
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9


| Part of a series on |
| Rail transport |
|---|
 |
|
|
| Infrastructure |
|
|
| Service and rolling stock |
|
| Special systems |
|
|
| Miscellanea |
|
|
A tram (called a streetcar or trolley in the United States and Canada) is a type of urban rail transit consisting of a rail vehicle, either individual railcars or self-propelled trains coupled by a multiple unit, that runs on tramway tracks on urban public streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way.[1][2][3] The tramlines or networks operated as public transport are called tramways or simply trams/streetcars. Many recently built tramways use the contemporary term light rail.
Tram vehicles are usually lighter and shorter than main line and rapid transit trains. Today, most trams use electrical power, usually fed by a pantograph sliding on an overhead line; older systems may use a trolley pole or a bow collector. In some cases, a contact shoe on a third rail is used. If necessary, they may have dual power systems—electricity in city streets and diesel in more rural environments. Occasionally, trams also carry freight. Trams are now commonly included in the wider term "light rail",[4] which also includes grade-separated systems. Some trams, known as tram-trains, may have segments that run on mainline railway tracks, similar to interurban systems. The differences between these modes of rail transport are often indistinct and a given system may combine multiple features.

One of the advantages over earlier forms of transit was the low rolling resistance of metal wheels on steel rails, allowing the trams to haul a greater load for a given effort. Another factor which contributed to the rise of trams was the high total cost of ownership of horses. Electric trams largely replaced animal power in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Improvements in other vehicles such as buses led to decline of trams in the mid 20th century. However, trams have seen resurgence in recent years.
History
Creation
The history of passenger trams, streetcars and trolley systems, began in the early nineteenth century. It can be divided into several distinct periods defined by the principal means of power used. Precursors to the tramway included the wooden or stone wagonways used in central Europe to transport mine carts with unflanged wheels since the 1500s, and the paved limestone trackways designed by the Romans for heavy horse and ox-drawn transportation. By the 1700s, paved plateways with cast iron rails were introduced in England for transporting coal, stone or iron ore from the mines to the urban factories and docks. The Swansea and Mumbles Railway (see below) originally operated as an industrial tramway from 1804-07.
Horse-drawn

The world's first passenger train or tram was the Swansea and Mumbles Railway, in Wales, UK. The British Parliament passed the Mumbles Railway Act in 1804, and horse-drawn service started in 1807.[5] The service closed in 1827, but was restarted in 1860, again using horses.[6] It was worked by steam from 1877, and then, from 1929, by very large (106-seater) electric tramcars, until closure in 1960.[7] The Swansea and Mumbles Railway was something of a one-off however, and no street tramway appeared in Britain until 1860 when one was built in Birkenhead by the American George Francis Train.[8]
Street railways developed in America before Europe, largely due to the poor paving of the streets in American cities which made them unsuitable for horsebuses, which were then common on the well-paved streets of European cities. Running the horsecars on rails allowed for a much smoother ride. There are records of a street railway running in Baltimore as early as 1828, however the first authenticated streetcar in America, was the New York and Harlem Railroad developed by the Irish coach builder John Stephenson, in New York City which began service in the year 1832.[9][10] The New York and Harlem Railroad's Fourth Avenue Line ran along the Bowery and Fourth Avenue in New York City. It was followed in 1835 by the New Orleans and Carrollton Railroad in New Orleans, Louisiana,[11] which still operates as the St. Charles Streetcar Line. Other American cities did not follow until the 1850s, after which the "animal railway" became an increasingly common feature in the larger towns.[11]
The first permanent tram line in continental Europe was opened in Paris in 1855 by Alphonse Loubat who had previously worked on American streetcar lines.[12] The tram was developed in numerous cities of Europe (some of the most extensive systems were found in Berlin, Budapest, Birmingham, Saint Petersburg, Lisbon, London, Manchester, Paris, Kyiv).

The first tram in South America opened in 1858 in Santiago, Chile. The first trams in Australia opened in 1860 in Sydney. Africa's first tram service started in Alexandria on 8 January 1863. The first trams in Asia opened in 1869 in Batavia (now Jakarta), Netherlands East Indies (now Indonesia).
Problems with horsecars included the fact that any given animal could only work so many hours on a given day, had to be housed, groomed, fed and cared for day in and day out, and produced prodigious amounts of manure, which the streetcar company was charged with storing and then disposing of. Since a typical horse pulled a streetcar for about a dozen miles a day and worked for four or five hours, many systems needed ten or more horses in stable for each horsecar. In 1905 the British newspaper Newcastle Daily Chronicle reported that, "A large number of London's discarded horse tramcars have been sent to Lincolnshire where they are used as sleeping rooms for potato pickers".[13]
Horsecars were largely replaced by electric-powered trams following the improvement of an overhead trolley system on trams for collecting electricity from overhead wires by Frank J. Sprague. His spring-loaded trolley pole used a wheel to travel along the wire. In late 1887 and early 1888, using his trolley system, Sprague installed the first successful large electric street railway system in Richmond, Virginia. Within a year, the economy of electric power had replaced more costly horsecars in many cities. By 1889, 110 electric railways incorporating Sprague's equipment had been begun or planned on several continents.[14]
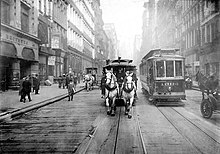
Horses continued to be used for light shunting well into the 20th century, and many large metropolitan lines lasted into the early 20th century. New York City had a regular horsecar service on the Bleecker Street Line until its closure in 1917.[15] Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, had its Sarah Street line drawn by horses until 1923. The last regular mule-drawn cars in the US ran in Sulphur Rock, Arkansas, until 1926 and were commemorated by a U.S. postage stamp issued in 1983.[16] The last mule tram service in Mexico City ended in 1932, and a mule tram in Celaya, Mexico, survived until 1954.[17] The last horse-drawn tram to be withdrawn from public service in the UK took passengers from Fintona railway station to Fintona Junction one mile away on the main Omagh to Enniskillen railway in Northern Ireland. The tram made its last journey on 30 September 1957 when the Omagh to Enniskillen line closed. The "van" now lies at the Ulster Transport Museum.
Horse-drawn trams still operate on the 1876-built Douglas Bay Horse Tramway on the Isle of Man, and at the 1894-built horse tram at Victor Harbor in South Australia. New horse-drawn systems have been established at the Hokkaidō Museum in Japan and also in Disneyland. A horse-tram route in Polish gmina Mrozy, first built in 1902, was reopened in 2012.
Zdroj:https://en.wikipedia.org?pojem=Electric_tramText je dostupný za podmienok Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších podmienok. Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky použitia.
Antropológia
Aplikované vedy
Bibliometria
Dejiny vedy
Encyklopédie
Filozofia vedy
Forenzné vedy
Humanitné vedy
Knižničná veda
Kryogenika
Kryptológia
Kulturológia
Literárna veda
Medzidisciplinárne oblasti
Metódy kvantitatívnej analýzy
Metavedy
Metodika
Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative
Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších
podmienok.
Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky
použitia.
www.astronomia.sk | www.biologia.sk | www.botanika.sk | www.dejiny.sk | www.economy.sk | www.elektrotechnika.sk | www.estetika.sk | www.farmakologia.sk | www.filozofia.sk | Fyzika | www.futurologia.sk | www.genetika.sk | www.chemia.sk | www.lingvistika.sk | www.politologia.sk | www.psychologia.sk | www.sexuologia.sk | www.sociologia.sk | www.veda.sk I www.zoologia.sk
