
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
| Demographics of Papua New Guinea | |
|---|---|
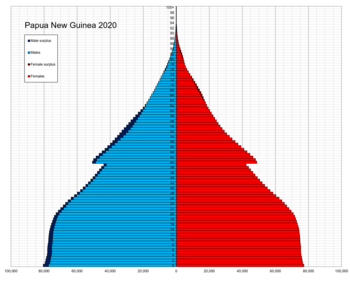 Population pyramid of Papua New Guinea in 2020 | |
| Population | 9,593,498 (2022 est.) |
| Growth rate | 2.35% (2022 est.) |
| Birth rate | 29.03 births/1,000 population (2022 est.) |
| Death rate | 5.54 deaths/1,000 population (2022 est.) |
| Life expectancy | 69.43 years |
| Fertility rate | 3.92 children born/woman (2022 est.) |
| Infant mortality rate | 33.59 deaths/1,000 live births |
| Net migration rate | 0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2022 est.) |
| Nationality | |
| Nationality | Papua New Guinean |
The indigenous population of Papua New Guinea is one of the most heterogeneous in the world. Papua New Guinea has several thousand separate communities, most with only a few hundred people. Divided by language, customs, and tradition, some of these communities have engaged in endemic warfare with their neighbors for centuries. It is the second most populous nation in Oceania, with a total population estimated variously as being between 9.5 and 10.1 million inhabitants.

The isolation created by the mountainous terrain is so great that some groups, until recently, were unaware of the existence of neighboring groups only a few kilometers away. The diversity, reflected in a folk saying, "For each village, a different culture", is perhaps best shown in the local languages. The island of New Guinea contains about 850 languages. The languages that are neither Austronesian nor Australian are considered Papuan languages; this is a geographical rather than linguistic demarcation.[1] Of the Papuan languages, the largest linguistic grouping is considered to be Trans-New Guinean, with between 300 and 500 languages likely belonging to the group in addition to a huge variety of dialects.[2] The remainder of the Papuan languages belong to smaller, unrelated groupings as well as to isolates. Native languages are spoken by a few hundred to a few thousand, although Enga language, used in Enga Province, is spoken by some 130,000 people.
Tok Pisin serves as the lingua franca. English is the language of business and government, and all schooling from Grade 2 Primary is in English.
The overall population density is low, although pockets of overpopulation exist. Papua New Guinea's Western Province averages one person per square kilometer (3 per sq. mi.). The Simbu Province in the New Guinea highlands averages 20 persons per square kilometer (52 persons/sq mi) and has areas containing up to 200 people farming a square kilometer of land. The highlands have 40% of the population.
A considerable urban drift towards Port Moresby and other major centers has occurred in recent years. Between 1978 and 1988, Port Moresby grew nearly 8% per year, Lae 6%, Mount Hagen 6.5%, Goroka 4%, and Madang 3%. The trend toward urbanization accelerated in the 1990s, bringing in its wake squatter settlements, unemployment, and attendant social problems. Almost two-thirds of the population is Christian. Of these, more than 700,000 are Roman Catholic, more than 500,000 Lutheran, and the balance are members of other Protestant denominations. Although the major churches are under indigenous leadership, a large number of missionaries remain in the country. The non-Christian portion of the indigenous population practices a wide variety of indigenous religions that are an integral part of traditional culture. These religions are mainly types of animism and veneration of the dead.
The World Bank estimates the number of international migrants in Papua New Guinea to be about 0.3% of the population.[3] According to the 2000 and 2011 census, the most common places of origin for international migrants were the United States, Australia, the Philippines, and Indonesia.[4] Since independence, about 900 foreigners have become naturalized citizens as of August 1999.[5] An estimated 20,000 Chinese people live in Papua New Guinea.[6]
The traditional Papua New Guinea social structure includes the following characteristics:
- The practice of subsistence economy;
- Recognition of bonds of kinship with obligations extending beyond the immediate family group;
- Generally egalitarian relationships with an emphasis on acquired, rather than inherited, status; and
- A strong attachment of the people to land.
Most Papua New Guineans still adhere strongly to this traditional social structure, which has its roots in village life.
Fertility and births
Total Fertility Rate (TFR) (Wanted Fertility Rate) and Crude Birth Rate (CBR):[7]
| Year | Total | Urban | Rural | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBR | TFR | CBR | TFR | CBR | TFR | |
| 2016-18 | 29 | 4.2 (3.0) | 28 | 3.5 (2.6) | 29 | 4.3 (3.1) |
Structure of the population
| Age group | Total | Percent |
|---|---|---|
| Total | 8 151 300 | 100 |
| 0–14 | 2 970 800 | 36.45 |
| 15–24 | 1 641 400 | 20.14 |
| 25-59 | 3 177 700 | 38.98 |
| 60+ | 361 400 | 4.43 |
Vital statistics
Registration of vital events in Papua New Guinea is not complete. The website Our World in Data prepared the following estimates based on statistics from the Population Department of the United Nations.[9]
| Mid-year population (thousands) | Live births (thousands) | Deaths (thousands) | Natural change (thousands) | Crude birth rate (per 1000) | Crude death rate (per 1000) | Natural change (per 1000) | Total fertility rate (TFR) | Infant mortality (per 1000 live births) | Life expectancy (in years) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 1 543 000 | 70 000 | 33 000 | 37 000 | 45.3 | 21.6 | 23.7 | 5.71 | 169.7 | 39.13 |
| 1951 | 1 574 000 | 72 000 | 38 000 | 35 000 | 45.9 | 24.0 | 21.9 | 5.74 | 170.3 | 36.49 |
| 1952 | 1 608 000 | 74 000 | 33 000 | 41 000 | 46.2 | 20.8 | 25.4 | 5.76 | 161.5 | 40.43 |
| 1953 | 1 648 000 | 77 000 | 34 000 | 43 000 | 46.5 | 20.4 | 26.1 | 5.79 | 157.5 | 41.12 |
| 1954 | 1 690 000 | 78 000 | 34 000 | 45 000 | 46.3 | 19.8 | 26.4 | 5.78 | 153.6 | 41.83 |
| 1955 | 1 735 000 | 80 000 | 34 000 | 47 000 | 46.2 | 19.4 | 26.9 | 5.82 | 149.9 | 42.46 |
| 1956 | 1 782 000 | 82 000 | 34 000 | 48 000 | 46.0 | 18.9 | 27.1 | 5.84 | 146.2 | 43.09 |
| 1957 | 1 831 000 | 84 000 | 34 000 | 50 000 | 45.7 | 18.3 | 27.4 | 5.89 | 142.5 | 43.83 |
| 1958 | 1 882 000 | 86 000 | 34 000 | 52 000 | 45.4 | 17.8 | 27.6 | 5.93 | 138.9 | 44.50 |
| 1959 | 1 933 000 | 87 000 | 34 000 | 53 000 | 44.9 | 17.4 | 27.6 | 5.96 | 135.3 | 45.08 |
| 1960 | 1 986 000 | 89 000 | 34 000 | 55 000 | 44.7 | 16.9 | 27.8 | 6.02 | 131.7 | 45.68 |
| 1961 | 2 036 000 | 91 000 | 34 000 | 57 000 | 44.4 | 16.4 | 28.0 | 6.07 | 128.2 | 46.29 |
| 1962 | 2 083 000 | 93 000 | 34 000 | 59 000 | 44.5 | 16.2 | 28.3 | 6.14 | 125.2 | 46.66 |
| 1963 | 2 129 000 | 95 000 | 33 000 | 61 000 | 44.3 | 15.5 | 28.8 | 6.15 | 121.4 | 47.60 |
| 1964 | 2 175 000 | 97 000 | 33 000 | 64 000 | 44.3 | 15.1 | 29.2 | 6.19 | 118.1 | 48.20 |
| 1965 | 2 222 000 | 99 000 | 33 000 | 66 000 | 44.2 | 14.7 | 29.6 | 6.20 | 114.8 | 48.82 |
| 1966 | 2 271 000 | 101 000 | 32 000 | 69 000 | 44.3 | 14.2 | 30.1 | 6.23 | 111.6 | 49.51 |
| 1967 | 2 323 000 | 103 000 | 32 000 | 71 000 | 44.1 | 13.7 | 30.4 | 6.24 | 108.5 | 50.14 |
| 1968 | 2 375 000 | 105 000 | 32 000 | 73 000 | 44.1 | 13.3 | 30.8 | 6.25 | 105.4 | 50.84 |
| 1969 | 2 431 000 | 107 000 | 31 000 | 76 000 | 43.9 | 12.8 | 31.1 | 6.26 | Zdroj:https://en.wikipedia.org?pojem=Demographics_of_Papua_New_Guinea
