
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
| Euglenozoa Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|
| |
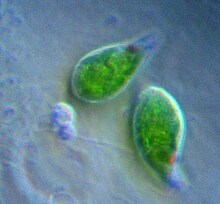
| Two Euglena | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Clade: | Discoba |
| Superphylum: | Discicristata |
| Phylum: | Euglenozoa Cavalier-Smith, 1981[2] |
| Classes | |
Euglenozoa are a large group of flagellate Discoba. They include a variety of common free-living species, as well as a few important parasites, some of which infect humans. Euglenozoa are represented by four major groups, i.e., Kinetoplastea, Diplonemea, Euglenida, and Symbiontida. Euglenozoa are unicellular, mostly around 15–40 μm (0.00059–0.00157 in) in size, although some euglenids get up to 500 μm (0.020 in) long.[3]
Structure
Most euglenozoa have two flagella, which are inserted parallel to one another in an apical or subapical pocket. In some these are associated with a cytostome or mouth, used to ingest bacteria or other small organisms. This is supported by one of three sets of microtubules that arise from the flagellar bases; the other two support the dorsal and ventral surfaces of the cell.[4]
Some other euglenozoa feed through absorption, and many euglenids possess chloroplasts, the only eukaryotes outside Diaphoretickes to do so without performing kleptoplasty,[5][failed verification] and so obtain energy through photosynthesis. These chloroplasts are surrounded by three membranes and contain chlorophylls A and B, along with other pigments, so are probably derived from a green alga, captured long ago in an endosymbiosis by a basal euglenozoan. Reproduction occurs exclusively through cell division. During mitosis, the nuclear membrane remains intact, and the spindle microtubules form inside of it.[4]
The group is characterized by the ultrastructure of the flagella. In addition to the normal supporting microtubules or axoneme, each contains a rod (called paraxonemal), which has a tubular structure in one flagellum and a latticed structure in the other. Based on this, two smaller groups have been included here: the diplonemids and Postgaardi.[6]
Classification
Historically, euglenozoans have been treated as either plants or animals, depending on whether they belong to largely photosynthetic groups or not. Hence they have names based on either the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICNafp) or the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN). For example, one family has the name Euglenaceae under the ICNafp and the name Euglenidae under the ICZN. As another example, the genus name Dinema is acceptable under the ICZN, but illegitimate under the ICNafp, as it is a later homonym of an orchid genus, so that the synonym Dinematomonas must be used instead.[7]
The Euglenozoa are generally accepted as monophyletic. They are related to Percolozoa; the two share mitochondria with disk-shaped cristae, which only occurs in a few other groups.[8] Both probably belong to a larger group of eukaryotes called the Excavata.[9] This grouping, though, has been challenged.[10]
Phylogeny
The phylogeny based on the work of Cavalier-Smith (2016):[11]
