
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
| Panoan | |
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution | southwestern Amazon |
| Linguistic classification | Pano–Tacanan?
|
| Glottolog | pano1256 |
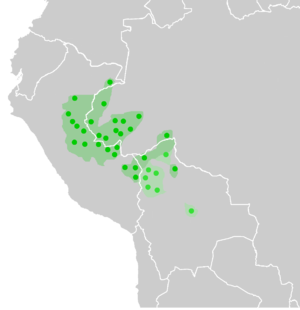 Panoan languages (dark green) and Takanan languages (light green). Spots indicate documented locations. | |
Panoan (also Pánoan, Panoano, Panoana, Páno) is a family of languages spoken in western Brazil, eastern Peru, and northern Bolivia. It is possibly a branch of a larger Pano–Tacanan family.
Genetic relations
The Panoan family is generally believed to be related to the Tacanan family, forming with it Pano–Tacanan, though this has not yet been established (Loos 1999).
Language contact
Jolkesky (2016) notes that there are lexical similarities with the Kechua, Mapudungun, Moseten-Tsimane, Tukano, Uru-Chipaya, Harakmbet, Arawak, Kandoshi, and Pukina language families due to contact.[1]
Languages
There are some 18 extant and 14 extinct Panoan languages.[2] In the list of Panoan languages below adapted from Fleck (2013), (†) means extinct, and (*) obsolescent (no longer spoken daily). Dialects are listed in parentheses.
- Panoan
- Mayoruna
- Tabatinga Mayoruna †
- Mayo
- Matses
- Matses (Peruvian Matses, Brazilian Matses, Paud Usunkid†)
- Kulino (of Curuça)* (Kapishtana*, Mawi*, Chema*)
- Demushbo †
- Korubo (Korubo, Chankueshbo*)
- Matis
- Matis
- Jandiatuba Mayoruna †
- Amazon Mayoruna † (two dialects)
- Matses
- Mainline Panoan
- Kasharari
- Kashibo (Kashibo, Rubo/Isunbo, Kakataibo, Nokaman)
- Nawa branch (from least to most divergent)
- Bolivian
- Madre de Dios †
- Atsawaka-Yamiaka † (Atsawaka, Yamiaka)
- Arazaire †
- Blanco River Remo †
- Tarauacá Kashinawa †
- Marubo
- Marubo
- Katukina (or Waninawa: Katukina of Olinda, Katukina of Sete Estrelas, Kanamari†)
- Olivença Kulina
- Poyanawa*
- Poyanawa †
- Iskonawa*
- Nukini †
- ?Môa Nawa*
- Jaquirana Remo †
- Chama
- Headwaters
- Ibuaçu Kashinawa (Brazilian Kashinawa, Peruvian Kashinawa, Juruá Kapanawa†, Parannawa†)
- Yaminawa (Brazilian Yaminawa dialects, Peruvian Yaminawa, Chaninawa, Chitonawa, Mastanawa, Parkenawa (= Yora), Shanenawa, Sharanawa/Marinawa, Shawannawa (= Arara), Yawanawa, Yaminawa-arara*, Nehanawa†)
- Amawaka (Peruvian Amawaka, Nishinawa†, Yumanawa†)
- Môa Remo † (resembles Amawaka)
- Tuchinawa † (resembles Yaminawa dialects)
- Mayoruna
Boundaries between the Poyanawa, Chama, and Headwaters groups are somewhat blurred. Karipuna and Môa River Nawa may not be distinct languages, and Chiriba may not be Panoan at all.
Hundreds of other Panoan "languages" have been reported in the literature. These are names of groups that may have been ethnically Panoan, but whose language is unattested. They sometimes are assumed to be Panoan on no other evidence than that the name ends in -nawa or -bo. A few, such as Maya (Pisabo), are unattested but reported to be mutually intelligible with a known Panoan language (in this case Matsés).[citation needed] The people speaking one of these supposed languages, Kontanáwa,[3] was rediscovered in 2002. However, no linguistic information is available, and it is not known if they speak a distinct language.[4]
Amarante Ribeiro (2005)
Classification of the Panoan languages according to Amarante Ribeiro (2005):[5]
- Panoan
- Group I
- Group II
- Group III
- Group IV
Oliveira (2014)
Internal classification by Oliveira (2014: 123):[6]
- Panoan
- Group 1: Kashíbo
- Group 2
- Shípibo-Kónibo, Kapanáwa
- Marúbo (?)
- Group 3: Chákobo, Kaxararí (?)
- Group 4: Yamináwa, Chanináwa, Sharanáwa
- Group 5: Shanenáwa, Katukína
- Group 6: Poyanáwa (?), Amawáka
- Group 7
- Kaxinawá, Marináwa
- Yawanawá
- Group 8: Mayorúna, Matís, Korúbo
Jolkesky (2016)
Internal classification by Jolkesky (2016):[1]
(† = extinct)
- Pano
- Pano, Northern
- Pano, Nuclear
- Kasharari
- Pano, Western
- Pano, Central
- Purus
- Jurua
- Nukini-Remo
- Atsawaka †
- Chakobo
- Shipibo-Kapanawa
Homonyms
Much of the confusion surrounding Panoan languages is the number of homonyms among different languages. The principal ambiguous names are as follows:[2]
| Name | Location or other name | Language |
|---|---|---|
| Kapanawa | on the Tapiche | dialect of Shipibo-Konibo |
| on the Juruá | dialect of Ibuaçu Kashinawa | |
| Kashinawa | on the Ibuaçu | Headwaters group |
| on the Tarauacá | Mainline branch | |
| Kulina | on the Curuçá | Mayoruna branch |
| of São Paulo de Olivençá | Mainline branch | |
| Marubo | in the Javari Basin | Mainline branch |
| of Maucallacta | Mayoruna branch | |
| Remo | on the Blanco | Nawa group |
| on the Môa | Headwaters group | |
| on the Jaquirana | Poyanawa group | |
| Southern Remo | Chama group | |
| Sinabo | of the Mamoré | Bolivian group |
| of the Ucayali Basin | Chama group | |
| Katukina | Waninawa | Marubo group |
| of Feijo' (Shanenawa) | dialect of Yaminawa | |
| Nawa | on the Môa | Poyanawa group |
| Parkenawa | dialect of Yaminawa | |
| Maroyuna | (various) | three languages in list above |
| Mates | Mates | |
| Barbudo | Chama group | |
| Demushbo | Matses group | |
| Chema | dialect of Curuçá Kulina |
Neighboring languages of other families may also share the names of Panoan language. The table below ignores other homonyms further afield:
| Family | Language |
|---|---|
| Arawakan | Kanamari, Kasharari, Kunibo, Mayoruna, Pakaguara |
| Takanan | Chama, Arasa, Atsahuaca, Yamiaka |
| Katukinan | Katukina, Kanamari |
| Tupian | Karipuna, Katukinarú |
| Arawan | Kulina, Arawá |
| Harakmbut | Arasairi |
Varieties
Below is a full list of Panoan language varieties listed by Loukotka (1968), including names of unattested varieties.[7]
- Northern languages
- Pano / Pánobo - spoken in the village of Contamana on the Ucayali River, Loreto province, Peru.
- Maruba / Maxuruna / Mayoruna / Pelado / Dallus - spoken on the Maruba River and Jandiatuba River, state of Amazonas.
- Culino - extinct language once spoken between the Jutaí River, Javarí River, and Jandiatuba River, Amazonas.
- Panau - spoken by only a few families in Seringal Barão, Rio Branco, territory of Acre, Brazil. (Unattested.)
- Cashibo / Cacataibo / Caxivo / Hagueti - spoken on the Pachitea River, Pisqui River, and Aguaytía River, Loreto, Peru.
- Manamabobo - extinct language once spoken on the Pachitea River, Peru. (Unattested.)
- Carapacho / Caliseca - once spoken on the Carapacho River, Peru. (Unattested.)
- Pichobo - once spoken at the mouth of the Paguamigua River in Peru. (Unattested.)
- Sobolbo / Bolbo - once spoken on the Cohengua River, Peru. (Unattested.)
- Mochobo - once spoken between the Guanie River and Guarimi River. (Unattested.)
- Maspo - once spoken on the Taco River and Manipaboro River. (Unattested.)
- Comobo / Univitsa - once spoken in the same region on the Inua River and Unini River. (Unattested.)
- Conibo / Cunibo / Curibeo - spoken along the Ucayali River between 8° 30' and 10° latitude.
- Cháma / Manava / Chipeo / Setebo / Shipibo / Puinahva - spoken on the Ucayali River north of the Conibo tribe.
- Nocamán - spoken at the sources of the Chesco River, Loreto.
- Ruanagua - spoken on the Corjuania River, Loreto. (Unattested.)
- Capanagua - spoken on the Tapiche River and Blanco River, Loreto.
- Busquipani - once spoken on the Alacrán River, Loreto. (Unattested.)
- Custanáwa - spoken on the upper course of the Purus River near the mouth of the Curanja River, Loreto. (Unattested.)
- Espino - spoken on the Curumaha River in the same region. (Unattested.)
- Yura - once spoken on the Piqueyaco River, Loreto. (Unattested.)
- Marináwa - spoken on the Furnaya River, Loreto. (Pike and Scott 1962.)
- Xaranáwa - spoken on the Curanja River, Loreto. (Unattested.)
- Canawari - extinct language once spoken on the Curumaha River and Rixalá River, Acre territory, Brazil
- Nucuini / Remo / Rheno - spoken at the sources of the Javari River and on the Moenalco River[further explanation needed] and Ipixuna River, state of Amazonas.
- Amahuaca / Sayaco / Impetineri - spoken on the Urubamba River and Ucayali River, Loreto, and on the Purus River and Juruá River, Acre.
- Mastináhua - spoken on the Purus River in the same territory. (Unattested.)
- Cachináua / Huñikui - spoken between the Embira River, Liberdade River, and Tarauacá River, state of Amazonas.
- Tuxináua - spoken on the Embira River and Humaitá River, Acre.
- Camanáwa - on the Môa River in Acre. (Unattested.)
- Pacanáwa - spoken at the sources of the Embira River, Acre. (Unattested.)
- Nehanáwa - spoken by a small tribe on the Jordão River, Acre.
- Nastanáwa - spoken on the upper course of the Jordão River.
- Cuyanáwa - spoken between the Môa River and Paraná dos Mouros River, Acre territory. (Unattested.)
- Sacuya - once spoken between the Juruá River and Tamaya River, Acre. (Unattested.)
- Xanindáua - spoken by a small tribe on the Riozinho River, Acre. (Unattested.)
- Coronáwa - spoken in the Acre territory, but exact location unknown. (Unattested.)
- Yauavo - once spoken between the Tejo River and Aturia River, Acre. (Unattested.)
- Yaminaua group
- Yaminaua - spoken at the sources of the Tarauaca River, territory of Acre.
- Poyanáwa - spoken in Acre territory on the Môa River.
- Yumanáwa - spoken on the Muruzinho River, Acre.
- Paran-náwa - spoken on the Muru River, Acre.
- Nixináwa - spoken on the Jordão River, Acre.
- Yawanáwa - spoken in Acre territory on the upper course of the Jordão River.
- Sanináwa / Shanináua - spoken on the Valparaiso River, Liberdade River, and Humaitá River, Acre.
- Xipináwa - spoken between the Valparaiso River and Liberdade River. (Unattested.)
- Aranáwa - spoken between the Humaitá River and Liberdade River. (Unattested.)
- Contanáwa - spoken in Acre on the upper course of the Tarauaca River and on the Humaitá River. (Unattested.)
- Yumináhua - spoken on the Tarauaca River, Acre. (Unattested.)
- Wamináua / Catoquino do Rio Gregorio - spoken in the same territory on the Gregorio River.
- Sensi group
- Sensi - spoken on the Huanachá River and Chanuya River, department of Loreto, Peru.
- Central group
- Yamiaca / Haauñeiri - spoken by a small tribe on the Yaguarmayo River, department of Madre de Dios, Peru.
- Arazaire - language spoken by a few families in the same region on the Marcapata River.
- Atsahuaca / Chaspa - spoken on the Carama River in Peru.
- Araua - extinct language once spoken on the Chiva River, territory of Colonia, Bolivia. (Unattested.)
- Eastern group
- Chacobo - spoken around Lake Rogoaguado, Beni province, Bolivia.
- Capuibo - once spoken on the Biata River in Beni province, Bolivia. (Unattested.)
- Pacaguara - language now probably extinct, once spoken between the Beni River and Abuña River.
- Sinabo / Shenabu / Gritones - language now probably extinct, once spoken on the Mamoré River near Los Almendrales, Beni Province. (Unattested.)
- Caripuna / Jaunavô / Shakáre / Éloe / Yacariá - spoken in the nineteenth century along the Madeira River and the sources of the Beni River, now only in a single village at the mouth of the Mutumparaná River, Rondônia.
- Pama / Pamainá - language of an unknown tribe of the Caldeirão River, territory of Rondônia. (Unattested.)
Grammatical features
Body-part prefixation
Exceptional to Panoan languages' predominantly suffixal morphology are sets of approximately 30 morphemes primarily referring to parts or features of prototypical human and animal bodies (and, by analogical extension, of botanicals, manufactures, landscapes, and abstract space) which have been found to occur in almost all attested languages of the family (Fleck 2006: 59; Ferreira 2007, 2008; Amarante Ribeiro and Cândido 2008; Zariquiey and Fleck 2012: 385–386).
That these monosyllabic forms are productively affixed to the front of verbal, nominal, or adjectival roots has led many Panoanists to describe them as prefixes (e.g. Prost 1967 and Zingg 1998 ; Faust 1973, Loriot et al. 1993, and Valenzuela 2003 ; Hyde 1980 ; Eakin 1991), while the forms' resemblance and loose semantic correspondence to unbound, polysyllabic 'body-part terms' has led others to describe them as incorporated nouns (e.g. Loos 1999). More recent and detailed analyses of this feature in Matses (Fleck 2006) and Kashibo-Kakataibo (Zariquiey and Fleck 2012) have demonstrated that most body-part prefixes in these languages are not readily analyzable as synchronic allomorphs of the nouns they resemble.
Many Panoan body-part prefixes semantically encompass a range of denotata beyond the strictly 'corporeal' by means of analogical extension. In Matses, for example, the prefix an- corresponds to the nouns ana 'mouth, tongue, palm (of hand), sole (of foot), (arm)pit'; anmaëşh 'gill slits (of fish)'; and anşhantuk 'swampy depression in the ground'; but can itself be glossed also as 'cavity, concave surface, interior, underside'; and 'center (of path of stream)' (Fleck 2006: 64). In the examples below, the prefix an- with the verb root kiad 'learn' expresses the learning of a specifically 'oral activity' while the prefix më- 'hand, mortar, forearm, wrist, projecting carpal bones, elbow, finger, knuckles, fingernail, branch' expresses the learning of a specifically 'manual' one:
an-kiad-o-bi
mouth-learn-PAST-1S
'I learned with respect to (my) mouth', i.e., 'I learned an oral activity' (a language, to speak, a song, to sing, to recite the alphabet, to whistle, to eat a type of food, etc.) (Fleck 2006: 78)
më-kiad-o-bi
hand-learn-PAST-1S
'I learned to weave, write, do math problems, fire shotgun, fletch arrows, or other manual tasks' (Fleck 2006: 78)
The following example illustrates how an- can express locative information in non-corporeal, topographical space:
nëid-ø
this.one-ABS
an-san-aşh
center-put:PL.O-after:S/A>S
we-ta
lie-IMP
ø
3.ABS
ke-pa-ak
say-TOP.CONT-NARR.PAST
ka-denne-k
tell-REM.PAST.IND
ke-onda-şh
tell-DIST.PAST-3
'"Put this one in the middle of the path and then lie down!" he the moon said, they used to tell, I was told' (Fleck 2006: 80).
While body-part prefixes in Kashibo-Kakataibo, as in Matses, are highly productive with verbs, they are used regularly with only a modest array of adjectives and nouns (Fleck 2006: 72; Zariquiey and Fleck 2012: 394–5). Zariquiey and Fleck (2012: 394) note that the Kashibo-Kakataibo "words for 'skin', 'hair', and 'flesh'" are regularly prefixed:
kapë
caiman
të-şhaka
neck-skin.ABS
mëra-aşh
find-S/A>S
...
'finding the caiman's neck skin ...' (Zariquiey and Fleck 2012: 395).
Due to the paucity of detailed studies of Panoan body-part prefixes, explanations of their grammaticalization remain largely speculative. Fleck has hypothesized that "Panoan (verb) prefixation evolved from past noun incorporation that co-existed with noun-noun and noun-adjective compounding that involved synchronic reduction of body-part roots" (2006: 92). In light of their analysis of Kashibo-Kakataibo prefixation, Zariquiey and Fleck present two diachronic scenarios to orient future comparative work: "(1) prefixation evolved from productive noun incorporation (prefixes have come from longer body-part nouns); or (2) Proto-Panoan body-part terms were monosyllabic forms that became bound, and most of the current body-part terms were later built up from these" (2012: 408).
Vocabularyedit
Loukotka (1968) lists the following basic vocabulary items.[7]
| Language | Branch | head | tooth | tongue | foot | one | two | three |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pánobo | I | mápu | séta | hána | tal'i | hawícho | dawuó | muken |
| Maruba | I | mápu | chitá | ána | tái | pazü | dabui | muken |
| Culino | I | mazu | sita | anú | whüta | uitü | rabü | taküma |
| Cashieo | I | mapo | dzeta | hana | tak | achapré | rabue | itsa |
| Conibo | I | mápo | seta | hana | tai | achapré | rabue | |
| Cháma | I | mápuro | seta | hana | tal | hávicho | ravué | pike |
| Nocamán | I | mápuro | téta | ána | tai | aindzinige | rawué | |
| Capanagua | II | mápu | shríta | hána | tahö | hawichu | rawík | |
| Canawari | II | |||||||
| Nucuini | II | mapú | sheta | aná | taki | usichari | narabe | narana |
| Amaguaca | II | mápu | teta | haná | taku | wuistéra | rábue | |
| Caxinaua | II | mápo | xeltá | hana | taö | böste | rabö | nadabö |
| Tuxináua | II | mapoː | anan | tai | ||||
| Nehanáwa | II | mapu | mátya | húna | tahʔ | |||
| Yawanáwa | Yaminaua II | mapo | sheta | hána | ||||
| Xanináwa | Yaminaua II | mi-fushha | shʔta | háda | tahʔ | |||
| Wanináwa | Yaminaua II | mapu | shötah | ana | tahö | |||
| Sensi | Yaminaua II | omátsi | küödsa | yáta | nawuístikoe | rawué | naravuekoe | |
| Yaminaua | Yaminaua I | woshka | shata | hanka | tai | huísti | rháhui | mapo |
| Poyanáwa | Yaminaua I | vouká | ritá | andá | tae | uesteː | arabiː | aranan |
| Yumanáwa | Yaminaua I | buska | sheta | xánda | táha | |||
| Paran-Nawa | Yaminaua I | buska | sheta | hána | tahe | Zdroj:https://en.wikipedia.org?pojem=Panoan_language
