
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|
Content theory is a subset of motivational theories that try to define what motivates people. Content theories of motivation often describe a system of needs that motivate peoples' actions. While process theories of motivation attempt to explain how and why our motivations affect our behaviors, content theories of motivation attempt to define what those motives or needs are. Content theory includes the work of David McClelland, Abraham Maslow and other psychologists.[1]
McGregor's Theory X and Theory Y
Douglas McGregor proposed two different motivational theories. Managers tend to believe one or the other and treat their employees accordingly. Theory X states that employees dislike and try to avoid work, so they must be coerced into doing it. Most workers do not want responsibilities, lack ambition, and value job security more than anything else.[2]
McGregor personally held that the more optimistic theory, Y, was more valid. This theory holds that employees can view work as natural, are creative, can be self-motivated, and appreciate responsibility. This type of thinking is popular now, with people becoming more aware of the productivity of self-empowered work teams.[3]
ERG theory
ERG Theory was introduced by Clayton Alderfer as an extension to the famous Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs.[4] In this theory, the existence or physiological needs are at the base. These include the needs for things such as food, drink, shelter, and safety. Next come the Relatedness Needs, the need to feel connected to other individuals or a group. These needs are fulfilled by establishing and maintaining relationships.
At the top of the hierarchy are Growth Needs, the needs for personal achievement and self-actualization. If a person is continuously frustrated in trying to satisfy growth needs, relatedness needs will re-emerge. This phenomenon is known as the frustration-regression process.
Herzberg's Motivation-Hygiene theory (Two-factor theory)
Frederick Herzberg felt that job satisfaction and dissatisfaction do not exist on the same continuum, but on dual scales. In other words, certain things, which Herzberg called hygiene factors, could cause a person to become unhappy with their job. These things, including pay, job security, and physical work environment, could never bring about job satisfaction. Motivating factors, on the other hand, can increase job satisfaction. Giving employees things such as a sense of recognition, responsibility, or achievement can bring satisfaction about.[citation needed]
Need theory
David McClelland proposed a context for understanding the needs in people, which holds significance in understanding their motivations and behaviors. It is subdivided into three categories: the Need for Achievement, the Need for Affiliation, and the Need for Power.[5]
The Need for Achievement refers to the notion of getting ahead and succeeding. The Need for Affiliation is the desire to be around people and be well received socially. It also includes the desire for being a member in a group and conformity. The Need for Power is the desire for control over others and over yourself. It confers the need to be able to exercise direction in the world surrounding you, and cause things to happen. Individuals who have high needs for achievement will tend to engage in competitive activities in order to fulfill this desire. Individuals who need to feel affiliated will tend to join clubs, groups and teams to satiate that want. Individuals who have the need for power will seek activities which likewise satisfy this need, such as, running for high positions in organizations and seeking opportunities to exercise that dominance.
This is not to say that one person cannot have needs spanning all three categories. A person may have the need for affiliation at the same time they have the need for power. While this may initially seem contradictory, there are instances where both needs can be fulfilled. Also, timing may connote different strengths of needs at different moments. So, while a person may strongly feel the need to affiliate during times of loneliness, they may at another time feel the strong need for power when instructed to organize an event. Needs may arise and change along with a change of context.
Maslow's hierarchy of needs
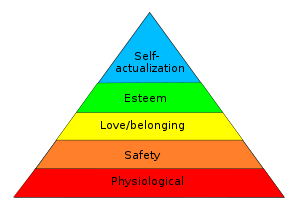
Content theory of human motivation includes both Abraham Maslow's hierarchy of needs and Herzberg's two-factor theory. Maslow's theory is one of the most widely discussed theories of motivation. Abraham Maslow believed that man is inherently good and argued that individuals possess a constantly growing inner drive that has great potential. The needs hierarchy system is a commonly used scheme for classifying human motives.[6]
The American motivation psychologist Abraham H. Maslow (1954) developed the hierarchy of needs consisting of five hierarchic classes. According to Maslow, people are motivated by unsatisfied needs. The needs, listed from basic (lowest-earliest) to most complex (highest-latest) are as follows:[7]
- Physiology (hunger, thirst, sleep, etc.)
- Safety/Security/Shelter/Health
- Social/Love/Friendship
- Self-esteem/Recognition/Achievement
- Self actualization/achievement of full potential
The basic requirements build upon the first step in the pyramid: physiology. If there are deficits on this level, all behavior will be oriented to satisfy this deficit. Essentially, if you have not slept or eaten adequately, you won't be interested in your self-esteem desires. Subsequently, we have the second level, which awakens a need for security. After securing those two levels, the motives shift to the social sphere, the third level. Psychological requirements comprise the fourth level, while the top of the hierarchy consists of self-realization and self-actualization.
Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory can be summarized as follows:
- Human beings have wants and desires which, when unsatisfied, may influence behavior.
- Differing levels of importance to human life are reflected in a hierarchical structure of needs.
- Needs at higher levels in the hierarchy are held in abeyance until lower-level needs are at least minimally satisfied.
- Needs at higher levels of the hierarchy are associated with individuality , humanness, and psychological health.
Sex, Hedonism, and Evolution
One of the first influential figures to discuss the topic of hedonism was Socrates, and he did so around 470–399 BCE in ancient Greece. Hedonism, as Socrates described it, is the motivation wherein a person will behave in a manner that will maximize pleasure and minimize pain. The only instance in which a person will behave in a manner that results in more pain than pleasure is when the knowledge of the effects of the behavior is lacking. Sex is one of the pleasures people pursue.[8][9]
Sex is on the first level of Maslow's hierarchy of needs. It is a necessary physiological need like air, warmth, or sleep, and if the body lacks it will not function optimally. Without the orgasm that comes with sex, a person will experience "pain," and as hedonism would predict, a person will minimize this pain by pursuing sex. That being said, sex as a basic need is different from the need for sexual intimacy, which is located on the third level in Maslow's hierarchy.[8]
There are multiple theories for why sex is a strong motivation, and many fall under the theory of evolution. On an evolutionary level, the motivation for sex likely has to do with a species' ability to reproduce. Species that reproduce more, survive and pass on their genes. Therefore, species have a sexual desire that leads to sexual intercourse as a means to create more offspring. Without this innate motivation, a species may determine that attaining intercourse is too costly in terms of effort, energy, and danger.[8][10]
In addition to sexual desire, the motivation for romantic love runs parallel in having an evolutionary function for the survival of a species. On an emotional level, romantic love satiates a psychological need for belonging. Therefore, this is another hedonistic pursuit of pleasure. From the evolutionary perspective, romantic love creates bonds with the parents of offspring. This bond will make it so that the parents will stay together and take care of and protect the offspring until it is independent. By rearing the child together, it increases the chances that the offspring will survive and pass on its genes themselves, therefore continuing the survival of the species. Without the romantic love bond, the male will pursue satiation of his sexual desire with as many mates as possible, leaving behind the female to rear the offspring by herself. Child-rearing with one parent is more difficult and provides less assurance of the offspring's survival than with two parents. Romantic love therefore solves the commitment problem of parents needing to be together; individuals that are loyal and faithful to one another will have mutual survival benefits.[8][11][12]
Additionally, under the umbrella of evolution, is Darwin's term sexual selection. This refers to how the female selects the male for reproduction. The male is motivated to attain sex because of all the aforementioned reasons, but how he attains it can vary based on his qualities. For some females, they are motivated by the will to survive mostly, and will prefer a mate that can physically defend her, or financially provide for her (among humans). Some females are more attracted to charm, as it is an indicator of being a good loyal lover that will in turn make for a dependable child-rearing partner. Altogether, sex is a hedonistic pleasure-seeking behavior that satiates physical and psychological needs and is instinctively guided by principles of evolution.[8][13]
Self-determination theory
Since the early 1970s Deci[14] and Ryan have developed and tested their self-determination theory (SDT). SDT identifies three innate needs that, if satisfied, allow optimal function and growth: competence,[15][16] relatedness,[17] and autonomy.[18][19] These three psychological needs are suggested to be essential for psychological health & well-being along with behavioral motivation.[20] There are three essential elements to the theory:[21]
- Humans are inherently proactive with their potential and at mastering their inner forces (such as drive and emotions).
- Humans have an inherent tendency towards growth, development, and integrated functioning.
- Optimal development and actions are inherent in humans but they do not happen automatically.
Within Self-Determination Theory, Deci & Ryan[22] distinguish between four different types of extrinsic motivation, differing in their levels of perceived autonomy:
- External regulation: This is the least autonomous of the four and is determined by external punishment or reward.
- Introjected regulation: This form of external motivation arises when the individuals have somewhat internalized regulations but do not fully accept them as their own. They may comply for self-esteem reasons or social acceptability - essentially internal reasons but externally driven.
- Identified regulation: This is more autonomously driven - when the individuals consciously perceive the actions as valuable.
- Integrated regulation: This is the most autonomous form of motivation and the action has been internalized and is aligned with the individual's values, beliefs and is perceived as necessary for their wellbeing. However, this is still classified as extrinsic motivation as it is still driven by external processes and not by inherent enjoyment for the task itself.
"16 basic desires" theory
Starting from studies involving more than 6,000 people, Reiss proposed that 16 basic desires guide nearly all human behavior.[23] In this model the basic desires that motivate our actions and define our personalities are:
- Acceptance, the need for approval
- Curiosity, the need to learn
- Eating, the need for food
- Family, the need to raise children
- Honor, the need to be loyal to the traditional values of one's clan/ethnic group
- Idealism, the need for social justice
- Independence, the need for individuality
- Order, the need for organized, stable, predictable environments
- Physical activity, the need for exercise
- Power, the need for influence of will
- Romance, the need for sex and for beauty
- Saving, the need to collect
- Social contact, the need for friends (peer relationships)
- Social status, the need for social standing/importance
- Tranquility, the need to be safe
- Vengeance, the need to strike back and to compete
Natural theories
The natural system assumes that people have higher-order needs, which contrasts with the rational theory that suggests that people dislike work and only respond to rewards and punishment.[24] According to McGregor's Theory Y, human behavior is based on satisfying a hierarchy of needs: physiological, safety, social, ego, and self-fulfillment.[25]
Physiological needs are the lowest and the most important level. These fundamental requirements include food, rest, shelter, and exercise. After the physiological needs are satisfied, employees can focus on safety needs, which include "protection against danger, threat and deprivation."[25] However, if management makes arbitrary or biased employment decisions, then an employee's safety needs are unfulfilled.
The next set of needs is social, which refers to the desire for acceptance, affiliation, reciprocal friendships, and love. As such, the natural system of management assumes that close-knit work teams are productive. Accordingly, if an employee's social needs are unmet, then he will act disobediently.[25]
There are two types of egoistic needs, the second-highest order of needs. The first type refers to one's self-esteem, which encompasses self-confidence, independence, achievement, competence, and knowledge. The second type of needs deals with reputation, status, recognition, and respect from colleagues.[25] Egoistic needs are much more difficult to satisfy.
The highest order of needs is for self-fulfillment, including recognition of one's full potential, areas for self-improvement, and the opportunity for creativity. This differs from the rational system, which assumes that people prefer routine and security to creativity.[24] Unlike the rational management system, which assumes that humans don't care about these higher-order needs, the natural system is based on these needs as a means for motivation.
The author of the reductionist motivation model is Sigmund Freud. According to the model, physiological needs raise tension, thereby forcing an individual to seek an outlet by satisfying those needs Ziegler, Daniel (1992). Personality Theories: Basic Assumptions, Research, and Applications.
Self-management through teamwork
To successfully manage and motivate employees, the natural system posits that being a part of a group is necessary.[26] Because of structural changes in the social order, the workplace is more fluid and adaptive according to Mayo. As a result, individual employees have lost their sense of stability and security, which can be provided by being a member of a group. However, if teams continuously change within jobs, then employees feel anxious, empty, and irrational and become harder to work with.[26] The innate desire for lasting human association and management "is not related to single workers, but always to working groups."[26] In groups, employees will self-manage and form relevant customs, duties, and traditions.
Wage incentives
Humans are motivated by additional factors besides wage incentives.[27] Unlike the rational theory of motivation, people are not driven toward economic interests per the natural system. For instance, the straight piecework system pays employees based on each unit of their output. Based on studies such as the Bank Wiring Observation Room, using a piece rate incentive system does not lead to higher production.[27] Employees actually set upper limits on each person's daily output. These actions stand "in direct opposition to the ideas underlying their system of financial incentive, which countenanced no upper limit to performance other than the physical capacity of the individual."[27] Therefore, as opposed to the rational system that depends on economic rewards and punishments, the natural system of management assumes that humans are also motivated by non-economic factors.
Autonomy: increased motivation for autonomous tasks
Employees seek autonomy and responsibility in their work, contrary to assumptions of the rational theory of management. Because supervisors have direct authority over employees, they must ensure that the employee's actions are in line with the standards of efficient conduct.[27] This creates a sense of restriction on the employee and these constraints are viewed as "annoying and seemingly functioned only as subordinating or differentiating mechanisms."[27] Accordingly, the natural management system assumes that employees prefer autonomy and responsibility on the job and dislike arbitrary rules and overwhelming supervision. An individual's motivation to complete a task is increased when the task is autonomous. When the motivation to complete a task comes from an "external pressure" that pressure then "undermines" the person's motivation, and as a result decreases the person's desire to complete the task.[28]
Rational motivations
The idea that human beings are rational and that the human behavior is guided by reason is an old one. However, recent research (on satisfying for example) has significantly undermined the idea of homo economicus or of perfect rationality in favor of a more bounded rationality. The field of behavioral economics is particularly concerned with the limits of rationality in economic agents.[29]
Incentive theories: intrinsic and extrinsic motivation
Motivation can be divided into two different theories known as intrinsic (internal or inherent in the activity itself) motivation and extrinsic (contingent on external rewards or punishment) motivation.
Intrinsic motivation
Intrinsic motivation has been studied since the early 1970s. Intrinsic motivation is a behavior that is driven by satisfying internal rewards. For example, an athlete may enjoy playing football for the experience, rather than for an award.[30] It is an interest or enjoyment in the task itself, and exists within the individual rather than relying on external pressures or a desire for consideration. Deci (1971) explained that some activities provide their own inherent reward, meaning certain activities are not dependent on external rewards.[31] The phenomenon of intrinsic motivation was first acknowledged within experimental studies of animal behavior. In these studies, it was evident that the organisms would engage in playful and curiosity-driven behaviors in the absence of reward. Intrinsic motivation is a natural motivational tendency and is a critical element in cognitive, social, and physical development.[32] The two necessary elements for intrinsic motivation are self-determination and an increase in perceived competence.[33] In short, the cause of the behavior must be internal, known as internal locus of causality, and the individual who engages in the behavior must perceive that the task increases their competence.[34] According to various research reported by Deci's published findings in 1971, and 1972, tangible rewards could actually undermine the intrinsic motivation of college students. However, these studies didn't just affect college students, Kruglanski, Friedman, and Zeevi (1971) repeated this study and found that symbolic and material rewards can undermine not just high school students, but preschool students as well.
Students who are intrinsically motivated are more likely to engage in the task willingly as well as work to improve their skills, which will increase their capabilities.[35] Students are likely to be intrinsically motivated if they...
- attribute their educational results to factors under their own control, also known as autonomy or locus of control
- believe they have the skills to be effective agents in reaching their desired goals, also known as self-efficacy beliefs
- are interested in mastering a topic, not just in achieving good grades
- don't act from pressure, but from interest
An example of intrinsic motivation is when an employee becomes an IT professional because he or she wants to learn about how computer users interact with computer networks. The employee has the intrinsic motivation to gain more knowledge, and will continue to want to learn even in the face of failure.[36] Art for art's sake is an example of intrinsic motivation in the domain of art.
Traditionally, researchers thought of motivations to use computer systems to be primarily driven by extrinsic purposes; however, many modern systems have their use driven primarily by intrinsic motivations.[37] Examples of such systems used primarily to fulfill users' intrinsic motivations, include on-line gaming, virtual worlds, online shopping,[38] learning/education, online dating, digital music repositories, social networking, online pornography, gamified systems, and general gamification. Even traditional management information systems (e.g., ERP, CRM) are being 'gamified' such that both extrinsic and intrinsic motivations must increasingly be considered. Deci's findings didn't come without controversy. Articles stretching over the span of 25 years from the perspective of behavioral theory argue that there isn't enough evidence to explain intrinsic motivation and this theory would inhibit "scientific progress." As stated above, we now can see technology such as various forms of computer systems are highly intrinsic.[31]
Not only can intrinsic motivation be used in a personal setting, but it can also be implemented and utilized in a social environment. Instead of attaining mature desires, such as those presented above via the internet which can be attained on one's own, intrinsic motivation can be used to assist extrinsic motivation to attain a goal. For example, Eli, a 4-year-old with autism, wants to achieve the goal of playing with a toy train.[39] To get the toy, he must first communicate to his therapist that he wants it. His desire to play is strong enough to be considered intrinsic motivation because it is a natural feeling, and his desire to communicate with his therapist to get the train can be considered extrinsic motivation because the outside object is a reward (see incentive theory). Communicating with the therapist is the first, the slightly more challenging goal that stands in the way of achieving his larger goal of playing with the train. Achieving these goals in attainable pieces is also known as the goal-setting theory. The three elements of goal-setting (STD) are Specific, Time-bound, and Difficult. Specifically, goals should be set in the 90th percentile of difficulty.[40]
Intrinsic motivation comes from one's desire to achieve or attain a goal.[30] Pursuing challenges and goals come easier and more enjoyable when one is intrinsically motivated to complete a certain objective because the individual is more interested in learning, rather than achieving the goal.[34] Edward Deci and Richard Ryan's theory of intrinsic motivation is essentially examining the conditions that "elicit and sustain" this phenomenon.[32]: 70–71 Deci and Ryan coined the term "cognitive evaluation theory" which concentrates on the needs of competence and autonomy. The CET essentially states that social-contextual events like feedback and reinforcement can cause feelings of competence and therefore increase intrinsic motivation. However, feelings of competence will not increase intrinsic motivation if there is no sense of autonomy. In situations where choices, feelings, and opportunities are present, intrinsic motivation is increased because people feel a greater sense of autonomy.[32]: 70–71 Offering people choices, responding to their feelings, and opportunities for self-direction have been reported to enhance intrinsic motivation via increased autonomy.[41][32]
An advantage (relative to extrinsic motivation) is that intrinsic motivators can be long-lasting, self-sustaining, and satisfying.[32] For this reason, efforts in education sometimes attempt to modify intrinsic motivation with the goal of promoting future student learning performance, creativity, and learning via long-term modifications in interests.[30] Intrinsic motivation has been found to be hard to modify, and attempts to recruit existing intrinsic motivators require a non-trivially difficult individualized approach, identifying and making relevant the different motivators needed to motivate different students,[30] possibly requiring additional skills and intrinsic motivation from the instructor.[42] In a workplace situation, intrinsic motivation is likely to be rare and risks being falsely identified, as most workers will always be subject to extrinsic motivation such as the fear of unemployment, the need to gain a living and fear of rejection by coworkers in cases of poor performance.[43]
Extrinsic motivation
Extrinsic motivation comes from influences outside of the individual. In extrinsic motivation, the harder question to answer is where do people get the motivation to carry out and continue to push with persistence. Usually, extrinsic motivation is used to attain outcomes that a person wouldn't get from intrinsic motivation.[32] Common extrinsic motivations are rewards (for example money or grades) for showing the desired behavior, and the threat of punishment following misbehavior. Competition is an extrinsic motivator because it encourages the performer to win and to beat others, not simply to enjoy the intrinsic rewards of the activity. A cheering crowd and the desire to win a trophy are also extrinsic incentives.[44] For example, if an individual plays the sport tennis to receive an award, that would be extrinsic motivation. VS. if the individual plays because he or she enjoys the game, which would be intrinsic motivation.[30]
The most simple distinction between extrinsic and intrinsic motivation is the type of reasons or goals that lead to an action. While intrinsic motivation refers to doing something because it is inherently interesting or enjoyable and satisfying, extrinsic motivation, refers to doing something because it leads to a separable outcome.[32] Extrinsic motivation thus contrasts with intrinsic motivation, which is doing an activity simply for the enjoyment of the activity itself, instead of for its instrumental value.[30]
Social psychological research has indicated that extrinsic rewards can lead to overjustification and a subsequent reduction in intrinsic motivation. In one study demonstrating this effect, children who expected to be (and were) rewarded with a ribbon and a gold star for drawing pictures spent less time playing with the drawing materials in subsequent observations than children who were assigned to an unexpected reward condition.[45] This shows how if an individual expects an award they don't care about the outcome. VS. if an individual doesn't expect a reward they will care more about the task.[32] However, another study showed that third graders who were rewarded with a book showed more reading behavior in the future, implying that some rewards do not undermine intrinsic motivation.[46] While the provision of extrinsic rewards might reduce the desirability of an activity, the use of extrinsic constraints, such as the threat of punishment, against performing an activity has actually been found to increase one's intrinsic interest in that activity. In one study, when children were given mild threats against playing with an attractive toy, it was found that the threat actually served to increase the child's interest in the toy, which was previously undesirable to the child in the absence of threat.[47]
Advantages of extrinsic motivators are that they easily promote motivation to work and persist to goal completion. Rewards are tangible and beneficial.[32] A disadvantage for extrinsic motivators relative to internal is that work does not persist long once external rewards are removed. As the task is completed for the reward, the quality of work may need to be monitored,[30] and it has been suggested that extrinsic motivators may diminish in value over time.[32]
Flow theory
Flow theory refers to desirable subjective state a person experiences when completely involved in some challenging activity that matches the individual's skills.[48]
Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi described Flow theory as "A state in which people are so involved in an activity that nothing else seems to matter; the experience is so enjoyable that people will continue to do it even at great cost, for the sheer sake of doing it."[49]
The idea of flow theory was first conceptualized by Csikszentmihalyi. Flow in the context of motivation can be seen as an activity that is not too hard, frustrating or madding, or too easy boring and done too fast. If one has achieved perfect flow, then the activity has reached maximum potential.[49]
Flow is a part of something called positive psychology of the psychology of happiness. Positive psychology looks into what makes a person happy. Flow can be considered as achieving happiness or at the very least positive feelings. A study that was published in the journal Emotion looked at flow experienced in college students playing Tetris. The students that were being evaluated on looks then told to wait and play Tetris. There were three categories; Easy, normal, and hard. The students that played Tetris on normal level experienced flow and were less stressed about the evaluation.[50]
Csikszentmihalyi describes 8 characteristics of flow as - the complete concentration on the task, clarity of goals & reward in mind and immediate feedback, transformation of time (speeding up/slowing down of time), the experience is intrinsically rewarding, effortlessness & ease, a balance between challenge and skills, merged actions and awareness, loss of self-conscious rumination and a feeling of control over the task.[49]
The activity no longer becomes something seen as a means to an end and it becomes something an individual wants to do. This can be seen as someone who likes to run for the sheer joy of running and not because they need to do it for exercise or because they want to brag about it. Peak flow can be different for each person. It could take an individual years to reach flow or only moments. If an individual becomes too good at an activity they can become bored. If the challenge becomes too hard then the individual could become discouraged and want to quit.[51]
Behaviorist theories
While many theories on motivation have a mentalistic perspective, behaviorists focus only on the observable behavior and the theories founded on experimental evidence. In the view of behaviorism, motivation is understood as a question about what factors cause, prevent, or withhold various behaviors, while the question of, for instance, conscious motivation would be ignored. Where others would speculate about such things as values, drives, or needs, that may not be observed directly, behaviorists are interested in the observable variables that affect the type, intensity, frequency, and duration of the observable behavior. Through the basic research of such scientists as Pavlov, Watson and Skinner, several basic mechanisms that govern behavior have been identified. The most important of these are classical conditioning and operant conditioning.
Classical and operant conditioning
In classical (or respondent) conditioning, behavior is understood as responses triggered by certain environmental or physical stimuli. They can be unconditioned, such as in-born reflexes, or learned through the pairing of an unconditioned stimulus with a different stimulus, which then becomes a conditioned stimulus. In relation to motivation, classical conditioning might be seen as one explanation as to why an individual performs certain responses and behaviors in certain situations.[52][53] For instance, a dentist might wonder why a patient does not seem motivated to show up for an appointment, with the explanation being that the patient has associated the dentist (conditioned stimulus) with the pain (unconditioned stimulus) that elicits a fear response (conditioned response), leading to the patient being reluctant to visit the dentist.
In operant conditioning, the type and frequency of behavior are determined mainly by its consequences. If a certain behavior, in the presence of a certain stimulus, is followed by a desirable consequence (a reinforcer), the emitted behavior will increase in frequency in the future, in the presence of the stimulus that preceded the behavior (or a similar one). Conversely, if the behavior is followed by something undesirable (a punisher), the behavior is less likely to occur in the presence of the stimulus. In a similar manner, the removal of a stimulus directly following the behavior might either increase or decrease the frequency of that behavior in the future (negative reinforcement or punishment).[52][53] For instance, a student that gained praise and a good grade after turning in a paper, might seem more motivated in writing papers in the future (positive reinforcement); if the same student put in a lot of work on a task without getting any praise for it, he or she might seem less motivated to do school work in the future (negative punishment). If a student starts to cause trouble in the class gets punished with something he or she dislikes, such as detention (positive punishment), that behavior would decrease in the future. The student might seem more motivated to behave in class, presumably in order to avoid further detention (negative reinforcement).
The strength of reinforcement or punishment is dependent on schedule and timing. A reinforcer or punisher affects the future frequency of a behavior most strongly if it occurs within seconds of the behavior. A behavior that is reinforced intermittently, at unpredictable intervals, will be more robust and persistent, compared to the ones that are reinforced every time the behavior is performed.[52][53] For example, if the misbehaving student in the above example was punished a week after the troublesome behavior, that might not affect future behavior.
In addition to these basic principles, environmental stimuli also affect behavior. Behavior is punished or reinforced in the context of whatever stimuli were present just before the behavior was performed, which means that a particular behavior might not be affected in every environmental context, or situation, after it is punished or reinforced in one specific context.[52][53] A lack of praise for school-related behavior might, for instance, not decrease after-school sports-related behavior that is usually reinforced by praise.
The various mechanisms of operant conditioning may be used to understand the motivation for various behaviors by examining what happens just after the behavior (the consequence), in what context the behavior is performed or not performed (the antecedent), and under what circumstances (motivating operators).[52][53]
Incentive motivation
Incentive theory is a specific theory of motivation, derived partly from behaviorist principles of reinforcement, which concerns an incentive or motive to do something. The most common incentive would be a compensation. Compensation can be tangible or intangible. It helps in motivating the employees in their corporate life, students in academics, and inspire them to do more and more to achieve profitability in every field. Studies show that if the person receives the reward immediately, the effect is greater, and decreases as delay lengthens.[citation needed] Repetitive action-reward combination can cause the action to become a habit[citation needed]
"Reinforcers and reinforcement principles of behavior differ from the hypothetical construct of reward." A reinforcer is anything that follows an action, with the intention that the action will now occur more frequently. From this perspective, the concept of distinguishing between intrinsic and extrinsic forces is irrelevant.
Incentive theory in psychology treats motivation and behavior of the individual as they are influenced by beliefs, such as engaging in activities that are expected to be profitable. Incentive theory is promoted by behavioral psychologists, such as B.F. Skinner. Incentive theory is especially supported by Skinner in his philosophy of Radical behaviorism, meaning that a person's actions always have social ramifications: and if actions are positively received, people are more likely to act in this manner, or if negatively received people are less likely to act in this manner.
Incentive theory distinguishes itself from other motivation theories, such as drive theory, in the direction of the motivation. In incentive theory, stimuli "attract" a person towards them, and push them towards the stimulus. In terms of behaviorism, incentive theory involves positive reinforcement: the reinforcing stimulus has been conditioned to make the person happier. As opposed to in drive theory, which involves negative reinforcement: a stimulus has been associated with the removal of the punishment—the lack of homeostasis in the body. For example, a person has come to know that if they eat when hungry, it will eliminate that negative feeling of hunger, or if they drink when thirsty, it will eliminate that negative feeling of thirst.[54]
Motivating operations
Motivating operations, MOs, relate to the field of motivation in that they help improve understanding aspects of behavior that are not covered by operant conditioning. In operant conditioning, the function of the reinforcer is to influence future behavior. The presence of a stimulus believed to function as a reinforcer does not according to this terminology explain the current behavior of an organism – only previous instances of reinforcement of that behavior (in the same or similar situations) do. Through the behavior-altering effect of MOs, it is possible to affect the current behavior of an individual, giving another piece of the puzzle of motivation.
Motivating operations are factors that affect learned behavior in a certain context. MOs have two effects: a value-altering effect, which increases or decreases the efficiency of a reinforcer, and a behavior-altering effect, which modifies learned behavior that has previously been punished or reinforced by a particular stimulus.[52]
When a motivating operation causes an increase in the effectiveness of a reinforcer or amplifies a learned behavior in some way (such as increasing frequency, intensity, duration, or speed of the behavior), it functions as an establishing operation, EO. A common example of this would be food deprivation, which functions as an EO in relation to food: the food-deprived organism will perform behaviors previously related to the acquisition of food more intensely, frequently, longer, or faster in the presence of food, and those behaviors would be especially strongly reinforced.[52] For instance, a fast-food worker earning minimal wage, forced to work more than one job to make ends meet, would be highly motivated by a pay raise, because of the current deprivation of money (a conditioned establishing operation). The worker would work hard to try to achieve the raise, and getting the raise would function as an especially strong reinforcer of work behavior.
Conversely, a motivating operation that causes a decrease in the effectiveness of a reinforcer, or diminishes a learned behavior related to the reinforcer, functions as an abolishing operation, AO. Again using the example of food, satiation of food prior to the presentation of a food stimulus would produce a decrease on food-related behaviors, and diminish or completely abolish the reinforcing effect of acquiring and ingesting the food.[52] Consider the board of a large investment bank, concerned with a too small profit margin, deciding to give the CEO a new incentive package in order to motivate him to increase firm profits. If the CEO already has a lot of money, the incentive package might not be a very good way to motivate him, because he would be satiated on the money. Getting even more money wouldn't be a strong reinforcer for profit-increasing behavior, and wouldn't elicit increased intensity, frequency, or duration of profit-increasing behavior.
Motivation and psychotherapy
Motivation lies at the core of many behaviorist approaches to psychological treatment. A person with autism-spectrum the disorder is seen as lacking motivation to perform socially relevant behaviors – social stimuli are not as reinforcing for people with autism compared to other people. Depression is understood as a lack of reinforcement (especially positive reinforcement) leading to the extinction of behavior in the depressed individual. A patient with specific phobia is not motivated to seek out the phobic stimulus because it acts as a punisher, and is over-motivated to avoid it (negative reinforcement). In accordance, therapies have been designed to address these problems, such as EIBI and CBT for major depression and specific phobia.
Socio-cultural theory
Sociocultural theory (also known as Social Motivation) emphasizes the impact of activity and actions mediated through social interaction, and within social contexts. Sociocultural theory represents a shift from traditional theories of motivation, which view the individual's innate drives or mechanistic operand learning as primary determinants of motivation. Critical elements to socio-cultural theory applied to motivation include, but are not limited to, the role of social interactions and the contributions from culturally-based knowledge and practice.[40] Sociocultural theory extends the social aspects of Cognitive Evaluation Theory, which espouses the important role of positive feedback from others during the action,[32] but requires the individual as the internal locus of causality. Sociocultural theory predicts that motivation has an external locus of causality, and is socially distributed among the social group.[40]
Motivation can develop through an individual's involvement within their cultural group. Personal motivation often comes from activities a person believes to be central to the everyday occurrences in their community.[55] An example of socio-cultural theory would be social settings where people work together to solve collective problems. Although individuals will have internalized goals, they will also develop internalized goals of others, as well as new interests and goals collectively with those that they feel socially connected to.[56] Oftentimes, it is believed that all cultural groups are motivated in the same way. However, motivation can come from different child-rearing practices and cultural behaviors that greatly vary between cultural groups.
In some indigenous cultures, collaboration between children and adults in the community and household tasks is seen as very important[57] A child from an indigenous community may spend a great deal of their time alongside family and community members doing different tasks and chores that benefit the community. After having seen the benefits of collaboration and work, and also have the opportunity to be included, the child will be intrinsically motivated to participate in similar tasks. In this example, because the adults in the community do not impose the tasks upon the children, the children therefore feel self-motivated and have a desire to participate and learn through the task.[58] As a result of the community values that surround the child, their source of motivation may vary according to the different communities and their different values.
In more Westernized communities, segregation between adults and children participating in work-related tasks is a common practice. As a result of this, these adolescents demonstrate less internalized motivation to do things within their environment than their parents. However, when the motivation to participate in activities is a prominent belief within the family, the adolescents autonomy is significantly higher. This therefore demonstrates that when collaboration and non-segregative tasks are norms within a child's upbringing, their internal motivation to participate in community tasks increases.[59] When given opportunities to work collaboratively with adults on shared tasks during childhood, children will therefore become more intrinsically motivated through adulthood.[60]
Social motivation is tied to one's activity in a group. It cannot form from a single mind alone. For example, bowling alone is naught but the dull act of throwing a ball into pins, and so people are much less likely to smile during the activity alone, even upon getting a strike because their satisfaction or dissatisfaction does not need to be communicated, and so it is internalized. However, when with a group, people are more inclined to smile regardless of their results because it acts as a positive communication that is beneficial for pleasurable interaction and teamwork.[56] Thus the act of bowling becomes a social activity as opposed to a dull action because it becomes an exercise in interaction, competition, team building and sportsmanship. It is because of this phenomenon that studies have shown that people are more intrigued in performing mundane activities so long as there is company because it provides the opportunity to interact in one way or another, be it for bonding, amusement, collaboration, or alternative perspectives.[56] Examples of activities that one may not be motivated to do alone but could be done with others for the social benefit are things such as throwing and catching a baseball with a friend, making funny faces with children, building a treehouse, and performing a debate.
Push and pull
Pushedit
Push motivations are those where people push themselves towards their goals or to achieve something, such as the desire for escape, rest & relaxation, prestige, health & fitness, adventure, and social interaction.[61]
However, with push motivation, it's also easy to get discouraged when there are obstacles present in the path of achievement. Push motivation acts as a willpower and people's willpower is only as strong as the desire behind the willpower.[62]
Additionally, a study has been conducted on social networking and its push and pull effects. One thing that is mentioned is "Regret and dissatisfaction correspond to push factors because regret and dissatisfaction are the negative factors that compel users to leave their current service provider."[63] So we now know that Push motivations can also be a negative force. In this case, that negative force is regret and dissatisfaction.
Pulledit
Pull motivation is the opposite of push. It is a type of motivation that is much stronger. "Some of the factors are those that emerge as a result of the attractiveness of a destination as it is perceived by those with the propensity to travel. They include both tangible resources, such as beaches, recreation facilities, and cultural attractions, and traveler's perceptions and expectation, such as novelty, benefit expectation, and marketing image."[61] Pull motivation can be seen as the desire to achieve a goal so badly that it seems that the goal is pulling us toward it. That is why pull motivation is stronger than push motivation. It is easier to be drawn to something rather than to push yourself for something you desire. It can also be an alternative force when compared to negative force. From the same study as previously mentioned, "Regret and dissatisfaction with an existing SNS service provider may trigger a heightened interest toward switching service providers, but such a motive will likely translate into reality in the presence of a good alternative. Therefore, alternative attractiveness can moderate the effects of regret and dissatisfaction with switching intention"[63] And so, pull motivation can be an attracting desire when negative influences come into the picture.
Self-controledit
The self-control aspect of motivation is increasingly considered to be a subset of emotional intelligence;[64] it is suggested that although a person may be classed as highly intelligent (as measured by many traditional intelligence tests), they may remain unmotivated to pursue intellectual endeavors. Vroom's "expectancy theory" provides an account of when people may decide to exert self-control in pursuit of a particular goal.
Drivesedit
A drive or desire can be described as a deficiency or need that activates behavior that is aimed at a goal or an incentive.[65] These drives are thought to originate within the individual and may not require external stimuli to encourage the behavior. Basic drives could be sparked by deficiencies such as hunger, which motivates a person to seek food whereas more subtle drives might be the desire for praise and approval, which motivates a person to behave in a manner pleasing to others.
Another basic drive is the sexual drive which just like food motivates us because it is essential to our survival.[66] The desire for sex is wired deep into the brain of all human beings as glands secrete hormones that travel through the blood to the brain and stimulates the onset of sexual desire.[66] The hormone involved in the initial onset of sexual desire is called Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA).[66] The hormonal basis of both men and women's sex drives is testosterone.[66] [need quotation to verify] Men naturally have more testosterone than women do and so are more likely than women to think about sex.[66] [need quotation to verify]
Drive-reduction theoryedit
Drive theory grows out of the concept that people have certain biological drives, such as hunger and thirst. As time passes, the strength of the drive increases if it is not satisfied (in this case by eating). Upon satisfying a drive, the drive's strength is reduced. Created by Clark Hull and further developed by Kenneth Spence, the theory became well known in the 1940s and 1950s. Many of the motivational theories that arose during the 1950s and 1960s were either based on Hull's original theory or were focused on providing alternatives to the drive-reduction theory, including Abraham Maslow's hierarchy of needs, which emerged as an alternative to Hull's approach.[67]
Drive theory has some intuitive validity. For instance, when preparing food, the drive model appears to be compatible with sensations of rising hunger as the food is prepared, and, after the food has been consumed, a decrease in subjective hunger.[68] There are several problems, however, that leave the validity of drive reduction open for debate[which?].
Cognitive dissonance theoryedit
As suggested by Leon Festinger, cognitive dissonance occurs when an individual experiences some degree of discomfort resulting from an inconsistency between two cognitions: their views on the world around them and their own personal feelings and actions.[citation needed] For example, a consumer may seek to reassure themselves regarding a purchase, feeling that another decision may have been preferable. Their feeling that another purchase would have been preferable is inconsistent with their action of purchasing the item. The difference between their feelings and beliefs causes dissonance, so they seek to reassure themselves.
While not a theory of motivation, per se, the theory of cognitive dissonance proposes that people have a motivational drive to reduce dissonance. The cognitive miser perspective makes people want to justify things in a simple way in order to reduce the effort they put into cognition. They do this by changing their attitudes, beliefs, or actions, rather than facing the inconsistencies, because dissonance is a mental strain. Dissonance is also reduced by justifying, blaming, and denying. It is one of the most influential and extensively studied theories in social psychology.
Temporal motivation theoryedit
A recent approach in developing a broad, integrative theory of motivation is temporal motivation theory. Introduced in a 2006 Academy of Management Review article,[69] it synthesizes into a single formulation, the primary aspects of several other major motivational theories, including Incentive Theory, Drive Theory, Need Theory, Self-Efficacy and Goal Setting. It simplifies the field of motivation and allows findings from one theory to be translated into the terms of another. Another journal article that helped to develop temporal motivation theory, "The Nature of Procrastination",[70] which received American Psychological Association's George A. Miller award for outstanding contribution to general science.
where Motivation is the desire for a particular outcome, Expectancy or self-efficacy is the probability of success, Value is the reward associated with the outcome, Impulsiveness is the individual's sensitivity to delay and Delay is the time to realization.[70]
Zdroj:https://en.wikipedia.org?pojem=Content_theoriesText je dostupný za podmienok Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších podmienok. Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky použitia.
Antropológia
Aplikované vedy
Bibliometria
Dejiny vedy
Encyklopédie
Filozofia vedy
Forenzné vedy
Humanitné vedy
Knižničná veda
Kryogenika
Kryptológia
Kulturológia
Literárna veda
Medzidisciplinárne oblasti
Metódy kvantitatívnej analýzy
Metavedy
Metodika
Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative
Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších
podmienok.
Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky
použitia.
www.astronomia.sk | www.biologia.sk | www.botanika.sk | www.dejiny.sk | www.economy.sk | www.elektrotechnika.sk | www.estetika.sk | www.farmakologia.sk | www.filozofia.sk | Fyzika | www.futurologia.sk | www.genetika.sk | www.chemia.sk | www.lingvistika.sk | www.politologia.sk | www.psychologia.sk | www.sexuologia.sk | www.sociologia.sk | www.veda.sk I www.zoologia.sk

