, England.[22][23] In 1872, along with two local doctors, they founded the world's first tennis club on Avenue Road, Leamington Spa.[24] This is where "lawn tennis" was used as the name of an activity by a club for the first time.
In Tennis: A Cultural History, Heiner Gillmeister reveals that on 8 December 1874, British army officer Walter Clopton Wingfield wrote to Harry Gem, commenting that he (Wingfield) had been experimenting with his version of lawn tennis "for a year and a half".[25] In December 1873, Wingfield designed and patented a game which he called sphairistikè (Greek: σφαιριστική, meaning "ball-playing"), and which was soon known simply as "sticky" – for the amusement of guests at a garden party on his friend's estate of Nantclwyd Hall, in Llanelidan, Wales.[26] According to R. D. C. Evans, turfgrass agronomist, "Sports historians all agree that deserves much of the credit for the development of modern tennis."[20][27] According to Honor Godfrey, museum curator at Wimbledon, Wingfield "popularized this game enormously. He produced a boxed set which included a net, poles, rackets, balls for playing the game – and most importantly you had his rules. He was absolutely terrific at marketing and he sent his game all over the world. He had very good connections with the clergy, the law profession, and the aristocracy and he sent thousands of sets out in the first year or so, in 1874."[28] The world's oldest annual tennis tournament took place at Leamington Lawn Tennis Club in Birmingham in 1874.[29] This was three years before the All England Lawn Tennis and Croquet Club would hold its first championships at Wimbledon, in 1877. The first Championships culminated in a significant debate on how to standardise the rules.[28]

In the United States in 1874, Mary Ewing Outerbridge, a young socialite, returned from Bermuda with a sphairistikè set. She became fascinated by the game of tennis after watching British army officers play.[30] She laid out a tennis court at the Staten Island Cricket Club at Camp Washington, Tompkinsville, Staten Island, New York. The first American National championship was played there in September 1880. An Englishman named O.E. Woodhouse won the singles title, and a silver cup worth $100, by defeating Canadian I. F. Hellmuth.[31] There was also a doubles match which was won by a local pair. There were different rules at each club. The ball in Boston was larger than the one normally used in New York.
On 21 May 1881, the oldest nationwide tennis organization in the world[32] was formed, the United States National Lawn Tennis Association (now the United States Tennis Association) in order to standardize the rules and organize competitions.[33] The US National Men's Singles Championship, now the US Open, was first held in 1881 at the Newport Casino, Newport, Rhode Island.[34] The US National Women's Singles Championships were first held in 1887 in Philadelphia.[35]

Tennis also became popular in France, where the French Championships date to 1891, although until 1925 they were open only to tennis players who were members of French clubs.[36] Thus, Wimbledon, the US Open, the French Open and the Australian Open (dating to 1905) became and have remained the most prestigious events in tennis.[37][38] Together, these four events are called the Majors or Slams (a term borrowed from bridge rather than baseball).[39]

In 1913, the International Lawn Tennis Federation (ILTF), now the International Tennis Federation (ITF), was founded and established three official tournaments as the major championships of the day. The World Grass Court Championships were awarded to Great Britain. The World Hard Court Championships were awarded to France; the term "hard court" was used for clay courts at the time. Some tournaments were held in Belgium instead. And the World Covered Court Championships for indoor courts were awarded annually; Sweden, France, Great Britain, Denmark, Switzerland and Spain each hosted the tournament.[40] At a meeting held on 16 March 1923 in Paris, the title "World Championship" was dropped and a new category of "Official Championship" was created for events in Great Britain, France, the US and Australia [41] – today's Grand Slam events.[40][42] The impact on the four recipient nations to replace the "world championships" with "official championships" was simple in a general sense: each became a major nation of the federation with enhanced voting power, and each now operated a major event.[40]
The comprehensive rules promulgated in 1924 by the ILTF have remained largely stable in the ensuing 80 years, the one major change being the addition of the tiebreak system designed by Jimmy Van Alen.[43] That same year, tennis withdrew from the Olympics after the 1924 Games, but returned 60 years later as a 21-and-under demonstration event in 1984. This reinstatement was credited by the efforts of then ITF president Philippe Chatrier, ITF general secretary David Gray and ITF vice president Pablo Llorens, with support from International Olympic Committee president Juan Antonio Samaranch. The success of the event was overwhelming, and the IOC decided to reintroduce tennis as a full-medal sport at Seoul in 1988.[44][45]

The Davis Cup, an annual competition between men's national teams, dates to 1900.[46] The analogous competition for women's national teams, the Fed Cup, was founded as the Federation Cup in 1963 to celebrate the 50th anniversary of the founding of the ITF.[47]
In 1926, promoter C. C. Pyle established the first professional tennis tour with a group of American and French tennis players playing exhibition matches to paying audiences.[38][48] The most notable of these early professionals were the American Vinnie Richards and the Frenchwoman Suzanne Lenglen.[38][49] Players turned pro, would no longer permitted to compete in the major (amateur) tournaments.[38]
In 1968, commercial pressures and rumours of some amateurs taking money under the table led to the abandonment of this distinction, inaugurating the Open Era, in which all players could compete in all tournaments, and top players were able to make their living from tennis.[50] With the beginning of the Open Era, the establishment of an international professional tennis circuit, and revenues from the sale of television rights, tennis's popularity has spread worldwide, and the sport has shed its middle-class English-speaking image[51] (although it is acknowledged that this stereotype still exists).[51][52]
In 1954, Van Alen founded the International Tennis Hall of Fame, a nonprofit museum in Newport, Rhode Island.[53] The building contains a large collection of tennis memorabilia as well as a hall of fame honouring prominent members and tennis players from all over the world.[54]
Equipment
Part of the appeal of tennis stems from the simplicity of equipment required for play. Beginners need only a racket and balls.[1]

Rackets

The components of a tennis racket include a handle, known as the grip, connected to a neck which joins a roughly elliptical frame that holds a matrix of tightly pulled strings. For the first 100 years of the modern game, rackets were made of wood and of standard size, and strings were of animal gut. Laminated wood construction yielded more strength in rackets used through most of the 20th century until first metal and then composites of carbon graphite, ceramics, and lighter metals such as titanium were introduced. These stronger materials enabled the production of oversized rackets that yielded yet more power. Meanwhile, technology led to the use of synthetic strings that match the feel of gut yet with added durability.
Under modern rules of tennis, the rackets must adhere to the following guidelines;[55]
- The hitting area, composed of the strings, must be flat and generally uniform.
- The frame of the hitting area may not be more than 29 inches (74 cm) in length and 12.5 inches (32 cm) in width.
- The entire racket must be of a fixed shape, size, weight, and weight distribution. There may not be any energy source built into the rackets.
- The rackets must not provide any kind of communication, instruction or advice to the player during the match.
The rules regarding rackets have changed over time, as material and engineering advances have been made. For example, the maximum length of the frame had been 32 inches (81 cm) until 1997, when it was shortened to 29 inches (74 cm).[56]
Many companies manufacture and distribute tennis rackets. Wilson, Head and Babolat are three of the most commonly used brands; however, many more companies exist.[57] The same companies sponsor players to use these rackets in the hopes that the company name will become better known by the public.
Strings
There are multiple types of tennis strings, including natural gut and synthetic stings made from materials such as nylon, kevlar, or polyester.[58]

Natural gut
The first type of tennis strings available were natural gut strings, introduced by Babolat. They were the only type used until synthetic strings were introduced in the 1950s. Natural gut strings are still used frequently by players such as Roger Federer. They are made from cow intestines, and provide increased power, and are easier on the arm than most strings.[59]
Synthetic
Most synthetic strings are made from monofilament or multifiliament nylon strings. Monofilament strings are cheap to buy, and are used widely by many recreational level players for their all round performance, while multifilament strings are created to mimic natural gut more closely by weaving together fibres, but are generally more expensive than their monofilament counterparts.[58] Polyester strings allow for more spin on the ball than any other string, due to their firm strings, while keeping control of the ball, and this is why many players use them, especially higher player ones.[60] Kevlar tennis strings are highly durable, and are mostly used by players that frequently break strings, because they maintain tension well, but these strings can be stiff on the arm.[61]
Hybrid strings
Hybrid stringing is when a tennis racket is strung with two different strings for the mains (the vertical strings) and the crosses (the horizontal strings). This is most commonly done with two different strings that are made of different materials, but can also be done with two different types of the same string. A notable example of a player using hybrid strings is Roger Federer, using natural gut strings in his mains and polyester strings in his crosses.[62]
Balls

Tennis balls were originally made of cloth strips stitched together with thread and stuffed with feathers.[63] Modern tennis balls are made of hollow vulcanized rubber with a felt coating. Traditionally white, the predominant colour was gradually changed to optic yellow in the latter part of the 20th century to allow for improved visibility. Tennis balls must conform to certain criteria for size, weight, deformation, and bounce to be approved for regulation play. The International Tennis Federation (ITF) defines the official diameter as 65.41–68.58 mm (2.575–2.700 in). Balls must weigh between 56.0 and 59.4 g (1.98 and 2.10 oz).[64] Tennis balls were traditionally manufactured in the United States and Europe. Although the process of producing the balls has remained virtually unchanged for the past 100 years, the majority of manufacturing now takes place in the Far East. The relocation is due to cheaper labour costs and materials in the region.[65] Tournaments that are played under the ITF Rules of Tennis must use balls that are approved by the International Tennis Federation (ITF) and be named on the official ITF list of approved tennis balls.[66]
Manner of play
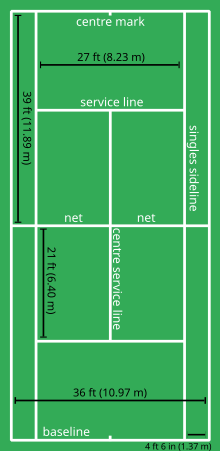
Court

Tennis is played on a rectangular, flat surface. The court is 78 feet (23.77 m) long, and 27 feet (8.2 m) wide for singles matches and 36 ft (11 m) for doubles matches.[67] Additional clear space around the court is required in order for players to reach overrun balls. A net is stretched across the full width of the court, parallel with the baselines, dividing it into two equal ends. It is held up by either a cord or metal cable of diameter no greater than 0.8 cm (1⁄3 in).[66] The net is 3 feet 6 inches (1.07 m) high at the posts and 3 feet (0.91 m) high in the centre.[67] The net posts are 3 feet (0.91 m) outside the doubles court on each side or, for a singles net, 3 feet (0.91 m) outside the singles court on each side.
The modern tennis court owes its design to Major Walter Clopton Wingfield. In 1873, Wingfield patented a court much the same as the current one for his stické tennis (sphairistike). This template was modified in 1875 to the court design that exists today, with markings similar to Wingfield's version, but with the hourglass shape of his court changed to a rectangle.[68]
Tennis is unusual in that it is played on a variety of surfaces.[69] Grass, clay, and hard courts of concrete or asphalt topped with acrylic are the most common. Occasionally carpet is used for indoor play, with hardwood flooring having been historically used. Artificial turf courts can also be found.
Lines
The lines that delineate the width of the court are called the baseline (farthest back) and the service line (middle of the court). The short mark in the centre of each baseline is referred to as either the hash mark or the centre mark. The outermost lines that make up the length are called the doubles sidelines; they are the boundaries for doubles matches. The lines to the inside of the doubles sidelines are the singles sidelines, and are the boundaries in singles play. The area between a doubles sideline and the nearest singles sideline is called the doubles alley, playable in doubles play. The line that runs across the centre of a player's side of the court is called the service line because the serve must be delivered into the area between the service line and the net on the receiving side. Despite its name, this is not where a player legally stands when making a serve.[70]
The line dividing the service line in two is called the centre line or centre service line. The boxes this centre line creates are called the service boxes; depending on a player's position, they have to hit the ball into one of these when serving.[71] A ball is out only if none of it has hit the area inside the lines, or the line, upon its first bounce. All lines are required to be between 1 and 2 inches (25 and 51 mm) in width, with the exception of the baseline which can be up to 4 inches (100 mm) wide, although in practice it is often the same width as the others.[70]
Play of a single point

The players or teams start on opposite sides of the net. One player is designated the server, and the opposing player is the receiver. The choice to be server or receiver in the first game and the choice of ends is decided by a coin toss before the warm-up starts. Service alternates game by game between the two players or teams. For each point, the server starts behind the baseline, between the centre mark and the sideline. The receiver may start anywhere on their side of the net. When the receiver is ready, the server will serve, although the receiver must play to the pace of the server.
For a service to be legal, the ball must travel over the net without touching it into the diagonally opposite service box. If the ball hits the net but lands in the service box, this is a let or net service, which is void, and the server retakes that serve. The player can serve any number of let services in a point and they are always treated as voids and not as faults. A fault is a serve that falls long or wide of the service box, or does not clear the net. There is also a "foot fault" when a player's foot touches the baseline or an extension of the centre mark before the ball is hit. If the second service, after a fault, is also a fault, the server double faults, and the receiver wins the point. However, if the serve is in, it is considered a legal service.
A legal service starts a rally, in which the players alternate hitting the ball across the net. A legal return consists of a player hitting the ball so that it falls in the server's court, before it has bounced twice or hit any fixtures except the net. A player or team cannot hit the ball twice in a row. The ball must travel over or round the net into the other players' court. A ball that hits the net during a rally is considered a legal return as long as it crosses into the opposite side of the court. The first player or team to fail to make a legal return loses the point. The server then moves to the other side of the service line at the start of a new point.[72]
Scoring
Game, set, match

Game
A game consists of a sequence of points played with the same player serving. A game is won by the first player to have won at least four points in total and at least two points more than the opponent. The running score of each game is described in a manner peculiar to tennis: scores from zero to three points are described as "love", "15", "30", and "40", respectively. If at least three points have been scored by each player, making the player's scores equal at 40 apiece, the score is not called out as "40–40", but rather as "deuce". If at least three points have been scored by each side and a player has one more point than his opponent, the score of the game is "advantage" for the player in the lead. During informal games, advantage can also be called "ad in" or "van in" when the serving player is ahead, and "ad out" or "van out" when the receiving player is ahead; alternatively, either player may simply call out "my ad" or "your ad".
The score of a tennis game during play is always read with the serving player's score first. In tournament play, the chair umpire calls the point count (e.g., "15–love") after each point. At the end of a game, the chair umpire also announces the winner of the game and the overall score.[73]
Set
A set consists of a sequence of games played with service alternating between games, ending when the count of games won meets certain criteria. Typically, a player wins a set by winning at least six games and at least two games more than the opponent. If one player has won six games and the opponent five, an additional game is played. If the leading player wins that game, the player wins the set 7–5. If the trailing player wins the game (tying the set 6–6) a tiebreak is played. A tiebreak, played under a separate set of rules, allows one player to win one more game and thus the set, to give a final set score of 7–6. A tiebreak game can be won by scoring at least seven points and at least two points more than the opponent. In a tiebreak, two players serve by 'ABBA' system which has been proven to be fair.[74] If a tiebreak is not played, the set is referred to as an advantage set, where the set continues without limit until one player leads by a two-game margin. A "love set" means that the loser of the set won zero games, colloquially termed a "jam donut" in the US.[75] In tournament play, the chair umpire announces the winner of the set and the overall score. The final score in sets is always read with the winning player's score first, e.g. "6–2, 4–6, 6–0, 7–5".
Match
A match consists of a sequence of sets. The outcome is determined through a best of three or five sets system. On the professional circuit, men play best-of-five-set matches at all four Grand Slam tournaments, Davis Cup, and the final of the Olympic Games and best-of-three-set matches at all other tournaments, while women play best-of-three-set matches at all tournaments. The first player to win two sets in a best-of-three, or three sets in a best-of-five, wins the match.[76] Only in the final sets of matches at the Olympic Games and Fed Cup are tiebreaks not played. In these cases, sets are played indefinitely until one player has a two-game lead, occasionally leading to some remarkably long matches.
In tournament play, the chair umpire announces the end of the match with the well-known phrase "Game, set, match" followed by the winning person's or team's name.
Special point terms
Game point
A game point occurs in tennis whenever the player who is in the lead in the game needs only one more point to win the game. The terminology is extended to sets (set point), matches (match point), and even championships (championship point). For example, if the player who is serving has a score of 40–love, the player has a triple game point (triple set point, etc.) as the player has three consecutive chances to win the game. Game points, set points, and match points are not part of official scoring and are not announced by the chair umpire in tournament play.
Break point
A break point occurs if the receiver, not the server, has a chance to win the game with the next point. Break points are of particular importance because serving is generally considered advantageous, with servers being expected to win games in which they are serving. A receiver who has one (score of 30–40 or advantage), two (score of 15–40) or three (score of love–40) consecutive chances to win the game has break point, double break point or triple break point, respectively. If the receiver does, in fact, win their break point, the game is awarded to the receiver, and the receiver is said to have converted their break point. If the receiver fails to win their break point it is called a failure to convert. Winning break points, and thus the game, is also referred to as breaking serve, as the receiver has disrupted, or broken the natural advantage of the server. If in the following game the previous server also wins a break point it is referred to as breaking back. Except where tiebreaks apply, at least one break of serve is required to win a set (otherwise a two-game lead would never occur).
Rule variations
- No ad
- From 'No advantage'. Scoring method created by Jimmy Van Alen. The first player or doubles team to win four points wins the game, regardless of whether the player or team is ahead by two points. When the game score reaches three points each, the receiver chooses which side of the court (advantage court or deuce court) the service is to be delivered on the seventh and game-deciding point. Utilized by World Team Tennis professional competition, ATP tours, WTA tours, ITF Pro Doubles and ITF Junior Doubles.[77][78]
- Pro set
- Instead of playing multiple sets, players may play one pro set. A pro set is first to 8 (or 10) games by a margin of two games, instead of first to 6 games. A 12-point tiebreak is usually played when the score is 8–8 (or 10–10). These are often played with no-ad scoring.
- Match tiebreak
- This is sometimes played instead of a third set. A match tiebreak (also called super tiebreak) is played like a regular tiebreak, but the winner must win ten points instead of seven. Match tiebreaks are used in the Hopman Cup, Grand Slams (excluding Wimbledon) and the Olympic Games for mixed doubles; on the ATP (since 2006), WTA (since 2007) and ITF (excluding four Grand Slam tournaments and the Davis Cup) tours for doubles and as a player's choice in USTA league play.
- Fast4
- Fast4 is a shortened format that offers a "fast" alternative, with four points, four games and four rules: there are no advantage scores, lets are played, tiebreakers apply at three games all, with it being first to five points with a "sudden death" point at four points all, and the first to four games wins the set. In the event of a no advantage deuce, the receiver gets to choose the service side. If a let occurs, the point continues as normal, and the non-receiver (in a doubles game) is permitted to return the serve. When players swap sides, they are not permitted to sit down and must be ready to play within sixty seconds. Between sets, players are permitted to sit down, and must be ready to play within ninety seconds.[79][80]
Another, however informal, tennis format is called Canadian doubles. This involves three players, with one person playing against a doubles team. The single player gets to utilize the alleys normally reserved only for a doubles team. Conversely, the doubles team does not use the alleys when executing a shot. The scoring is the same as for a regular game. This format is not sanctioned by any official body.
"Australian doubles", another informal and unsanctioned form of tennis, is played with similar rules to the Canadian doubles style, only in this version, players rotate court position after each game, each player taking a turn at playing alone against the other two. As such, each player plays doubles and singles over the course of a match, with the singles player always serving. Scoring styles vary, but one popular method is to assign a value of 2 points to each game, with the server taking both points if he or she holds serve and the doubles team each taking one if they break serve.
Wheelchair tennis can be played by able-bodied players as well as people who require a wheelchair for mobility. An extra bounce is permitted. This rule makes it possible to have mixed wheelchair and able-bodied matches. It is possible for a doubles team to consist of a wheelchair player and an able-bodied player (referred to as "one-up, one-down"), or for a wheelchair player to play against an able-bodied player. In such cases, the extra bounce is permitted for the wheelchair users only.
Match play

Continuity
A tennis match is intended to be continuous.[81] Because stamina is a relevant factor, arbitrary delays are not permitted. In most cases, service is required to occur no more than 20 seconds after the end of the previous point.[81] This is increased to 90 seconds when the players change ends (after every odd-numbered game), and a 2-minute break is permitted between sets.[81] Other than this, breaks are permitted only when forced by events beyond the players' control, such as rain, damaged footwear, damaged racket, or the need to retrieve an errant ball. Should a player be deemed to be stalling repeatedly, the chair umpire may initially give a warning followed by subsequent penalties of "point", "game", and default of the match for the player who is consistently taking longer than the allowed time limit.[82]
In the event of a rain delay, darkness or other external conditions halting play, the match is resumed at a later time, with the same score as at the time of the delay, and each player at the same end of the court as when rain halted play, or as close to the same relative compass point if play is resumed on a different court.
Ball changes
Balls wear out quickly in serious play and, therefore, in ATP and WTA tournaments, they are changed after every nine games with the first change occurring after only seven games, because the first set of balls is also used for the pre-match warm-up.[64] In ITF tournaments like Fed Cup, the balls are changed after every eleven games (rather than nine) with the first change occurring after only nine games (instead of seven). An exception is that a ball change may not take place at the beginning of a tiebreaker, in which case the ball change is delayed until the beginning of the second game of the next set.[66] As a courtesy to the receiver, the server will often signal to the receiver before the first serve of the game in which new balls are used as a reminder that they are using new balls. Continuity of the balls' condition is considered part of the game, so if a re-warm-up is required after an extended break in play (usually due to rain), then the re-warm-up is done using a separate set of balls, and use of the match balls is resumed only when play resumes.
On-court coaching
A recent rule change is to allow coaching on court on a limited basis during a match.[83][84][85][86] This has been introduced in women's tennis for WTA Tour events in 2009 and allows the player to request her coach once per set.[87]
Stance
Stance refers to the way a player prepares themselves in order to best be able to return a shot. Essentially, it enables them to move quickly in order to achieve a particular stroke. There are four main stances in modern tennis: open, semi-open, closed, and neutral. All four stances involve the player crouching in some manner: as well as being a more efficient striking posture, it allows them to isometrically preload their muscles in order to play the stroke more dynamically. What stance is selected is strongly influenced by shot selection. A player may quickly alter their stance depending on the circumstances and the type of shot they intend to play. Any given stance also alters dramatically based upon the actual playing of the shot with dynamic movements and shifts of body weight occurring.[88][89]
Open stance
This is the most common stance in tennis. The player's feet are placed parallel to the net. They may be pointing sideways, directly at the net or diagonally towards it. This stance allows for a high degree of torso rotation which can add significant power to the stroke. This process is sometimes likened to the coiling and uncoiling of a spring. i.e. the torso is rotated as a means of preloading the muscular system in preparation for playing the stroke: this is the coiling phase. When the stroke is played the torso rotates to face forwards again, called uncoiling, and adds significant power to the stroke. A disadvantage of this stance is that it does not always allow ‘for proper weight transfer and maintenance of balance’[88] when making powerful strokes. It is commonly used for forehand strokes; double-handed backhands can also be made effectively from it.
Semi-open stance
This stance is somewhere between open and closed and is a very flexible stance. The feet are aligned diagonally towards the net. It allows for a lot of shoulder rotation and the torso can be coiled, before being uncoiled into the shot in order to increase the power of the shot. It is commonly used in modern tennis especially by ‘top professional players on the forehand’.[90] Two-handed backhands can also be employed from this stance.
Closed stance
The closed stance is the least commonly used of the three main stances. One foot is placed further towards the net with the other foot further from it; there is a diagonal alignment between the feet. It allows for effective torso rotation in order to increase the power of the shot. It is usually used to play backhand shots and it is rare to see forehand shots played from it. A stroke from this stance may entail the rear foot coming completely off the floor with bodyweight being transferred entirely to the front foot.[88] [89]
Neutral stance
This is sometimes also referred to as the square stance. One foot is positioned closer to the net and ahead of the other which is behind and in line with it. Both feet are aligned at a 90 degree angle to the net. The neutral stance is often taught early because ‘It allows beginners to learn about shifting weight and rotation of the body.’[89] Forehands and backhands may be made from it.[91]
Shots
Competent tennis players have eight basic shots in their repertoire: the serve, forehand, backhand, volley, half-volley, overhead smash, drop shot, and lob.
Grip
A grip is a way of holding the racket in order to hit shots during a match. The grip affects the angle of the racket face when it hits the ball and influences the pace, spin, and placement of the shot. Players use various grips during play, including the Continental (The "Handshake Grip"), Eastern (either semi-eastern or full eastern, usually used for backhands), and Western (semi-western or full western, usually for forehand grips) grips. Most players change grips during a match depending on what shot they are hitting; for example, slice shots and serves call for a Continental grip.[92]
Serve

A serve (or, more formally, a "service") in tennis is a shot to start a point. The serve is initiated by tossing the ball into the air and hitting it (usually near the apex of its trajectory) into the diagonally opposite service box without touching the net. The serve may be hit under- or overhand although underhand serving remains a rarity.[93] If the ball hits the net on the first serve and bounces over into the correct diagonal box then it is called a "let" and the server gets two more additional serves to get it in. There can also be a let if the server serves the ball and the receiver isn't prepared.[66] If the server misses his or her first serve and gets a let on the second serve, then they get one more try to get the serve in the box.
Experienced players strive to master the conventional overhand serve to maximize its power and placement. The server may employ different types of serve including flat serve, topspin serve, slice serve, and kick (American twist) serve. A reverse type of spin serve is hit in a manner that spins the ball opposite the natural spin of the server, the spin direction depending upon right- or left-handedness. If the ball is spinning counterclockwise, it will curve right from the hitter's point of view and curve left if spinning clockwise.[94]
Some servers are content to use the serve simply to initiate the point; however, advanced players often try to hit a winning shot with their serve. A winning serve that is not touched by the opponent is called an "ace".
Forehand

For a right-handed player, the forehand is a stroke that begins on the right side of the body, continues across the body as contact is made with the ball, and ends on the left side of the body. There are various grips for executing the forehand, and their popularity has fluctuated over the years. The most important ones are the continental, the eastern, the semi-western, and the western. For a number of years, the small, frail 1920s player Bill Johnston was considered by many to have had the best forehand of all time, a stroke that he hit shoulder-high using a western grip. Few top players used the western grip after the 1920s, but in the latter part of the 20th century, as shot-making techniques and equipment changed radically, the western forehand made a strong comeback and is now used by many modern players. No matter which grip is used, most forehands are generally executed with one hand holding the racket, but there have been fine players with two-handed forehands. In the 1940s and 50s, the Ecuadorian/American player Pancho Segura used a two-handed forehand to achieve a devastating effect against larger, more powerful players. Players such as Monica Seles or France's Fabrice Santoro and Marion Bartoli are also notable players known for their two-handed forehands.[95]
Backhand

For right-handed players, the backhand is a stroke that begins on the left side of their body, continues across their body as contact is made with the ball, and ends on the right side of their body. It can be executed with either one hand or with both and is generally considered more difficult to master than the forehand. For most of the 20th century, the backhand was performed with one hand, using either an eastern or a continental grip. The first notable players to use two hands were the 1930s Australians Vivian McGrath and John Bromwich, but they were lone exceptions. The two-handed grip gained popularity in the 1970s as Björn Borg, Chris Evert, Jimmy Connors, and later Mats Wilander and Marat Safin used it to great effect, and it is now used by a large number of the world's best players, including Novak Djokovic, Rafael Nadal and Serena Williams.[96]
Two hands give the player more control, while one hand can generate a slice shot, applying backspin on the ball to produce a low trajectory bounce. Reach is also limited with the two-handed shot. The player long considered to have had the best backhand of all time, Don Budge, had a powerful one-handed stroke in the 1930s and 1940s that imparted topspin onto the ball. Ken Rosewall, another player noted for his one-handed backhand, used a very accurate slice backhand through the 1950s and 1960s. A small number of players, notably Monica Seles, use two hands on both the backhand and forehand sides.
Other shots
A volley is a shot returned to the opponent in mid-air before the ball bounces, generally performed near the net, and is usually made with a stiff-wristed punching motion to hit the ball into an open area of the opponent's court. The half volley is made by hitting the ball on the rise just after it has bounced, also generally in the vicinity of the net, and played with the racket close to the ground.[97] The swinging volley is hit out of the air as the player approaches the net. It is an offensive shot used to take preparation time away from the opponent, as it returns the ball into the opponent's court much faster than a standard volley.
From a poor defensive position on the baseline, the lob can be used as either an offensive or defensive weapon, hitting the ball high and deep into the opponent's court to either enable the lobber to get into better defensive position or to win the point outright by hitting it over the opponent's head. If the lob is not hit deeply enough into the other court, however, an opponent near the net may then hit an overhead smash, a hard, serve-like shot, to try to end the point.
Zdroj:https://en.wikipedia.org?pojem=Tennis
Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších podmienok. Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky použitia.
Antropológia
Aplikované vedy
Bibliometria
Dejiny vedy
Encyklopédie
Filozofia vedy
Forenzné vedy
Humanitné vedy
Knižničná veda
Kryogenika
Kryptológia
Kulturológia
Literárna veda
Medzidisciplinárne oblasti
Metódy kvantitatívnej analýzy
Metavedy
Metodika
Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative
Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších
podmienok.
Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky
použitia.
www.astronomia.sk | www.biologia.sk | www.botanika.sk | www.dejiny.sk | www.economy.sk | www.elektrotechnika.sk | www.estetika.sk | www.farmakologia.sk | www.filozofia.sk | Fyzika | www.futurologia.sk | www.genetika.sk | www.chemia.sk | www.lingvistika.sk | www.politologia.sk | www.psychologia.sk | www.sexuologia.sk | www.sociologia.sk | www.veda.sk I www.zoologia.sk
