
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
Allegheny County | |
|---|---|
 | |
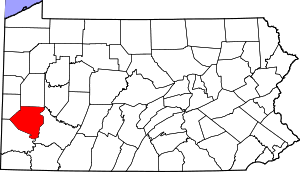 Location within the U.S. state of Pennsylvania | |
 Pennsylvania's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 40°26′08″N 80°01′28″W / 40.4356°N 80.0244°W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | September 24, 1788 |
| Named for | Allegheny River |
| Seat | Pittsburgh |
| Largest city | Pittsburgh |
| Area | |
| • Total | 745 sq mi (1,930 km2) |
| • Land | 730 sq mi (1,900 km2) |
| • Water | 14 sq mi (40 km2) 1.9% |
| Population (2020) | |
| • Total | 1,250,578 |
| • Density | 1,700/sq mi (700/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| Congressional districts | 12th, 17th |
| Website | www |
| Designated | December 30, 1982[1] |
Allegheny County (/ˌælɪˈɡeɪni/ AL-ig-AY-nee) is a county in Pennsylvania, United States. As of the 2020 census, the population was 1,250,578, making it the state's second-most populous county, after Philadelphia County. Its county seat and most populous city is Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania's second most populous city.[2] The county is part of the Greater Pittsburgh region of the state[a], and is the center of the Pittsburgh media market.
Allegheny was the first county in Pennsylvania to be given a Native American name. It was named after the Lenape word for the Allegheny River. The meaning of "Allegheny" is uncertain. It is usually said to mean "fine river". Stewart says that the name may come from a Lenape account of an ancient mythical tribe called "Allegewi", who lived along the river before being taken over by the Lenape.[3]
History
This section needs additional citations for verification. (January 2019) |

Prior to European contact, this area was settled for thousands of years by succeeding cultures of indigenous peoples. During the colonial era, historic native groups known by the colonists to settle in the area included members of western nations of the Iroquois, such as the Seneca; the Lenape, who had been pushed from the East by European-American settlers; the Shawnee, who also had territory in Ohio; and the Mingo, a group made up of a variety of peoples from more eastern tribes.
European fur traders such as Peter Chartier established trading posts in the region in the early eighteenth century.
In 1749, Captain Pierre Joseph Céloron de Blainville claimed the Ohio Valley and all of western Pennsylvania for King Louis XV of France. The captain traveled along the Ohio and Allegheny rivers. He installed lead plates in the ground to mark the land for France.
Most of the towns during that era were developed along waterways, which were the primary transportation routes, as well as providing water for domestic uses. Through the eighteenth century, both the French and the British competed for control over the local rivers in this frontier territory of North America. Native American bands and tribes allied with the colonists to differing degrees, often based on their trading relationships. The British sent Major George Washington to expel the French from their posts, with no success. He also nearly drowned in the ice-filled Allegheny River while returning to camp.
The English tried again in 1754 to establish a post in the area. They sent 41 Virginians to build Fort Prince George. The French learned of the plan and sent an army to capture the fort. They resumed building it and added increased defensive fortification, renaming it as Fort Duquesne.
Given its strategic location at the Ohio, Fort Duquesne became an important focal point of the French and Indian War. The first British attempt to retake the fort, the Braddock Expedition, failed miserably.[4] In 1758 British forces under General John Forbes recaptured the fort; he had it destroyed to prevent any use by the French. The British built a new, larger fort on the site, including a moat, and named it Fort Pitt. The historic site has been preserved as Pittsburgh's Point State Park.
Under their colonial charters, both Pennsylvania and Virginia claimed the region that is now Allegheny County. Pennsylvania administered most of the region as part of its Westmoreland County. Virginia considered everything south of the Ohio River and east of the Allegheny River to be part of its Yohogania County, and governed it from Fort Dunmore. In addition, parts of the county were located in the proposed British colony of Vandalia and the proposed U.S. state of Westsylvania. The overlapping boundaries, multiple governments, and confused deed claims soon proved unworkable. Near the end of the American Revolutionary War, in 1780 Pennsylvania and Virginia agreed to extend the Mason–Dixon line westward. This region was assigned to Pennsylvania. From 1781 until 1788, much of what Virginia had claimed as part of Yohogania County was administered as a part of the newly created Washington County, Pennsylvania.
Allegheny County was officially created on September 24, 1788, from parts of Washington and Westmoreland counties. It was formed to respond to pressure from the increase in settlers living in the area around Pittsburgh; this was designated as the county seat in 1791. The county originally extended north to the shores of Lake Erie; it was reduced to its current borders by 1800. As population increased in the territory, other counties were organized.
In the 1790s, the United States federal government imposed a whiskey excise tax. Farmers who had depended on whiskey income refused to pay and started the so-called Whiskey Rebellion after driving off tax collector John Neville. After a series of demonstrations by farmers, President George Washington sent troops to suppress the frontier rebellion.
The area developed rapidly through the 1800s with industrialization. It became the nation's prime steel producer by the late 19th century and Pittsburgh was nicknamed "Steel Capital of the World".
In 1913, the county's 125th anniversary was celebrated with a week-long series of events. The final day, September 27, was marked by a steamboat parade of 30 paddle wheelers. They traveled from Monongahela Wharf down the Ohio to the Davis Island Dam. The boats in line were the Steel City (formerly the Pittsburgh and Cincinnati packet Virginia), the flag ship; City of Parkersburg, Charles Brown, Alice Brown, Exporter, Sam Brown, Boaz, Raymond Horner, Swan, Sunshine, I. C. Woodward, Cruiser, Volunteer, A. R. Budd, J. C. Risher, Clyde, Rival, Voyager, Jim Brown, Rover, Charlie Clarke, Robt. J. Jenkins, Slipper, Bertha, Midland Sam Barnum, Cadet, Twilight, and Troubadour.[5]
On October 27, 2018, during a Sabbath course and a Torah study a domestic terrorist attack occurred at the Tree of Life – Or L'Simcha Congregation killing 11 people and harming six others, marking it one of the deadliest terrorist attacks in Pennsylvania history.
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 745 square miles (1,930 km2), of which 730 square miles (1,900 km2) is land and 14 square miles (36 km2) (1.9%) is water.[6]
Three major rivers traverse Allegheny County: the Allegheny River and the Monongahela River converge at Downtown Pittsburgh to form the Ohio River. The Youghiogheny River flows into the Monongahela River at McKeesport, 10 miles (16 km) to the southeast. There are several islands in these courses. The rivers drain via the Mississippi River into the Gulf of Mexico. Although the county's industrial growth resulted in clearcutting of the area's forests at one time, there has been regrowth and a significant woodland remains.
Adjacent counties
- Butler County (north)
- Armstrong County (northeast)
- Beaver County (northwest)
- Westmoreland County (east and south)
- Washington County (southwest)
Major roads and highways
Climate
Allegheny has a humid continental climate which is hot-summer, (Dfa) except in higher elevations, where it is warm-summer (Dfb).
| Climate data for Pittsburgh (Pittsburgh International Airport), 1991–2020 normals,[b] extremes 1874–present[c] | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 75 (24) |
78 (26) |
84 (29) |
90 (32) |
95 (35) |
98 (37) |
103 (39) |
103 (39) |
102 (39) |
91 (33) |
82 (28) |
74 (23) |
103 (39) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 61.5 (16.4) |
63.2 (17.3) |
73.5 (23.1) |
81.5 (27.5) |
86.8 (30.4) |
90.4 (32.4) |
91.3 (32.9) |
90.3 (32.4) |
88.2 (31.2) |
79.9 (26.6) |
70.8 (21.6) |
62.6 (17.0) |
92.6 (33.7) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 36.3 (2.4) |
39.6 (4.2) |
49.1 (9.5) |
62.4 (16.9) |
71.9 (22.2) |
79.4 (26.3) |
82.9 (28.3) |
81.7 (27.6) |
75.1 (23.9) |
63.1 (17.3) |
50.9 (10.5) |
40.6 (4.8) |
61.1 (16.2) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 28.8 (−1.8) |
31.4 (−0.3) |
39.7 (4.3) |
51.5 (10.8) |
61.2 (16.2) |
69.4 (20.8) |
73.2 (22.9) |
71.8 (22.1) |
64.9 (18.3) |
53.4 (11.9) |
42.6 (5.9) |
33.7 (0.9) |
51.8 (11.0) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 21.4 (−5.9) |
23.2 (−4.9) |
30.3 (−0.9) |
40.7 (4.8) |
50.6 (10.3) |
59.3 (15.2) |
63.4 (17.4) |
62.0 (16.7) |
54.8 (12.7) |
43.7 (6.5) |
34.3 (1.3) |
26.7 (−2.9) |
42.5 (5.8) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | 1.0 (−17.2) |
5.0 (−15.0) |
11.7 (−11.3) |
25.4 (−3.7) |
35.6 (2.0) |
45.2 (7.3) |
52.5 (11.4) |
51.1 (10.6) |
41.2 (5.1) |
29.5 (−1.4) |
19.3 (−7.1) |
9.7 (−12.4) |
−1.5 (−18.6) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −22 (−30) |
−20 (−29) |
−5 (−21) |
11 (−12) |
26 (−3) |
34 (1) |
42 (6) |
39 (4) |
31 (−1) |
16 (−9) |
−1 (−18) |
−12 (−24) |
−22 (−30) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 2.96 (75) |
2.62 (67) |
3.15 (80) |
3.32 (84) |
3.83 (97) |
4.12 (105) |
4.26 (108) |
3.52 (89) |
3.30 (84) |
2.83 (72) |
2.86 (73) |
2.84 (72) |
39.61 (1,006) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 13.3 (34) |
11.7 (30) |
7.6 (19) |
1.0 (2.5) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.4 (1.0) |
2.4 (6.1) |
7.7 (20) |
44.1 (112) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 16.8 | 13.9 | 14.0 | 13.9 | 13.5 | 12.4 | 11.2 | 10.5 | 9.8 | 11.1 | 12.0 | Zdroj:https://en.wikipedia.org?pojem=Allegheny_County||



