
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9


Arc length is the distance between two points along a section of a curve.
Determining the length of an irregular arc segment by approximating the arc segment as connected (straight) line segments is also called curve rectification. A rectifiable curve has a finite number of segments in its rectification (so the curve has a finite length).
If a curve can be parameterized as an injective and continuously differentiable function (i.e., the derivative is a continuous function) , then the curve is rectifiable (i.e., it has a finite length).
The advent of infinitesimal calculus led to a general formula that provides closed-form solutions in some cases.
General approach
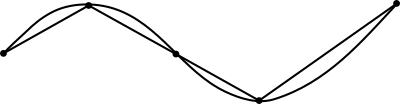
A curve in the plane can be approximated by connecting a finite number of points on the curve using (straight) line segments to create a polygonal path. Since it is straightforward to calculate the length of each linear segment (using the Pythagorean theorem in Euclidean space, for example), the total length of the approximation can be found by summation of the lengths of each linear segment; that approximation is known as the (cumulative) chordal distance.[1]
If the curve is not already a polygonal path, then using a progressively larger number of line segments of smaller lengths will result in better curve length approximations. Such a curve length determination by approximating the curve as connected (straight) line segments is called rectification of a curve. The lengths of the successive approximations will not decrease and may keep increasing indefinitely, but for smooth curves they will tend to a finite limit as the lengths of the segments get arbitrarily small.
For some curves, there is a smallest number that is an upper bound on the length of all polygonal approximations (rectification). These curves are called rectifiable and the arc length is defined as the number .
A signed arc length can be defined to convey a sense of orientation or "direction" with respect to a reference point taken as origin in the curve (see also: curve orientation and signed distance).[2]
Formula for a smooth curve
Let be an injective and continuously differentiable (i.e., the derivative is a continuous function) function. The length of the curve defined by can be defined as the limit of the sum of linear segment lengths for a regular partition of as the number of segments approaches infinity. This means
where with for This definition is equivalent to the standard definition of arc length as an integral:
The last equality is proved by the following steps:
- The second fundamental theorem of calculus shows where over maps to and . In the below step, the following equivalent expression is used.Analytika
Antropológia
Aplikované vedy
Bibliometria
Dejiny vedy
Encyklopédie
Filozofia vedy
Forenzné vedy
Humanitné vedy
Knižničná veda
Kryogenika
Kryptológia
Kulturológia
Literárna veda
Medzidisciplinárne oblasti
Metódy kvantitatívnej analýzy
Metavedy
Metodika
Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších podmienok.
Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky použitia.
www.astronomia.sk | www.biologia.sk | www.botanika.sk | www.dejiny.sk | www.economy.sk | www.elektrotechnika.sk | www.estetika.sk | www.farmakologia.sk | www.filozofia.sk | Fyzika | www.futurologia.sk | www.genetika.sk | www.chemia.sk | www.lingvistika.sk | www.politologia.sk | www.psychologia.sk | www.sexuologia.sk | www.sociologia.sk | www.veda.sk I www.zoologia.sk














