
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
| Khmer | |
|---|---|
| Cambodian | |
| ភាសាខ្មែរ
/ ខេមរភាសា Phéasa Khmêr / Khémôrôphéasa | |
 Phéasa Khmêr "Khmer language" written in Khmer script | |
| Pronunciation | [pʰiəsaː kʰmae] [kʰeːmarapʰiəsaː] |
| Native to | |
| Ethnicity | Khmer |
| speakers | L1: 17 million (2019)[1] L2: 1 million (no date)[1] |
Austroasiatic
| |
Early forms | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | |
Recognised minority language in | |
| Regulated by | Royal Academy of Cambodia, National Council of Khmer Language[2] |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | km Central Khmer |
| ISO 639-2 | khm Central Khmer |
| ISO 639-3 | Either:khm – Khmerkxm – Northern Khmer |
| Glottolog | khme1253 Khmericcent1989 Central Khmer |
| Linguasphere | 46-FBA-a |
 Khmer | |
Khmer (/kəˈmɛər/ kə-MAIR;[3] ខ្មែរ, UNGEGN: Khmêr [kʰmae]) is an Austroasiatic language spoken by the Khmer people, and the official and national language of Cambodia. Khmer has been influenced considerably by Sanskrit and Pali, especially in the royal and religious registers, through Hinduism and Buddhism. It is also the earliest recorded and earliest written language of the Mon–Khmer family, predating Mon and Vietnamese,[4] due to Old Khmer being the language of the historical empires of Chenla, Angkor and, presumably, their earlier predecessor state, Funan.
The vast majority of Khmer speakers speak Central Khmer, the dialect of the central plain where the Khmer are most heavily concentrated. Within Cambodia, regional accents exist in remote areas but these are regarded as varieties of Central Khmer. Two exceptions are the speech of the capital, Phnom Penh, and that of the Khmer Khe in Stung Treng province, both of which differ sufficiently enough from Central Khmer to be considered separate dialects of Khmer.
Outside of Cambodia, three distinct dialects are spoken by ethnic Khmers native to areas that were historically part of the Khmer Empire. The Northern Khmer dialect is spoken by over a million Khmers in the southern regions of Northeast Thailand and is treated by some linguists as a separate language. Khmer Krom, or Southern Khmer, is the first language of the Khmer of Vietnam, while the Khmer living in the remote Cardamom Mountains speak a very conservative dialect that still displays features of the Middle Khmer language.
Khmer is primarily an analytic, isolating language. There are no inflections, conjugations or case endings. Instead, particles and auxiliary words are used to indicate grammatical relationships. General word order is subject–verb–object, and modifiers follow the word they modify. Classifiers appear after numbers when used to count nouns, though not always so consistently as in languages like Chinese. In spoken Khmer, topic-comment structure is common, and the perceived social relation between participants determines which sets of vocabulary, such as pronouns and honorifics, are proper.
Khmer differs from neighboring languages such as Burmese, Thai, Lao, and Vietnamese in that it is not a tonal language. Words are stressed on the final syllable, hence many words conform to the typical Mon–Khmer pattern of a stressed syllable preceded by a minor syllable. The language has been written in the Khmer script, an abugida descended from the Brahmi script via the southern Indian Pallava script, since at least the 7th century. The script's form and use has evolved over the centuries; its modern features include subscripted versions of consonants used to write clusters and a division of consonants into two series with different inherent vowels.
Classification
Khmer is a member of the Austroasiatic language family, the autochthonous family in an area that stretches from the Malay Peninsula through Southeast Asia to East India.[5] Austroasiatic, which also includes Mon, Vietnamese and Munda, has been studied since 1856 and was first proposed as a language family in 1907.[6] Despite the amount of research, there is still doubt about the internal relationship of the languages of Austroasiatic.[7]
Diffloth places Khmer in an eastern branch of the Mon-Khmer languages.[8] In these classification schemes Khmer's closest genetic relatives are the Bahnaric and Pearic languages.[9] More recent classifications doubt the validity of the Mon-Khmer sub-grouping and place the Khmer language as its own branch of Austroasiatic equidistant from the other 12 branches of the family.[7]
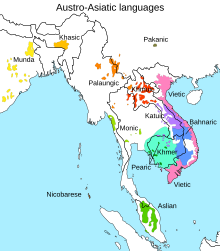
Geographic distribution and dialects

Khmer is spoken by some 13 million people in Cambodia, where it is the official language. It is also a second language for most of the minority groups and indigenous hill tribes there. Additionally there are a million speakers of Khmer native to southern Vietnam (1999 census)[10] and 1.4 million in northeast Thailand (2006).[11]
Khmer dialects, although mutually intelligible, are sometimes quite marked. Notable variations are found in speakers from Phnom Penh (Cambodia's capital city), the rural Battambang area, the areas of Northeast Thailand adjacent to Cambodia such as Surin province, the Cardamom Mountains, and southern Vietnam.[12][13][14] The dialects form a continuum running roughly north to south. Standard Cambodian Khmer is mutually intelligible with the others but a Khmer Krom speaker from Vietnam, for instance, may have great difficulty communicating with a Khmer native of Sisaket Province in Thailand.
The following is a classification scheme showing the development of the modern Khmer dialects.[15][16]
- Middle Khmer
- Cardamom (Western) Khmer
- Central Khmer
- Surin (Northern) Khmer
- Standard Khmer and related dialects (including Khmer Krom)
Standard Khmer, or Central Khmer, the language as taught in Cambodian schools and used by the media, is based on the dialect spoken throughout the Central Plain,[17] a region encompassed by the northwest and central provinces.
Northern Khmer (called Khmer Surin in Khmer) refers to the dialects spoken by many in several border provinces of present-day northeast Thailand. After the fall of the Khmer Empire in the early 15th century, the Dongrek Mountains served as a natural border leaving the Khmer north of the mountains under the sphere of influence of the Kingdom of Lan Xang. The conquests of Cambodia by Naresuan the Great for Ayutthaya furthered their political and economic isolation from Cambodia proper, leading to a dialect that developed relatively independently from the midpoint of the Middle Khmer period.[18]
This has resulted in a distinct accent influenced by the surrounding tonal languages Lao and Thai, lexical differences, and phonemic differences in both vowels and distribution of consonants. Syllable-final /r/, which has become silent in other dialects of Khmer, is still pronounced in Northern Khmer. Some linguists classify Northern Khmer as a separate but closely related language rather than a dialect.[19][20]
Western Khmer, also called Cardamom Khmer or Chanthaburi Khmer, is spoken by a very small, isolated population in the Cardamom mountain range extending from western Cambodia into eastern Central Thailand. Although little studied, this variety is unique in that it maintains a definite system of vocal register that has all but disappeared in other dialects of modern Khmer.[5]
Phnom Penh Khmer is spoken in the capital and surrounding areas. This dialect is characterized by merging or complete elision of syllables, which speakers from other regions consider a "relaxed" pronunciation. For instance, "Phnom Penh" is sometimes shortened to "m'Penh". Another characteristic of Phnom Penh speech is observed in words with an "r" either as an initial consonant or as the second member of a consonant cluster (as in the English word "bread"). The "r", trilled or flapped in other dialects, is either pronounced as a uvular trill or not pronounced at all.[21]
This alters the quality of any preceding consonant, causing a harder, more emphasized pronunciation. Another unique result is that the syllable is spoken with a low-rising or "dipping" tone much like the "hỏi" tone in Vietnamese. For example, some people pronounce ត្រី ('fish') as : the is dropped and the vowel begins by dipping much lower in tone than standard speech and then rises, effectively doubling its length. Another example is the word រៀន ('study'), which is pronounced , with the uvular "r" and the same intonation described above.[21]
Khmer Krom or Southern Khmer is spoken by the indigenous Khmer population of the Mekong Delta, formerly controlled by the Khmer Empire but part of Vietnam since 1698. Khmers are persecuted by the Vietnamese government for using their native language and, since the 1950s, have been forced to take Vietnamese names.[22] Consequently, very little research has been published regarding this dialect. It has been generally influenced by Vietnamese for three centuries and accordingly displays a pronounced accent, tendency toward monosyllabic words and lexical differences from Standard Khmer.[23]
Khmer Khe is spoken in the Se San, Srepok and Sekong river valleys of Sesan and Siem Pang districts in Stung Treng Province. Following the decline of Angkor, the Khmer abandoned their northern territories, which the Lao then settled. In the 17th century, Chey Chetha XI led a Khmer force into Stung Treng to retake the area. The Khmer Khe living in this area of Stung Treng in modern times are presumed to be the descendants of this group. Their dialect is thought to resemble that of pre-modern Siem Reap.[24]
Historical periods

Linguistic study of the Khmer language divides its history into four periods one of which, the Old Khmer period, is subdivided into pre-Angkorian and Angkorian.[25] Pre-Angkorian Khmer is the Old Khmer language from 600 CE through 800. Angkorian Khmer is the language as it was spoken in the Khmer Empire from the 9th century until the 13th century.[26]
The following centuries saw changes in morphology, phonology and lexicon. The language of this transition period, from about the 14th to 18th centuries, is referred to as Middle Khmer and saw borrowings from Thai in the literary register.[26] Modern Khmer is dated from the 19th century to today.[25]
The following table shows the conventionally accepted historical stages of Khmer.[15]
| Historical stage | Date |
|---|---|
| Pre- or Proto-Khmer | Before 600 CE |
| Pre-Angkorian Old Khmer | 600–800 |
| Angkorian Old Khmer | 800 to mid-14th century |
| Middle Khmer | Mid-14th century to 18th century |
| Modern Khmer | 1800–present |
Just as modern Khmer was emerging from the transitional period represented by Middle Khmer, Cambodia fell under the influence of French colonialism.[27] Thailand, which had for centuries claimed suzerainty over Cambodia and controlled succession to the Cambodian throne, began losing its influence on the language.[28] In 1887 Cambodia was fully integrated into French Indochina, which brought in a French-speaking aristocracy. This led to French becoming the language of higher education and the intellectual class. By 1907, the French had wrested over half of modern-day Cambodia, including the north and northwest where Thai had been the prestige language, back from Thai control and reintegrated it into the country.[28]
Many native scholars in the early 20th century, led by a monk named Chuon Nath, resisted the French and Thai influences on their language. Forming the government sponsored Cultural Committee to define and standardize the modern language, they championed Khmerization, purging of foreign elements, reviving affixation, and the use of Old Khmer roots and historical Pali and Sanskrit to coin new words for modern ideas.[27][29] Opponents, led by Keng Vannsak, who embraced "total Khmerization" by denouncing the reversion to classical languages and favoring the use of contemporary colloquial Khmer for neologisms, and Ieu Koeus, who favored borrowing from Thai, were also influential.[29]
Koeus later joined the Cultural Committee and supported Nath. Nath's views and prolific work won out and he is credited with cultivating modern Khmer-language identity and culture, overseeing the translation of the entire Pali Buddhist canon into Khmer. He also created the modern Khmer language dictionary that is still in use today, helping preserve Khmer during the French colonial period.[27]
Phonology
| Part of a series on the |
| Khmer language |
|---|
 |
| Aspects |
| Dialects |
| Stages |
The phonological system described here is the inventory of sounds of the standard spoken language,[17] represented using the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA).
Consonants
| Labial | Alveolar | Palatal | Velar | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ɲ | ŋ | ||
| Plosive | voiceless | p (pʰ) | t (tʰ) | c (cʰ) | k (kʰ) | ʔ |
| voiced | ɓ ~ b | ɗ ~ d | ||||
| Fricative | s | (ç) | h | |||
| Liquid | rhotic | r | ||||
| lateral | l | |||||
| Approximant | ʋ ~ w | j | ||||
The voiceless plosives /p/, /t/, /c/, /k/ may occur with or without aspiration (as vs. , etc.); this difference is contrastive before a vowel. However, the aspirated sounds in that position may be analyzed as sequences of two phonemes: /ph/, /th/, /ch/, /kh/. This analysis is supported by the fact that infixes can be inserted between the stop and the aspiration; for example ('big') becomes ('size') with a nominalizing infix. When one of these plosives occurs initially before another consonant, aspiration is no longer contrastive and can be regarded as mere phonetic detail:[30][31] slight aspiration is expected when the following consonant is not one of /ʔ/, /b/, /d/, /r/, /s/, /h/ (or /ŋ/ if the initial plosive is /k/).
The voiced plosives are pronounced as implosives by most speakers, but this feature is weak in educated speech, where they become .[32]
In syllable-final position, /h/ and /ʋ/ approach and respectively. The stops /p/, /t/, /c/, /k/ are unaspirated and have no audible release when occurring as syllable finals.[17]
In addition, the consonants /ɡ/, /f/, /ʃ/ and /z/ occur occasionally in recent loan words in the speech of Cambodians familiar with French and other languages.
Vowels
Various authors have proposed slightly different analyses of the Khmer vowel system. This may be in part because of the wide degree of variation in pronunciation between individual speakers, even within a dialectal region.[33] The description below follows Huffman (1970).[17] The number of vowel nuclei and their values vary between dialects; differences exist even between the Standard Khmer system and that of the Battambang dialect on which the standard is based.[34]

| Front | Central | Back | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| short | long | short | long | short | long | |
| Close | i | iː | ɨ | ɨː | u | uː |
| Close-mid | e | eː | ə | əː | o | oː |
| Open-mid | ɛː | ɔː | ||||
| Open | a | aː | ɑ | ɑː | ||
| Front | Central | Back | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Short | centering | ĕə | ŏə, ŭə | |
| Long | centering | iə | ɨə | ɔə, uə |
| mid closing | ei | əɨ | ou | |
| open closing | ae | aə | ao | |
In addition, some diphthongs and triphthongs are analyzed as a vowel nucleus plus a semivowel (/j/ or ?pojem=) coda because they cannot be followed by a final consonant. These include: (with short monophthongs) /ɨw/, /əw/, /aj/, /aw/, /uj/; (with long monophthongs) /əːj/, /aːj/; (with long diphthongs) /iəj/, /iəw/, /ɨəj/, /aoj/, /aəj/ and /uəj/.[35]
Syllable structure
A Khmer syllable begins with a single consonant, or else with a cluster of two, or rarely three, consonants. The only possible clusters of three consonants at the start of a syllable are /str/, /skr/,[36] and (with aspirated consonants analyzed as two-consonant sequences) /sth/, /lkh/. There are 85 possible two-consonant clusters (including etc. analyzed as /ph/ etc.). All the clusters are shown in the following table, phonetically, i.e. superscript ʰ can mark either contrastive or non-contrastive aspiration (see above).
| p | ɓ | t | ɗ | c | k | ʔ | m | n | ɲ | ŋ | j | l | r | s | h | ʋ | t+h | k+h | t+r | k+r | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | pʰt- | pɗ- | pʰc- | pʰk- | pʔ- | pʰn- | pʰɲ- | pʰŋ- | pʰj- | pʰl- | pr- | ps- | pʰ- | ||||||||
| t | tʰp- | tɓ- | tʰk- | tʔ- | tʰm- | tʰn- | tʰŋ- | tʰj- | tʰl- | tr- | tʰ- | tʰʋ- | |||||||||
| c | cʰp- | cɓ- | cɗ- | cʰk- | cʔ- | cʰm- | cʰn- | cʰŋ- | cʰl- | cr- | cʰ- | cʰʋ- | |||||||||
| k | kʰp- | Zdroj:https://en.wikipedia.org?pojem=Cambodian_language
