A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
This article's use of external links may not follow Wikipedia's policies or guidelines. (July 2022) |
| |||

| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Sulfuric acid
| |||
Other names
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.763 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| E number | E513 (acidity regulators, ...) | ||
| 2122 | |||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1830 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
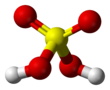
| H2SO4, sometimes expressed (HO)2SO2 | |||
| Molar mass | 98.079 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Colorless viscous liquid | ||
| Odor | Odorless | ||
| Density | 1.8302 g/cm3, liquid[1] | ||
| Melting point | 10.31[1] °C (50.56 °F; 283.46 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 337[1] °C (639 °F; 610 K) When sulfuric acid is above 300 °C (572 °F; 573 K), it gradually decomposes to SO3 + H2O | ||
| miscible, exothermic | |||
| Vapor pressure | 0.001 mmHg (20 °C)[2] | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | pKa1 = −2.8 pKa2 = 1.99 | ||
| Conjugate base | Bisulfate | ||
| Viscosity | 26.7 cP (20 °C) | ||
| Structure[3] | |||
| monoclinic | |||
| C2/c | |||
a = 818.1(2) pm, b = 469.60(10) pm, c = 856.3(2) pm α = 90°, β = 111.39(3)
°, γ = 90° | |||
Formula units (Z)
|
4 | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
157 J/(mol·K)[4] | ||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−814 kJ/mol[4] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
 
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H314 | |||
| P260, P264, P280, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P321, P363, P405, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | Non-flammable | ||
Threshold limit value (TLV)
|
15 mg/m3 (IDLH), 1 mg/m3 (TWA), 2 mg/m3 (STEL) | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
2140 mg/kg (rat, oral)[5] | ||
LC50 (median concentration)
|
| ||
LCLo (lowest published)
|
87 mg/m3 (guinea pig, 2.75 hr)[5] | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 1 mg/m3[2] | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 1 mg/m3[2] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
15 mg/m3[2] | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related strong acids
|
|||
Related compounds
|
|||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |||
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid (Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen, and hydrogen, with the molecular formula H2SO4. It is a colorless, odorless, and viscous liquid that is miscible with water.[6]
Pure sulfuric acid does not occur naturally due to its strong affinity to water vapor; it is hygroscopic and readily absorbs water vapor from the air.[6] Concentrated sulfuric acid is highly corrosive towards other materials, from rocks to metals, since it is an oxidant with powerful dehydrating properties. Phosphorus pentoxide is a notable exception in that it is not dehydrated by sulfuric acid but, to the contrary, dehydrates sulfuric acid to sulfur trioxide. Upon addition of sulfuric acid to water, a considerable amount of heat is released; thus, the reverse procedure of adding water to the acid should not be performed since the heat released may boil the solution, spraying droplets of hot acid during the process. Upon contact with body tissue, sulfuric acid can cause severe acidic chemical burns and even secondary thermal burns due to dehydration.[7][8] Dilute sulfuric acid is substantially less hazardous without the oxidative and dehydrating properties; however, it should still be handled with care for its acidity.
Sulfuric acid is a very important commodity chemical; a country's sulfuric acid production is a good indicator of its industrial strength.[9] Many methods for its production are known, including the contact process, the wet sulfuric acid process, and the lead chamber process.[10] Sulfuric acid is also a key substance in the chemical industry. It is most commonly used in fertilizer manufacture[11] but is also important in mineral processing, oil refining, wastewater processing, and chemical synthesis. It has a wide range of end applications, including in domestic acidic drain cleaners,[12] as an electrolyte in lead-acid batteries, in dehydrating a compound, and in various cleaning agents. Sulfuric acid can be obtained by dissolving sulfur trioxide in water.
Physical properties
Grades of sulfuric acid
Although nearly 100% sulfuric acid solutions can be made, the subsequent loss of SO3 at the boiling point brings the concentration to 98.3% acid. The 98.3% grade, which is more stable in storage, is the usual form of what is described as "concentrated sulfuric acid". Other concentrations are used for different purposes. Some common concentrations are:[13][14]